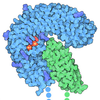
登録情報 データベース : PDB / ID : 8vsdタイトル avb8/L-TGF-b1/GARP (Transforming growth factor ...) x 2 Integrin alpha-V heavy chain Integrin beta-8 キーワード / / 機能・相同性 分子機能 ドメイン・相同性 構成要素
/ / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / 生物種 Homo sapiens (ヒト)手法 / / / 解像度 : 3.2 Å データ登録者 Jin, M. / Cheng, Y. / Nishimura, S.L. 資金援助 組織 認可番号 国 National Institutes of Health/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NIH/NHLBI) HL134183
ジャーナル : Cell / 年 : 2024タイトル : Dynamic allostery drives autocrine and paracrine TGF-β signaling.著者: Mingliang Jin / Robert I Seed / Guoqing Cai / Tiffany Shing / Li Wang / Saburo Ito / Anthony Cormier / Stephanie A Wankowicz / Jillian M Jespersen / Jody L Baron / Nicholas D Carey / Melody G ... 著者 : Mingliang Jin / Robert I Seed / Guoqing Cai / Tiffany Shing / Li Wang / Saburo Ito / Anthony Cormier / Stephanie A Wankowicz / Jillian M Jespersen / Jody L Baron / Nicholas D Carey / Melody G Campbell / Zanlin Yu / Phu K Tang / Pilar Cossio / Weihua Wen / Jianlong Lou / James Marks / Stephen L Nishimura / Yifan Cheng / 要旨 : TGF-β, essential for development and immunity, is expressed as a latent complex (L-TGF-β) non-covalently associated with its prodomain and presented on immune cell surfaces by covalent association ... TGF-β, essential for development and immunity, is expressed as a latent complex (L-TGF-β) non-covalently associated with its prodomain and presented on immune cell surfaces by covalent association with GARP. Binding to integrin αvβ8 activates L-TGF-β1/GARP. The dogma is that mature TGF-β must physically dissociate from L-TGF-β1 for signaling to occur. Our previous studies discovered that αvβ8-mediated TGF-β autocrine signaling can occur without TGF-β1 release from its latent form. Here, we show that mice engineered to express TGF-β1 that cannot release from L-TGF-β1 survive without early lethal tissue inflammation, unlike those with TGF-β1 deficiency. Combining cryogenic electron microscopy with cell-based assays, we reveal a dynamic allosteric mechanism of autocrine TGF-β1 signaling without release where αvβ8 binding redistributes the intrinsic flexibility of L-TGF-β1 to expose TGF-β1 to its receptors. Dynamic allostery explains the TGF-β3 latency/activation mechanism and why TGF-β3 functions distinctly from TGF-β1, suggesting that it broadly applies to other flexible cell surface receptor/ligand systems. 履歴 登録 2024年1月23日 登録サイト / 処理サイト 改定 1.0 2024年9月11日 Provider / タイプ 改定 1.1 2024年10月2日 Group / Database references / カテゴリ / citation_author / em_adminItem _citation.country / _citation.journal_abbrev ... _citation.country / _citation.journal_abbrev / _citation.journal_id_ASTM / _citation.journal_id_CSD / _citation.journal_id_ISSN / _citation.pdbx_database_id_DOI / _citation.pdbx_database_id_PubMed / _citation.title / _em_admin.last_update 改定 1.2 2024年11月13日 Group / Database references / Structure summaryカテゴリ citation / em_admin ... citation / em_admin / pdbx_entry_details / pdbx_modification_feature Item _citation.journal_volume / _citation.page_first ... _citation.journal_volume / _citation.page_first / _citation.page_last / _em_admin.last_update / _pdbx_entry_details.has_protein_modification 改定 1.3 2024年11月20日 Group / Database references / カテゴリ / em_admin / Item / _em_admin.last_update
すべて表示 表示を減らす
 データを開く
データを開く 基本情報
基本情報 要素
要素 キーワード
キーワード 機能・相同性情報
機能・相同性情報 Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト) データ登録者
データ登録者 米国, 1件
米国, 1件  引用
引用 ジャーナル: Cell / 年: 2024
ジャーナル: Cell / 年: 2024
 構造の表示
構造の表示 Molmil
Molmil Jmol/JSmol
Jmol/JSmol ダウンロードとリンク
ダウンロードとリンク ダウンロード
ダウンロード 8vsd.cif.gz
8vsd.cif.gz PDBx/mmCIF形式
PDBx/mmCIF形式 pdb8vsd.ent.gz
pdb8vsd.ent.gz PDB形式
PDB形式 8vsd.json.gz
8vsd.json.gz PDBx/mmJSON形式
PDBx/mmJSON形式 その他のダウンロード
その他のダウンロード 8vsd_validation.pdf.gz
8vsd_validation.pdf.gz wwPDB検証レポート
wwPDB検証レポート 8vsd_full_validation.pdf.gz
8vsd_full_validation.pdf.gz 8vsd_validation.xml.gz
8vsd_validation.xml.gz 8vsd_validation.cif.gz
8vsd_validation.cif.gz https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vs/8vsd
https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vs/8vsd ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vs/8vsd
ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vs/8vsd リンク
リンク 集合体
集合体
 要素
要素 Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: LRRC32, D11S833E / 発現宿主:
Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: LRRC32, D11S833E / 発現宿主:  Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 参照: UniProt: Q14392
Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 参照: UniProt: Q14392 Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: TGFB1, TGFB / 発現宿主:
Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: TGFB1, TGFB / 発現宿主:  Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: ITGAV, MSK8, VNRA, VTNR
Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: ITGAV, MSK8, VNRA, VTNR
 Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: ITGB8
Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: ITGB8




 試料調製
試料調製 電子顕微鏡撮影
電子顕微鏡撮影
 FIELD EMISSION GUN / 加速電圧: 300 kV / 照射モード: FLOOD BEAM
FIELD EMISSION GUN / 加速電圧: 300 kV / 照射モード: FLOOD BEAM 解析
解析 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー











 PDBj
PDBj