+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Human DNA polymerase theta helicase domain tetramer, apo-form | |||||||||
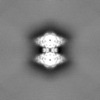
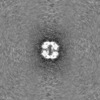
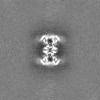
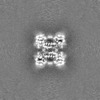
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | DNA repair / helicase / ATPase / TRANSFERASE / DNA BINDING PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationdouble-strand break repair via alternative nonhomologous end joining / HDR through MMEJ (alt-NHEJ) / single-stranded DNA helicase activity / replication fork processing / mitochondrial nucleoid / site of DNA damage / 5'-deoxyribose-5-phosphate lyase activity / error-prone translesion synthesis / negative regulation of double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / somatic hypermutation of immunoglobulin genes ...double-strand break repair via alternative nonhomologous end joining / HDR through MMEJ (alt-NHEJ) / single-stranded DNA helicase activity / replication fork processing / mitochondrial nucleoid / site of DNA damage / 5'-deoxyribose-5-phosphate lyase activity / error-prone translesion synthesis / negative regulation of double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / somatic hypermutation of immunoglobulin genes / DNA helicase activity / base-excision repair / protein homooligomerization / RNA-directed DNA polymerase / RNA-directed DNA polymerase activity / double-strand break repair / site of double-strand break / DNA helicase / DNA-directed DNA polymerase / damaged DNA binding / DNA-directed DNA polymerase activity / DNA repair / DNA damage response / chromatin binding / magnesium ion binding / Golgi apparatus / ATP hydrolysis activity / nucleoplasm / ATP binding / identical protein binding / nucleus / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
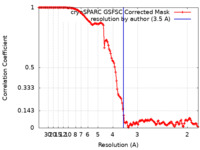
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.5 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Ito F / Li Z / Chen XS | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation | Journal: bioRxiv / Year: 2024 Title: Structural Basis for Polθ-Helicase DNA Binding and Microhomology-Mediated End-Joining. Authors: Fumiaki Ito / Ziyuan Li / Leonid Minakhin / Htet A Khant / Richard T Pomerantz / Xiaojiang S Chen /  Abstract: DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) present a critical threat to genomic integrity, often precipitating genomic instability and oncogenesis. Repair of DSBs predominantly occurs through homologous ...DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) present a critical threat to genomic integrity, often precipitating genomic instability and oncogenesis. Repair of DSBs predominantly occurs through homologous recombination (HR) and non-homologous end joining (NHEJ). In HR-deficient cells, DNA polymerase theta (Polθ) becomes critical for DSB repair via microhomology-mediated end joining (MMEJ), also termed theta-mediated end joining (TMEJ). Thus, Polθ is synthetically lethal with BRCA1/2 and other HR factors, underscoring its potential as a therapeutic target in HR-deficient cancers. However, the molecular mechanisms governing Polθ-mediated MMEJ remain poorly understood. Here we present a series of cryo-electron microscopy structures of the Polθ helicase domain (Polθ-hel) in complex with DNA containing 3'-overhang. The structures reveal the sequential conformations adopted by Polθ-hel during the critical phases of DNA binding, microhomology searching, and microhomology annealing. The stepwise conformational changes within the Polθ-hel subdomains and its functional dimeric state are pivotal for aligning the 3'-overhangs, facilitating the microhomology search and subsequent annealing necessary for DSB repair via MMEJ. Our findings illustrate the essential molecular switches within Polθ-hel that orchestrate the MMEJ process in DSB repair, laying the groundwork for the development of targeted therapies against the Polθ-hel. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_43818.map.gz emd_43818.map.gz | 125.