+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 9ask | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Human DNA polymerase theta helicase domain dimer, apo-form | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components | DNA polymerase theta | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSFERASE / DNA BINDING PROTEIN / DNA repair / helicase / ATPase | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationdouble-strand break repair via alternative nonhomologous end joining / HDR through MMEJ (alt-NHEJ) / single-stranded DNA helicase activity / replication fork processing / mitochondrial nucleoid / 5'-deoxyribose-5-phosphate lyase activity / error-prone translesion synthesis / negative regulation of double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / site of DNA damage / somatic hypermutation of immunoglobulin genes ...double-strand break repair via alternative nonhomologous end joining / HDR through MMEJ (alt-NHEJ) / single-stranded DNA helicase activity / replication fork processing / mitochondrial nucleoid / 5'-deoxyribose-5-phosphate lyase activity / error-prone translesion synthesis / negative regulation of double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / site of DNA damage / somatic hypermutation of immunoglobulin genes / DNA helicase activity / protein homooligomerization / base-excision repair / RNA-directed DNA polymerase / RNA-directed DNA polymerase activity / double-strand break repair / site of double-strand break / DNA-directed DNA polymerase / damaged DNA binding / DNA helicase / DNA-directed DNA polymerase activity / DNA repair / DNA damage response / chromatin binding / magnesium ion binding / Golgi apparatus / ATP hydrolysis activity / nucleoplasm / ATP binding / identical protein binding / nucleus / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.6 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Ito, F. / Li, Z. / Chen, X.S. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2025 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2025Title: Structural basis for Polθ-helicase DNA binding and microhomology-mediated end-joining. Authors: Fumiaki Ito / Ziyuan Li / Leonid Minakhin / Htet A Khant / Richard T Pomerantz / Xiaojiang S Chen /  Abstract: DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) present a critical threat to genomic integrity, often precipitating genomic instability and oncogenesis. Repair of DSBs predominantly occurs through homologous ...DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) present a critical threat to genomic integrity, often precipitating genomic instability and oncogenesis. Repair of DSBs predominantly occurs through homologous recombination (HR) and non-homologous end joining (NHEJ). In HR-deficient cells, DNA polymerase theta (Polθ) becomes critical for DSB repair via microhomology-mediated end joining (MMEJ), also termed theta-mediated end joining (TMEJ). Thus, Polθ is synthetically lethal with BRCA1/2 and other HR factors, underscoring its potential as a therapeutic target in HR-deficient cancers. However, the molecular mechanisms governing Polθ-mediated MMEJ remain poorly understood. Here we present a series of cryo-electron microscopy structures of the Polθ helicase domain (Polθ-hel) in complex with DNA containing different 3'-ssDNA overhangs. The structures reveal the sequential conformations adopted by Polθ-hel during the critical phases of DNA binding, microhomology searching, and microhomology annealing. The stepwise conformational changes within the Polθ-hel subdomains and its functional dimeric state are pivotal for aligning the 3'-ssDNA overhangs, facilitating the microhomology search and subsequent annealing necessary for DSB repair via MMEJ. Our findings illustrate the essential molecular switches within Polθ-hel that orchestrate the MMEJ process in DSB repair, laying the groundwork for the development of targeted therapies against the Polθ-hel. #1: Journal: bioRxiv / Year: 2024 Title: Structural Basis for Polθ-Helicase DNA Binding and Microhomology-Mediated End-Joining. Authors: Fumiaki Ito / Ziyuan Li / Leonid Minakhin / Htet A Khant / Richard T Pomerantz / Xiaojiang S Chen /  Abstract: DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) present a critical threat to genomic integrity, often precipitating genomic instability and oncogenesis. Repair of DSBs predominantly occurs through homologous ...DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) present a critical threat to genomic integrity, often precipitating genomic instability and oncogenesis. Repair of DSBs predominantly occurs through homologous recombination (HR) and non-homologous end joining (NHEJ). In HR-deficient cells, DNA polymerase theta (Polθ) becomes critical for DSB repair via microhomology-mediated end joining (MMEJ), also termed theta-mediated end joining (TMEJ). Thus, Polθ is synthetically lethal with BRCA1/2 and other HR factors, underscoring its potential as a therapeutic target in HR-deficient cancers. However, the molecular mechanisms governing Polθ-mediated MMEJ remain poorly understood. Here we present a series of cryo-electron microscopy structures of the Polθ helicase domain (Polθ-hel) in complex with DNA containing 3'-overhang. The structures reveal the sequential conformations adopted by Polθ-hel during the critical phases of DNA binding, microhomology searching, and microhomology annealing. The stepwise conformational changes within the Polθ-hel subdomains and its functional dimeric state are pivotal for aligning the 3'-overhangs, facilitating the microhomology search and subsequent annealing necessary for DSB repair via MMEJ. Our findings illustrate the essential molecular switches within Polθ-hel that orchestrate the MMEJ process in DSB repair, laying the groundwork for the development of targeted therapies against the Polθ-hel. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  9ask.cif.gz 9ask.cif.gz | 262.7 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb9ask.ent.gz pdb9ask.ent.gz | 209 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  9ask.json.gz 9ask.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/as/9ask https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/as/9ask ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/as/9ask ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/as/9ask | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  43817MC  8w0aC  9asjC  9aslC  9c5qC  40760  40761 M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 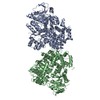
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 99802.539 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: POLQ, POLH / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: POLQ, POLH / Production host:  Has protein modification | N | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Human DNA polymerase theta helicase domain dimer, apo-form Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.199 MDa / Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Conc.: 1 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Microscopy | Model: TFS GLACIOS |
|---|---|
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 150000 X / Nominal defocus max: 3000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm / Cs: 2 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 50 µm |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 8 sec. / Electron dose: 58 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON IV (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 4511 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 3961362 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.6 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 280269 / Num. of class averages: 1 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj


