[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-8xbw: The cryo-EM structure of the RAD51 N-terminal lobe domain bound t... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8xbw | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | The cryo-EM structure of the RAD51 N-terminal lobe domain bound to the histone H4 tail of the nucleosome | ||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | DNA BINDING PROTEIN/DNA / Nucleosome / Recombinase / DNA BINDING PROTEIN-DNA Complex | ||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpresynaptic intermediate filament cytoskeleton / response to glucoside / mitotic recombination-dependent replication fork processing / DNA recombinase assembly / cellular response to camptothecin / chromosome organization involved in meiotic cell cycle / telomere maintenance via telomere lengthening / double-strand break repair involved in meiotic recombination / nuclear ubiquitin ligase complex / cellular response to cisplatin ...presynaptic intermediate filament cytoskeleton / response to glucoside / mitotic recombination-dependent replication fork processing / DNA recombinase assembly / cellular response to camptothecin / chromosome organization involved in meiotic cell cycle / telomere maintenance via telomere lengthening / double-strand break repair involved in meiotic recombination / nuclear ubiquitin ligase complex / cellular response to cisplatin / DNA strand invasion / cellular response to hydroxyurea / mitotic recombination / DNA strand exchange activity / replication-born double-strand break repair via sister chromatid exchange / lateral element / regulation of DNA damage checkpoint / Impaired BRCA2 binding to PALB2 / telomere maintenance via recombination / single-stranded DNA helicase activity / reciprocal meiotic recombination / Homologous DNA Pairing and Strand Exchange / Defective homologous recombination repair (HRR) due to BRCA1 loss of function / Defective HDR through Homologous Recombination Repair (HRR) due to PALB2 loss of BRCA1 binding function / Defective HDR through Homologous Recombination Repair (HRR) due to PALB2 loss of BRCA2/RAD51/RAD51C binding function / Resolution of D-loop Structures through Synthesis-Dependent Strand Annealing (SDSA) / Resolution of D-loop Structures through Holliday Junction Intermediates / HDR through Single Strand Annealing (SSA) / ATP-dependent DNA damage sensor activity / regulation of double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / nuclear chromosome / Impaired BRCA2 binding to RAD51 / Transcriptional Regulation by E2F6 / replication fork processing / Presynaptic phase of homologous DNA pairing and strand exchange / response to X-ray / ATP-dependent activity, acting on DNA / interstrand cross-link repair / negative regulation of megakaryocyte differentiation / protein localization to CENP-A containing chromatin / Chromatin modifying enzymes / Replacement of protamines by nucleosomes in the male pronucleus / condensed chromosome / CENP-A containing nucleosome / DNA polymerase binding / Packaging Of Telomere Ends / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected purine / Cleavage of the damaged purine / Deposition of new CENPA-containing nucleosomes at the centromere / telomere organization / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected pyrimidine / Cleavage of the damaged pyrimidine / Interleukin-7 signaling / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Opening / epigenetic regulation of gene expression / Inhibition of DNA recombination at telomere / Assembly of the ORC complex at the origin of replication / Meiotic synapsis / SUMOylation of chromatin organization proteins / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by the Human Silencing Hub (HUSH) complex / DNA methylation / Condensation of Prophase Chromosomes / Chromatin modifications during the maternal to zygotic transition (MZT) / SIRT1 negatively regulates rRNA expression / HCMV Late Events / condensed nuclear chromosome / ERCC6 (CSB) and EHMT2 (G9a) positively regulate rRNA expression / cellular response to ionizing radiation / PRC2 methylates histones and DNA / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by KRAB-ZFP proteins / male germ cell nucleus / Defective pyroptosis / meiotic cell cycle / HDACs deacetylate histones / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Escape / Nonhomologous End-Joining (NHEJ) / Transcriptional regulation by small RNAs / Formation of the beta-catenin:TCF transactivating complex / cellular response to gamma radiation / Activated PKN1 stimulates transcription of AR (androgen receptor) regulated genes KLK2 and KLK3 / RUNX1 regulates genes involved in megakaryocyte differentiation and platelet function / HDMs demethylate histones / double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / G2/M DNA damage checkpoint / PML body / NoRC negatively regulates rRNA expression / B-WICH complex positively regulates rRNA expression / PKMTs methylate histone lysines / DNA Damage/Telomere Stress