+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 9fgq | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of human APC3loop 375-381 bound to the NCP | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | CELL CYCLE / Arginine anchor / NCP / APC3 / Complex | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationConversion from APC/C:Cdc20 to APC/C:Cdh1 in late anaphase / Inactivation of APC/C via direct inhibition of the APC/C complex / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of mitotic proteins / anaphase-promoting complex / regulation of meiotic cell cycle / Aberrant regulation of mitotic exit in cancer due to RB1 defects / anaphase-promoting complex-dependent catabolic process / protein branched polyubiquitination / metaphase/anaphase transition of mitotic cell cycle / Phosphorylation of the APC/C ...Conversion from APC/C:Cdc20 to APC/C:Cdh1 in late anaphase / Inactivation of APC/C via direct inhibition of the APC/C complex / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of mitotic proteins / anaphase-promoting complex / regulation of meiotic cell cycle / Aberrant regulation of mitotic exit in cancer due to RB1 defects / anaphase-promoting complex-dependent catabolic process / protein branched polyubiquitination / metaphase/anaphase transition of mitotic cell cycle / Phosphorylation of the APC/C / protein K11-linked ubiquitination / Regulation of APC/C activators between G1/S and early anaphase / Transcriptional Regulation by VENTX / protein K48-linked ubiquitination / negative regulation of megakaryocyte differentiation / protein localization to CENP-A containing chromatin / Chromatin modifying enzymes / Replacement of protamines by nucleosomes in the male pronucleus / CENP-A containing nucleosome / Packaging Of Telomere Ends / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected purine / Cleavage of the damaged purine / Deposition of new CENPA-containing nucleosomes at the centromere / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of Cyclin B / regulation of mitotic cell cycle / telomere organization / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected pyrimidine / Cleavage of the damaged pyrimidine / Interleukin-7 signaling / APC-Cdc20 mediated degradation of Nek2A / epigenetic regulation of gene expression / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Opening / Inhibition of DNA recombination at telomere / Assembly of the ORC complex at the origin of replication / Meiotic synapsis / SUMOylation of chromatin organization proteins / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by the Human Silencing Hub (HUSH) complex / DNA methylation / Condensation of Prophase Chromosomes / Chromatin modifications during the maternal to zygotic transition (MZT) / SIRT1 negatively regulates rRNA expression / HCMV Late Events / ERCC6 (CSB) and EHMT2 (G9a) positively regulate rRNA expression / PRC2 methylates histones and DNA / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by KRAB-ZFP proteins / Autodegradation of Cdh1 by Cdh1:APC/C / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of Securin / Defective pyroptosis / Negative Regulation of CDH1 Gene Transcription / HDACs deacetylate histones / Assembly of the pre-replicative complex / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) / Cdc20:Phospho-APC/C mediated degradation of Cyclin A / Nonhomologous End-Joining (NHEJ) / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Escape / Transcriptional regulation by small RNAs / Formation of the beta-catenin:TCF transactivating complex / Activated PKN1 stimulates transcription of AR (androgen receptor) regulated genes KLK2 and KLK3 / HDMs demethylate histones / RUNX1 regulates genes involved in megakaryocyte differentiation and platelet function / APC/C:Cdh1 mediated degradation of Cdc20 and other APC/C:Cdh1 targeted proteins in late mitosis/early G1 / G2/M DNA damage checkpoint / NoRC negatively regulates rRNA expression / B-WICH complex positively regulates rRNA expression / PKMTs methylate histone lysines / DNA Damage/Telomere Stress Induced Senescence / CDK-mediated phosphorylation and removal of Cdc6 / Pre-NOTCH Transcription and Translation / Meiotic recombination / spindle / Activation of anterior HOX genes in hindbrain development during early embryogenesis / Metalloprotease DUBs / Transcriptional regulation of granulopoiesis / RMTs methylate histone arginines / neuron projection development / HCMV Early Events / mitotic spindle / structural constituent of chromatin / Separation of Sister Chromatids / UCH proteinases / heterochromatin formation / nucleosome / Antigen processing: Ubiquitination & Proteasome degradation / nucleosome assembly / E3 ubiquitin ligases ubiquitinate target proteins / Recruitment and ATM-mediated phosphorylation of repair and signaling proteins at DNA double strand breaks / HATs acetylate histones / RUNX1 regulates transcription of genes involved in differentiation of HSCs / Factors involved in megakaryocyte development and platelet production / MLL4 and MLL3 complexes regulate expression of PPARG target genes in adipogenesis and hepatic steatosis / chromatin organization / Processing of DNA double-strand break ends / Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype (SASP) / protein phosphatase binding / Oxidative Stress Induced Senescence / Estrogen-dependent gene expression / chromosome, telomeric region / Ub-specific processing proteases / protein ubiquitination / cadherin binding Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.5 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Young, R.V.C. / Muhammad, R. / Alfieri, C. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 2items United Kingdom, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: EMBO J / Year: 2024 Journal: EMBO J / Year: 2024Title: Spatial control of the APC/C ensures the rapid degradation of cyclin B1. Authors: Luca Cirillo / Rose Young / Sapthaswaran Veerapathiran / Annalisa Roberti / Molly Martin / Azzah Abubacar / Camilla Perosa / Catherine Coates / Reyhan Muhammad / Theodoros I Roumeliotis / ...Authors: Luca Cirillo / Rose Young / Sapthaswaran Veerapathiran / Annalisa Roberti / Molly Martin / Azzah Abubacar / Camilla Perosa / Catherine Coates / Reyhan Muhammad / Theodoros I Roumeliotis / Jyoti S Choudhary / Claudio Alfieri / Jonathon Pines /  Abstract: The proper control of mitosis depends on the ubiquitin-mediated degradation of the right mitotic regulator at the right time. This is effected by the Anaphase Promoting Complex/Cyclosome (APC/C) ...The proper control of mitosis depends on the ubiquitin-mediated degradation of the right mitotic regulator at the right time. This is effected by the Anaphase Promoting Complex/Cyclosome (APC/C) ubiquitin ligase that is regulated by the Spindle Assembly Checkpoint (SAC). The SAC prevents the APC/C from recognising Cyclin B1, the essential anaphase and cytokinesis inhibitor, until all chromosomes are attached to the spindle. Once chromosomes are attached, Cyclin B1 is rapidly degraded to enable chromosome segregation and cytokinesis. We have a good understanding of how the SAC inhibits the APC/C, but relatively little is known about how the APC/C recognises Cyclin B1 as soon as the SAC is turned off. Here, by combining live-cell imaging, in vitro reconstitution biochemistry, and structural analysis by cryo-electron microscopy, we provide evidence that the rapid recognition of Cyclin B1 in metaphase requires spatial regulation of the APC/C. Using fluorescence cross-correlation spectroscopy, we find that Cyclin B1 and the APC/C primarily interact at the mitotic apparatus. We show that this is because Cyclin B1, like the APC/C, binds to nucleosomes, and identify an 'arginine-anchor' in the N-terminus as necessary and sufficient for binding to the nucleosome. Mutating the arginine anchor on Cyclin B1 reduces its interaction with the APC/C and delays its degradation: cells with the mutant, non-nucleosome-binding Cyclin B1 become aneuploid, demonstrating the physiological relevance of our findings. Together, our data demonstrate that mitotic chromosomes promote the efficient interaction between Cyclin B1 and the APC/C to ensure the timely degradation of Cyclin B1 and genomic stability. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  9fgq.cif.gz 9fgq.cif.gz | 395.7 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb9fgq.ent.gz pdb9fgq.ent.gz | 235.8 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  9fgq.json.gz 9fgq.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fg/9fgq https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fg/9fgq ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fg/9fgq ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fg/9fgq | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  50416MC 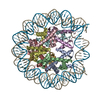 9fh9C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 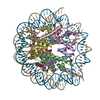
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 5 types, 10 molecules KLAEBFCGDH
| #1: Protein | Mass: 32788.488 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Details: This is a disorder loop of human APC3 residues 177-446 fused to a SpyTag via a 27 residue GSA linker. Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CDC27, ANAPC3, D0S1430E, D17S978E / Plasmid: pFastBac1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CDC27, ANAPC3, D0S1430E, D17S978E / Plasmid: pFastBac1 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P30260 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P30260#2: Protein | Mass: 15437.167 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Details: Human histone H3.1 / Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)Gene: HIST1H3A, H3FA, HIST1H3B, H3FL, HIST1H3C, H3FC, HIST1H3D, H3FB, HIST1H3E, H3FD, HIST1H3F, H3FI, HIST1H3G, H3FH, HIST1H3H, H3FK, HIST1H3I, H3FF, HIST1H3J, H3FJ Production host:  #3: Protein | Mass: 11394.426 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Details: Human histone H4 / Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)Gene: HIST1H4A, H4/A, H4FA, HIST1H4B, H4/I, H4FI, HIST1H4C, H4/G, H4FG, HIST1H4D, H4/B, H4FB, HIST1H4E, H4/J, H4FJ, HIST1H4F, H4/C, H4FC, HIST1H4H, H4/H, H4FH, HIST1H4I, H4/M, H4FM, HIST1H4J, H4/E, ...Gene: HIST1H4A, H4/A, H4FA, HIST1H4B, H4/I, H4FI, HIST1H4C, H4/G, H4FG, HIST1H4D, H4/B, H4FB, HIST1H4E, H4/J, H4FJ, HIST1H4F, H4/C, H4FC, HIST1H4H, H4/H, H4FH, HIST1H4I, H4/M, H4FM, HIST1H4J, H4/E, H4FE, HIST1H4K, H4/D, H4FD, HIST1H4L, H4/K, H4FK, HIST2H4A, H4/N, H4F2, H4FN, HIST2H4, HIST2H4B, H4/O, H4FO, HIST4H4 Production host:  #4: Protein | Mass: 14125.549 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Details: This is a H2A/H2B fusion protein with a SpyCatcher tag attached Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)Gene: H2AC18, H2AFO, HIST2H2AA, HIST2H2AA3, H2AC19, HIST2H2AA4 Plasmid: pET-14b / Production host:  #5: Protein | Mass: 29445.771 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Details: This is a H2A/H2B fusion protein with a SpyCatcher tag attached,This is a H2A/H2B fusion protein with a SpyCatcher tag attached Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: H2BC3, H2BFF, HIST1H2BB / Plasmid: pET-14b / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: H2BC3, H2BFF, HIST1H2BB / Plasmid: pET-14b / Production host:  |
|---|
-DNA chain , 2 types, 2 molecules IJ
| #6: DNA chain | Mass: 64911.336 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Details: The Widom 147 bp sequence with 32 nucleotides of DNA on either side Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Production host:  |
|---|---|
| #7: DNA chain | Mass: 65382.633 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Details: Widom 147 DNA sequence flanked with 32 nucleotides on either side Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Production host:  |
-Non-polymers , 1 types, 75 molecules 
| #8: Water | ChemComp-HOH / |
|---|
-Details
| Has protein modification | N |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: APC3 motif bound to the NCP acidic patch / Type: COMPLEX Details: Recombinant protein sample of residues 375-381 of APC3 Entity ID: #1-#3, #6-#7 / Source: RECOMBINANT | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 / Details: 20 mM HEPEs pH8.0, 50 mM NaCl, 0.5 mM TCEP | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK III / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: TFS KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1600 nm / Nominal defocus min: 600 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 62 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 2698450 Details: Template base particel picking and Topaz trained particle picking | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.5 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 414277 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Cross valid method: NONE Stereochemistry target values: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 50.81 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 PDBj
PDBj

















