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-43818-v30.xml emd-43818-v30.xml emd-43818.xml emd-43818.xml | 19.1 KB 19.1 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_43818_fsc.xml emd_43818_fsc.xml | 13.1 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_43818.png emd_43818.png | 89 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-43818.cif.gz emd-43818.cif.gz | 6.5 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_43818_half_map_1.map.gz emd_43818_half_map_1.map.gz emd_43818_half_map_2.map.gz emd_43818_half_map_2.map.gz | 226.2 MB 226.2 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-43818 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-43818 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-43818 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-43818 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_43818_validation.pdf.gz emd_43818_validation.pdf.gz | 928.5 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_43818_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_43818_full_validation.pdf.gz | 928 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_43818_validation.xml.gz emd_43818_validation.xml.gz | 22.1 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_43818_validation.cif.gz emd_43818_validation.cif.gz | 28.7 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-43818 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-43818 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-43818 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-43818 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  9aslMC  8w0aC  9asjC  9askC  9c5qC  40760  40761 M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_43818.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 244.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_43818.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 244.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.92 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
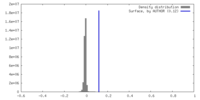
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_43818_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_43818_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Human DNA polymerase theta helicase domain tetramer, apo-form
| Entire | Name: Human DNA polymerase theta helicase domain tetramer, apo-form |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Human DNA polymerase theta helicase domain tetramer, apo-form
| Supramolecule | Name: Human DNA polymerase theta helicase domain tetramer, apo-form type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 398 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: DNA polymerase theta
| Macromolecule | Name: DNA polymerase theta / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: DNA-directed DNA polymerase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 99.802539 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MNLLRRSGKR RRSESGSDSF SGSGGDSSAS PQFLSGSVLS PPPGLGRCLK AAAAGECKPT VPDYERDKLL LANWGLPKAV LEKYHSFGV KKMFEWQAEC LLLGQVLEGK NLVYSAPTSA GKTLVAELLI LKRVLEMRKK ALFILPFVSV AKEKKYYLQS L FQEVGIKV ...String: MNLLRRSGKR RRSESGSDSF SGSGGDSSAS PQFLSGSVLS PPPGLGRCLK AAAAGECKPT VPDYERDKLL LANWGLPKAV LEKYHSFGV KKMFEWQAEC LLLGQVLEGK NLVYSAPTSA GKTLVAELLI LKRVLEMRKK ALFILPFVSV AKEKKYYLQS L FQEVGIKV DGYMGSTSPS RHFSSLDIAV CTIERANGLI NRLIEENKMD LLGMVVVDEL HMLGDSHRGY LLELLLTKIC YI TRKSASC QADLASSLSN AVQIVGMSAT LPNLELVASW LNAELYHTDF RPVPLLESVK VGNSIYDSSM KLVREFEPML QVK GDEDHV VSLCYETICD NHSVLLFCPS KKWCEKLADI IAREFYNLHH QAEGLVKPSE CPPVILEQKE LLEVMDQLRR LPSG LDSVL QKTVPWGVAF HHAGLTFEER DIIEGAFRQG LIRVLAATST LSSGVNLPAR RVIIRTPIFG GRPLDILTYK QMVGR AGRK GVDTVGESIL ICKNSEKSKG IALLQGSLKP VRSCLQRREG EEVTGSMIRA ILEIIVGGVA STSQDMHTYA ACTFLA ASM KEGKQGIQRN QESVQLGAIE ACVMWLLENE FIQSTEASDG TEGKVYHPTH LGSATLSSSL SPADTLDIFA DLQRAMK GF VLENDLHILY LVTPMFEDWT TIDWYRFFCL WEKLPTSMKR VAELVGVEEG FLARCVKGKV VARTERQHRQ MAIHKRFF T SLVLLDLISE VPLREINQKY GCNRGQIQSL QQSAAVYAGM ITVFSNRLGW HNMELLLSQF QKRLTFGIQR ELCDLVRVS LLNAQRARVL YASGFHTVAD LARANIVEVE VILKNAVPFK SARKAVDEEE EAVEERRNMR TIWVTGRKGL TEREAAALIV EEARMILQQ DLVEM UniProtKB: DNA polymerase theta |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 1 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS GLACIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON IV (4k x 4k) / Number grids imaged: 1 / Number real images: 4511 / Average exposure time: 8.0 sec. / Average electron dose: 58.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 200 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 50.0 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.0 mm / Nominal defocus max: 3.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm / Nominal magnification: 150000 |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller










 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)