Induced Senescence / HDR through Homologous Recombination (HRR) / Pre-NOTCH Transcription and Translation / Meiotic recombination / response to toxic substance / Activation of anterior HOX genes in hindbrain development during early embryogenesis / RMTs methylate histone arginines / Transcriptional regulation of granulopoiesis / HCMV Early Events / structural constituent of chromatin / nucleosome Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)synthetic construct (others) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.89 Å | ||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Shioi, T. / Hatazawa, S. / Ogasawara, M. / Takizawa, Y. / Kurumizaka, H. | ||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Japan, 5items Japan, 5items
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2024 Journal: Nature / Year: 2024Title: Cryo-EM structures of RAD51 assembled on nucleosomes containing a DSB site. Authors: Takuro Shioi / Suguru Hatazawa / Eriko Oya / Noriko Hosoya / Wataru Kobayashi / Mitsuo Ogasawara / Takehiko Kobayashi / Yoshimasa Takizawa / Hitoshi Kurumizaka /  Abstract: RAD51 is the central eukaryotic recombinase required for meiotic recombination and mitotic repair of double-strand DNA breaks (DSBs). However, the mechanism by which RAD51 functions at DSB sites in ...RAD51 is the central eukaryotic recombinase required for meiotic recombination and mitotic repair of double-strand DNA breaks (DSBs). However, the mechanism by which RAD51 functions at DSB sites in chromatin has remained elusive. Here we report the cryo-electron microscopy structures of human RAD51-nucleosome complexes, in which RAD51 forms ring and filament conformations. In the ring forms, the N-terminal lobe domains (NLDs) of RAD51 protomers are aligned on the outside of the RAD51 ring, and directly bind to the nucleosomal DNA. The nucleosomal linker DNA that contains the DSB site is recognized by the L1 and L2 loops-active centres that face the central hole of the RAD51 ring. In the filament form, the nucleosomal DNA is peeled by the RAD51 filament extension, and the NLDs of RAD51 protomers proximal to the nucleosome bind to the remaining nucleosomal DNA and histones. Mutations that affect nucleosome-binding residues of the RAD51 NLD decrease nucleosome binding, but barely affect DNA binding in vitro. Consistently, yeast Rad51 mutants with the corresponding mutations are substantially defective in DNA repair in vivo. These results reveal an unexpected function of the RAD51 NLD, and explain the mechanism by which RAD51 associates with nucleosomes, recognizes DSBs and forms the active filament in chromatin. | ||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8xbw.cif.gz 8xbw.cif.gz | 94.5 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8xbw.ent.gz pdb8xbw.ent.gz | 60.9 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8xbw.json.gz 8xbw.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/xb/8xbw https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/xb/8xbw ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/xb/8xbw ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/xb/8xbw | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  38231MC  8jndC  8jneC  8jnfC  8xbtC  8xbuC  8xbvC  8xbxC  8xbyC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 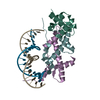
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 15719.445 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)Gene: H3C1, H3FA, HIST1H3A, H3C2, H3FL, HIST1H3B, H3C3, H3FC HIST1H3C, H3C4, H3FB, HIST1H3D, H3C6, H3FD, HIST1H3E, H3C7, H3FI, HIST1H3F, H3C8, H3FH, HIST1H3G, H3C10, H3FK, HIST1H3H, H3C11, H3FF, ...Gene: H3C1, H3FA, HIST1H3A, H3C2, H3FL, HIST1H3B, H3C3, H3FC HIST1H3C, H3C4, H3FB, HIST1H3D, H3C6, H3FD, HIST1H3E, H3C7, H3FI, HIST1H3F, H3C8, H3FH, HIST1H3G, H3C10, H3FK, HIST1H3H, H3C11, H3FF, HIST1H3I, H3C12, H3FJ, HIST1H3J Production host:  |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 11676.703 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: H4C1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: H4C1 / Production host:  |
| #3: DNA chain | Mass: 47976.699 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.) synthetic construct (others) / Production host:  |
| #4: DNA chain | Mass: 47371.070 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.) synthetic construct (others) / Production host:  |
| #5: Protein | Mass: 37291.398 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: RAD51, RAD51A, RECA / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: RAD51, RAD51A, RECA / Production host:  |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: RAD51-nucleosome complex / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 60 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
|---|---|
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.89 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 411212 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj














































