[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-9fmt: Cryo-EM structure of the BcsB hexameric crown from the E. coli ce... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 9fmt | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
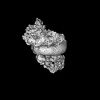
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the BcsB hexameric crown from the E. coli cellulose secretion macrocomplex | ||||||
 Components Components | Cyclic di-GMP-binding protein | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / Bacterial cellulose secretion | ||||||
| Function / homology | Cellulose synthase, subunit B / Cellulose synthase BcsB, bacterial / Bacterial cellulose synthase subunit / cellulose biosynthetic process / UDP-alpha-D-glucose metabolic process / plasma membrane / Cyclic di-GMP-binding protein Function and homology information Function and homology information | ||||||
| Biological species |  | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.35 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Anso, I. / Krasteva, P.V. | ||||||
| Funding support | European Union, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2024 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2024Title: Structural basis for synthase activation and cellulose modification in the E. coli Type II Bcs secretion system. Authors: Itxaso Anso / Samira Zouhir / Thibault Géry Sana / Petya Violinova Krasteva /   Abstract: Bacterial cellulosic polymers constitute a prevalent class of biofilm matrix exopolysaccharides that are synthesized by several types of bacterial cellulose secretion (Bcs) systems, which include ...Bacterial cellulosic polymers constitute a prevalent class of biofilm matrix exopolysaccharides that are synthesized by several types of bacterial cellulose secretion (Bcs) systems, which include conserved cyclic diguanylate (c-di-GMP)-dependent cellulose synthase modules together with diverse accessory subunits. In E. coli, the biogenesis of phosphoethanolamine (pEtN)-modified cellulose relies on the BcsRQABEFG macrocomplex, encompassing inner-membrane and cytosolic subunits, and an outer membrane porin, BcsC. Here, we use cryogenic electron microscopy to shed light on the molecular mechanisms of BcsA-dependent recruitment and stabilization of a trimeric BcsG pEtN-transferase for polymer modification, and a dimeric BcsF-dependent recruitment of an otherwise cytosolic BcsERQ regulatory complex. We further demonstrate that BcsE, a secondary c-di-GMP sensor, can remain dinucleotide-bound and retain the essential-for-secretion BcsRQ partners onto the synthase even in the absence of direct c-di-GMP-synthase complexation, likely lowering the threshold for c-di-GMP-dependent synthase activation. Such activation-by-proxy mechanism could allow Bcs secretion system activity even in the absence of substantial intracellular c-di-GMP increase, and is reminiscent of other widespread synthase-dependent polysaccharide secretion systems where dinucleotide sensing and/or synthase stabilization are carried out by key co-polymerase subunits. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  9fmt.cif.gz 9fmt.cif.gz | 728.1 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb9fmt.ent.gz pdb9fmt.ent.gz | 602.1 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  9fmt.json.gz 9fmt.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fm/9fmt https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fm/9fmt ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fm/9fmt ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fm/9fmt | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  50567MC  9fmvC  9fmzC  9fnnC  9fo7C  9fp0C  9fp2C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 83345.844 Da / Num. of mol.: 6 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Has protein modification | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Locally refined hexameric BcsB periplasmic crown from the E. coli cellulose secretion system Type: COMPLEX Details: Local refinement in the context of an assembled macrocomplex Entity ID: all / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.99 MDa / Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 Details: 120 mM NaCL 20 mM HEPES pH8 5 mM MgCl2 10 uM ApppCp 4 uM c-di-GMP 0.01% LM-NPG |
| Specimen | Conc.: 2 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES Details: Purified Bcs macrocomplex with stoichiometry BcsA-BcsB6-BcsR2-BcsQ2-BcsE2-BcsF2-BcsG3 |
| Specimen support | Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: UltrAuFoil R1.2/1.3 |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2100 nm / Nominal defocus min: 300 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 49.35 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 2 / Num. of real images: 20022 |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter name: GIF Quantum LS / Energyfilter slit width: 20 eV |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Image processing | Details: GIF Quantum LS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Details: cryoSPARC V.4 / Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 1359795 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.35 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 834077 / Num. of class averages: 1 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT / Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | PDB-ID: 6yg8 Pdb chain-ID: C / Accession code: 6yg8 / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj

