[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-8uxq: Structure of Heterochromatin Protein 1 (HP1) alpha in complex wit... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8uxq | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of Heterochromatin Protein 1 (HP1) alpha in complex with an H2A.Z nucleosome | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | STRUCTURAL PROTEIN / heterochromatin / nucleosome / chromatin / GENE REGULATION | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationchromocenter / histone H3K9me2/3 reader activity / nucleosomal DNA binding / histone deacetylase complex / Transcriptional Regulation by E2F6 / : / histone methyltransferase complex / site of DNA damage / ribonucleoprotein complex binding / RNA polymerase II core promoter sequence-specific DNA binding ...chromocenter / histone H3K9me2/3 reader activity / nucleosomal DNA binding / histone deacetylase complex / Transcriptional Regulation by E2F6 / : / histone methyltransferase complex / site of DNA damage / ribonucleoprotein complex binding / RNA polymerase II core promoter sequence-specific DNA binding / pericentric heterochromatin / heterochromatin / transcription repressor complex / SUMOylation of chromatin organization proteins / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by KRAB-ZFP proteins / cellular response to estradiol stimulus / euchromatin / kinetochore / histone deacetylase binding / structural constituent of chromatin / nuclear envelope / heterochromatin formation / nucleosome / nucleosome assembly / Factors involved in megakaryocyte development and platelet production / chromatin organization / protein-macromolecule adaptor activity / DNA-binding transcription factor binding / chromosome, telomeric region / RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding / protein heterodimerization activity / ribonucleoprotein complex / negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription / DNA damage response / chromatin binding / protein-containing complex binding / nucleolus / negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / protein-containing complex / DNA binding / nucleoplasm / identical protein binding / nucleus Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) synthetic construct (others) | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 6.3 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Tan, D. / Sokolova, V. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2items United States, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Structure / Year: 2024 Journal: Structure / Year: 2024Title: Structural mechanism of HP1⍺-dependent transcriptional repression and chromatin compaction. Authors: Vladyslava Sokolova / Jacob Miratsky / Vladimir Svetlov / Michael Brenowitz / John Vant / Tyler S Lewis / Kelly Dryden / Gahyun Lee / Shayan Sarkar / Evgeny Nudler / Abhishek Singharoy / Dongyan Tan /  Abstract: Heterochromatin protein 1 (HP1) plays a central role in establishing and maintaining constitutive heterochromatin. However, the mechanisms underlying HP1-nucleosome interactions and their ...Heterochromatin protein 1 (HP1) plays a central role in establishing and maintaining constitutive heterochromatin. However, the mechanisms underlying HP1-nucleosome interactions and their contributions to heterochromatin functions remain elusive. Here, we present the cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM) structure of an HP1α dimer bound to an H2A.Z-nucleosome, revealing two distinct HP1α-nucleosome interfaces. The primary HP1α binding site is located at the N terminus of histone H3, specifically at the trimethylated lysine 9 (K9me3) region, while a secondary binding site is situated near histone H2B, close to nucleosome superhelical location 4 (SHL4). Our biochemical data further demonstrates that HP1α binding influences the dynamics of DNA on the nucleosome. It promotes DNA unwrapping near the nucleosome entry and exit sites while concurrently restricting DNA accessibility in the vicinity of SHL4. Our study offers a model for HP1α-mediated heterochromatin maintenance and gene silencing. It also sheds light on the H3K9me-independent role of HP1 in responding to DNA damage. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8uxq.cif.gz 8uxq.cif.gz | 296.7 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8uxq.ent.gz pdb8uxq.ent.gz | 228 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8uxq.json.gz 8uxq.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ux/8uxq https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ux/8uxq ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ux/8uxq ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ux/8uxq | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  42774MC C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 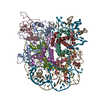
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 5 types, 10 molecules ACEKFLGMHN
| #1: Protein | Mass: 22651.398 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CBX5, HP1A / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CBX5, HP1A / Production host:  #2: Protein | Mass: 15303.930 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Mutation: C110A Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  #3: Protein | Mass: 11263.231 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  #4: Protein | Mass: 13450.601 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   #5: Protein | Mass: 13848.097 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  |
|---|
-DNA Widom601 (208bp) ... , 2 types, 2 molecules IJ
| #6: DNA chain | Mass: 64456.039 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) |
|---|---|
| #7: DNA chain | Mass: 63988.711 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) |
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | N |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: HP1alpha dimer bound to H2A.Z nucleosome / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: MULTIPLE SOURCES |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.288 MDa / Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 400 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK III / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 39.2 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Calibrated magnification: 81000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2250 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 100 µm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter name: GIF Bioquantum / Energyfilter slit width: 10 eV |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 6.3 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 74257 / Algorithm: BACK PROJECTION / Num. of class averages: 1 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Target criteria: Cross-correlation coefficient | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Accession code: P45973 / Source name: AlphaFold / Type: in silico model |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 PDBj
PDBj








































