+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8u4s | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
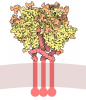
| Title | Structure of trimeric CXCR4 in complex with REGN7663 Fab | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | SIGNALING PROTEIN/IMMUNE SYSTEM / GPCR / chemokine receptor / trimer / oligomer / antibody / SIGNALING PROTEIN-IMMUNE SYSTEM complex | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationC-X-C motif chemokine 12 receptor activity / positive regulation of macrophage migration inhibitory factor signaling pathway / myosin light chain binding / CXCL12-activated CXCR4 signaling pathway / Specification of primordial germ cells / myelin maintenance / C-X-C chemokine receptor activity / positive regulation of vasculature development / Signaling by ROBO receptors / regulation of chemotaxis ...C-X-C motif chemokine 12 receptor activity / positive regulation of macrophage migration inhibitory factor signaling pathway / myosin light chain binding / CXCL12-activated CXCR4 signaling pathway / Specification of primordial germ cells / myelin maintenance / C-X-C chemokine receptor activity / positive regulation of vasculature development / Signaling by ROBO receptors / regulation of chemotaxis / Formation of definitive endoderm / C-C chemokine receptor activity / Developmental Lineage of Pancreatic Acinar Cells / C-C chemokine binding / anchoring junction / Chemokine receptors bind chemokines / dendritic cell chemotaxis / cellular response to cytokine stimulus / cell leading edge / positive regulation of oligodendrocyte differentiation / Binding and entry of HIV virion / regulation of cell adhesion / coreceptor activity / neurogenesis / ubiquitin binding / cell chemotaxis / calcium-mediated signaling / brain development / G protein-coupled receptor activity / response to virus / late endosome / positive regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis / actin binding / positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration / virus receptor activity / cytoplasmic vesicle / G alpha (i) signalling events / response to hypoxia / early endosome / lysosome / positive regulation of cell migration / immune response / G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / inflammatory response / external side of plasma membrane / apoptotic process / ubiquitin protein ligase binding / cell surface / protein-containing complex / extracellular exosome / plasma membrane / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.35 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Saotome, K. / McGoldrick, L.L. / Franklin, M.C. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2025 Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2025Title: Structural insights into CXCR4 modulation and oligomerization. Authors: Kei Saotome / Luke L McGoldrick / Jo-Hao Ho / Trudy F Ramlall / Sweta Shah / Michael J Moore / Jee Hae Kim / Raymond Leidich / William C Olson / Matthew C Franklin /  Abstract: Activation of the chemokine receptor CXCR4 by its chemokine ligand CXCL12 regulates diverse cellular processes. Previously reported crystal structures of CXCR4 revealed the architecture of an ...Activation of the chemokine receptor CXCR4 by its chemokine ligand CXCL12 regulates diverse cellular processes. Previously reported crystal structures of CXCR4 revealed the architecture of an inactive, homodimeric receptor. However, many structural aspects of CXCR4 remain poorly understood. Here, we use cryo-electron microscopy to investigate various modes of human CXCR4 regulation. CXCL12 activates CXCR4 by inserting its N terminus deep into the CXCR4 orthosteric pocket. The binding of US Food and Drug Administration-approved antagonist AMD3100 is stabilized by electrostatic interactions with acidic residues in the seven-transmembrane-helix bundle. A potent antibody blocker, REGN7663, binds across the extracellular face of CXCR4 and inserts its complementarity-determining region H3 loop into the orthosteric pocket. Trimeric and tetrameric structures of CXCR4 reveal modes of G-protein-coupled receptor oligomerization. We show that CXCR4 adopts distinct subunit conformations in trimeric and tetrameric assemblies, highlighting how oligomerization could allosterically regulate chemokine receptor function. #1:  Journal: Biorxiv / Year: 2024 Journal: Biorxiv / Year: 2024Title: Structural insights into CXCR4 modulation and oligomerization Authors: Saotome, K. / McGoldrick, L.L. / Ho, J. / Ramlall, T. / Shah, S. / Moore, M.J. / Kim, J.H. / Leidich, R. / Olson, W.C. / Franklin, M.C. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8u4s.cif.gz 8u4s.cif.gz | 372.9 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8u4s.ent.gz pdb8u4s.ent.gz | 267.8 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8u4s.json.gz 8u4s.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/u4/8u4s https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/u4/8u4s ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/u4/8u4s ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/u4/8u4s | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  41893MC  8u4nC  8u4oC  8u4pC  8u4qC  8u4rC  8u4tC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Noncrystallographic symmetry (NCS) | NCS domain:
NCS domain segments:
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller









 PDBj
PDBj