[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-8tua: Full-length P-Rex1 in complex with inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosp... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8tua | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
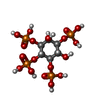
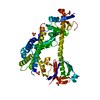
| Title | Full-length P-Rex1 in complex with inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate (IP4) | ||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components | Phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate-dependent Rac exchanger 1 protein | ||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | SIGNALING PROTEIN / Rho guanine-nucleotide exchange factor / Dbl homology domain / pleckstrin homology domain / Phosphatidylinositol 3 / 4 / 5-trisphosphate binding | ||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationregulation of dendrite development / regulation of actin filament polymerization / neutrophil activation / negative regulation of TOR signaling / regulation of small GTPase mediated signal transduction / RHOB GTPase cycle / superoxide metabolic process / NRAGE signals death through JNK / RHOC GTPase cycle / RHOJ GTPase cycle ...regulation of dendrite development / regulation of actin filament polymerization / neutrophil activation / negative regulation of TOR signaling / regulation of small GTPase mediated signal transduction / RHOB GTPase cycle / superoxide metabolic process / NRAGE signals death through JNK / RHOC GTPase cycle / RHOJ GTPase cycle / RHOQ GTPase cycle / CDC42 GTPase cycle / T cell differentiation / RHOG GTPase cycle / RHOA GTPase cycle / RAC2 GTPase cycle / RAC3 GTPase cycle / protein serine/threonine kinase inhibitor activity / actin filament polymerization / RAC1 GTPase cycle / neutrophil chemotaxis / positive regulation of substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading / GTPase activator activity / guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity / dendritic shaft / phospholipid binding / G alpha (12/13) signalling events / growth cone / intracellular signal transduction / positive regulation of cell migration / G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / perinuclear region of cytoplasm / enzyme binding / plasma membrane / cytosol Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.1 Å | ||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Cash, J.N. / Tesmer, J.J.G. | ||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 5items United States, 5items
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Elife / Year: 2024 Journal: Elife / Year: 2024Title: Full-length P-Rex1 in complex with inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate (IP4) Authors: Ravala, S.K. / Adame-Garcia, S.R. / Li, S. / Chen, C. / Cianfrocco, M.A. / Gutkind, J.S. / Cash, J.N. / Tesmer, J.J.G. #1: Journal: Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol / Year: 2019 Title: Macromolecular structure determination using X-rays, neutrons and electrons: recent developments in Phenix. Authors: Dorothee Liebschner / Pavel V Afonine / Matthew L Baker / Gábor Bunkóczi / Vincent B Chen / Tristan I Croll / Bradley Hintze / