+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 9awk | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
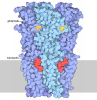
| Title | Bovine fetal muscle nAChR resting state | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / Bovine muscle / nicotinic acetylcholine receptor | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationHighly sodium permeable postsynaptic acetylcholine nicotinic receptors / Highly calcium permeable postsynaptic nicotinic acetylcholine receptors / Highly calcium permeable nicotinic acetylcholine receptors / postsynaptic membrane organization / skeletal muscle tissue growth / musculoskeletal movement / acetylcholine receptor activity / excitatory extracellular ligand-gated monoatomic ion channel activity / acetylcholine-gated channel complex / behavioral response to nicotine ...Highly sodium permeable postsynaptic acetylcholine nicotinic receptors / Highly calcium permeable postsynaptic nicotinic acetylcholine receptors / Highly calcium permeable nicotinic acetylcholine receptors / postsynaptic membrane organization / skeletal muscle tissue growth / musculoskeletal movement / acetylcholine receptor activity / excitatory extracellular ligand-gated monoatomic ion channel activity / acetylcholine-gated channel complex / behavioral response to nicotine / neuromuscular synaptic transmission / acetylcholine-gated monoatomic cation-selective channel activity / muscle cell development / acetylcholine binding / synaptic transmission, cholinergic / nervous system process / acetylcholine receptor signaling pathway / postsynaptic specialization membrane / membrane depolarization / monoatomic cation transport / muscle contraction / response to nicotine / transmitter-gated monoatomic ion channel activity involved in regulation of postsynaptic membrane potential / neuromuscular junction / transmembrane signaling receptor activity / channel activity / monoatomic ion transmembrane transport / chemical synaptic transmission / postsynaptic membrane / neuron projection / synapse / signal transduction / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species | synthetic construct (others) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.14 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Li, H. / Hibbs, R.E. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2024 Journal: Nature / Year: 2024Title: Structural switch in acetylcholine receptors in developing muscle. Authors: Huanhuan Li / Jinfeng Teng / Ryan E Hibbs /  Abstract: During development, motor neurons originating in the brainstem and spinal cord form elaborate synapses with skeletal muscle fibres. These neurons release acetylcholine (ACh), which binds to nicotinic ...During development, motor neurons originating in the brainstem and spinal cord form elaborate synapses with skeletal muscle fibres. These neurons release acetylcholine (ACh), which binds to nicotinic ACh receptors (AChRs) on the muscle, initiating contraction. Two types of AChR are present in developing muscle cells, and their differential expression serves as a hallmark of neuromuscular synapse maturation. The structural principles underlying the switch from fetal to adult muscle receptors are unknown. Here, we present high-resolution structures of both fetal and adult muscle nicotinic AChRs, isolated from bovine skeletal muscle in developmental transition. These structures, obtained in the absence and presence of ACh, provide a structural context for understanding how fetal versus adult receptor isoforms are tuned for synapse development versus the all-or-none signalling required for high-fidelity skeletal muscle contraction. We find that ACh affinity differences are driven by binding site access, channel conductance is tuned by widespread surface electrostatics and open duration changes result from intrasubunit interactions and structural flexibility. The structures further reveal pathogenic mechanisms underlying congenital myasthenic syndromes. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  9awk.cif.gz 9awk.cif.gz | 822.5 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb9awk.ent.gz pdb9awk.ent.gz | 696.7 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  9awk.json.gz 9awk.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/aw/9awk https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/aw/9awk ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/aw/9awk ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/aw/9awk | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  43926MC  9avuC  9avvC  9awjC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Acetylcholine receptor subunit ... , 4 types, 5 molecules ACEDB
| #1: Protein | Mass: 49949.828 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #2: Protein | | Mass: 55111.832 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #3: Protein | | Mass: 56543.926 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #5: Protein | | Mass: 55994.680 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|
-Protein / Non-polymers , 2 types, 9 molecules FG

| #11: Chemical | ChemComp-POV / ( #4: Protein | Mass: 6993.089 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.) synthetic construct (others) / Production host:  |
|---|
-Sugars , 6 types, 7 molecules 
| #6: Polysaccharide | alpha-D-mannopyranose-(1-2)-alpha-D-mannopyranose-(1-3)-[alpha-D-mannopyranose-(1-2)-alpha-D- ...alpha-D-mannopyranose-(1-2)-alpha-D-mannopyranose-(1-3)-[alpha-D-mannopyranose-(1-2)-alpha-D-mannopyranose-(1-6)]alpha-D-mannopyranose-(1-6)-[alpha-D-mannopyranose-(1-2)-alpha-D-mannopyranose-(1-3)]beta-D-mannopyranose-(1-4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose-(1-4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose Type: oligosaccharide / Mass: 1721.527 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #7: Polysaccharide | Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source #8: Polysaccharide | alpha-D-mannopyranose-(1-2)-alpha-D-mannopyranose-(1-2)-alpha-D-mannopyranose-(1-3)-[alpha-D- ...alpha-D-mannopyranose-(1-2)-alpha-D-mannopyranose-(1-2)-alpha-D-mannopyranose-(1-3)-[alpha-D-mannopyranose-(1-2)-alpha-D-mannopyranose-(1-3)-[alpha-D-mannopyranose-(1-2)-alpha-D-mannopyranose-(1-6)]alpha-D-mannopyranose-(1-6)]beta-D-mannopyranose-(1-4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose-(1-4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose | Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source #9: Polysaccharide | alpha-D-mannopyranose-(1-3)-alpha-D-mannopyranose-(1-6)-[alpha-D-mannopyranose-(1-3)]beta-D- ...alpha-D-mannopyranose-(1-3)-alpha-D-mannopyranose-(1-6)-[alpha-D-mannopyranose-(1-3)]beta-D-mannopyranose-(1-4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose-(1-4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose | Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source #10: Polysaccharide | 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose-(1-4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose | Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source #12: Sugar | ChemComp-NAG / | |
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Bovine muscle nicotinic acetylcholine receptor / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#5 / Source: MULTIPLE SOURCES |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2200 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1600 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON III (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software | Name: PHENIX / Category: model refinement |
|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.14 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 168720 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj