+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | avb8/L-TGF-b1/GARP | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | L-TGF-b1/GARP/avb8 | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Integrin / Complex / SIGNALING PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationestablishment of protein localization to extracellular region / ganglioside metabolic process / Langerhans cell differentiation / secondary palate development / integrin alphav-beta8 complex / integrin alphav-beta6 complex / transforming growth factor beta production / negative regulation of entry of bacterium into host cell / integrin alphav-beta5 complex / opsonin binding ...establishment of protein localization to extracellular region / ganglioside metabolic process / Langerhans cell differentiation / secondary palate development / integrin alphav-beta8 complex / integrin alphav-beta6 complex / transforming growth factor beta production / negative regulation of entry of bacterium into host cell / integrin alphav-beta5 complex / opsonin binding / integrin alphav-beta1 complex / Cross-presentation of particulate exogenous antigens (phagosomes) / extracellular matrix protein binding / Laminin interactions / placenta blood vessel development / integrin alphav-beta3 complex / negative regulation of lipoprotein metabolic process / receptor ligand inhibitor activity / entry into host cell by a symbiont-containing vacuole / alphav-beta3 integrin-PKCalpha complex / alphav-beta3 integrin-HMGB1 complex / negative regulation of lipid transport / hard palate development / regulation of phagocytosis / Elastic fibre formation / alphav-beta3 integrin-IGF-1-IGF1R complex / transforming growth factor beta binding / positive regulation of small GTPase mediated signal transduction / filopodium membrane / extracellular matrix binding / cartilage development / wound healing, spreading of epidermal cells / apolipoprotein A-I-mediated signaling pathway / negative regulation of low-density lipoprotein particle clearance / apoptotic cell clearance / integrin complex / heterotypic cell-cell adhesion / Molecules associated with elastic fibres / cell adhesion mediated by integrin / negative chemotaxis / negative regulation of cytokine production / Mechanical load activates signaling by PIEZO1 and integrins in osteocytes / Syndecan interactions / positive regulation of osteoblast proliferation / negative regulation of activated T cell proliferation / microvillus membrane / cell-substrate adhesion / endodermal cell differentiation / PECAM1 interactions / TGF-beta receptor signaling activates SMADs / fibronectin binding / lamellipodium membrane / positive regulation of intracellular signal transduction / negative regulation of macrophage derived foam cell differentiation / negative regulation of lipid storage / ECM proteoglycans / Integrin cell surface interactions / vasculogenesis / specific granule membrane / voltage-gated calcium channel activity / coreceptor activity / phagocytic vesicle / ERK1 and ERK2 cascade / extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in absence of ligand / substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading / positive regulation of cell adhesion / transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway / Turbulent (oscillatory, disturbed) flow shear stress activates signaling by PIEZO1 and integrins in endothelial cells / protein kinase C binding / cell-matrix adhesion / integrin-mediated signaling pathway / Signal transduction by L1 / negative regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway / negative regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway / cell-cell adhesion / VEGFA-VEGFR2 Pathway / calcium ion transmembrane transport / integrin binding / extracellular matrix / response to virus / ruffle membrane / positive regulation of angiogenesis / cell migration / positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration / virus receptor activity / protease binding / angiogenesis / cell adhesion / positive regulation of cell migration / immune response / negative regulation of gene expression / external side of plasma membrane / focal adhesion / positive regulation of cell population proliferation / Neutrophil degranulation / symbiont entry into host cell / positive regulation of gene expression / cell surface / extracellular space / extracellular exosome Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.2 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Jin M / Cheng Y / Nishimura SL | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell / Year: 2024 Journal: Cell / Year: 2024Title: Dynamic allostery drives autocrine and paracrine TGF-β signaling. Authors: Mingliang Jin / Robert I Seed / Guoqing Cai / Tiffany Shing / Li Wang / Saburo Ito / Anthony Cormier / Stephanie A Wankowicz / Jillian M Jespersen / Jody L Baron / Nicholas D Carey / Melody ...Authors: Mingliang Jin / Robert I Seed / Guoqing Cai / Tiffany Shing / Li Wang / Saburo Ito / Anthony Cormier / Stephanie A Wankowicz / Jillian M Jespersen / Jody L Baron / Nicholas D Carey / Melody G Campbell / Zanlin Yu / Phu K Tang / Pilar Cossio / Weihua Wen / Jianlong Lou / James Marks / Stephen L Nishimura / Yifan Cheng /  Abstract: TGF-β, essential for development and immunity, is expressed as a latent complex (L-TGF-β) non-covalently associated with its prodomain and presented on immune cell surfaces by covalent association ...TGF-β, essential for development and immunity, is expressed as a latent complex (L-TGF-β) non-covalently associated with its prodomain and presented on immune cell surfaces by covalent association with GARP. Binding to integrin αvβ8 activates L-TGF-β1/GARP. The dogma is that mature TGF-β must physically dissociate from L-TGF-β1 for signaling to occur. Our previous studies discovered that αvβ8-mediated TGF-β autocrine signaling can occur without TGF-β1 release from its latent form. Here, we show that mice engineered to express TGF-β1 that cannot release from L-TGF-β1 survive without early lethal tissue inflammation, unlike those with TGF-β1 deficiency. Combining cryogenic electron microscopy with cell-based assays, we reveal a dynamic allosteric mechanism of autocrine TGF-β1 signaling without release where αvβ8 binding redistributes the intrinsic flexibility of L-TGF-β1 to expose TGF-β1 to its receptors. Dynamic allostery explains the TGF-β3 latency/activation mechanism and why TGF-β3 functions distinctly from TGF-β1, suggesting that it broadly applies to other flexible cell surface receptor/ligand systems. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_43494.map.gz emd_43494.map.gz | 483.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-43494-v30.xml emd-43494-v30.xml emd-43494.xml emd-43494.xml | 18.1 KB 18.1 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_43494.png emd_43494.png | 94.9 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-43494.cif.gz emd-43494.cif.gz | 7.1 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-43494 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-43494 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-43494 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-43494 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8vsdMC 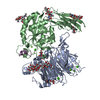 8vs6C 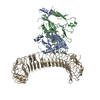 8vsbC  8vscC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_43494.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 512 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_43494.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 512 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | L-TGF-b1/GARP/avb8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.1742 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
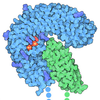
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : avb8/L-TGF-b1/GARP complex
+Supramolecule #1: avb8/L-TGF-b1/GARP complex
+Supramolecule #2: avb8 complex
+Supramolecule #3: L-TGF-b1/GARP complex
+Macromolecule #1: Transforming growth factor beta activator LRRC32
+Macromolecule #2: Integrin alpha-V heavy chain
+Macromolecule #3: Integrin beta-8
+Macromolecule #4: Transforming growth factor beta-1 proprotein
+Macromolecule #7: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose
+Macromolecule #8: CALCIUM ION
+Macromolecule #9: MAGNESIUM ION
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 68.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.8 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: NONE |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.2 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 46771 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: NOT APPLICABLE |
| Final angle assignment | Type: NOT APPLICABLE |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller
























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)






















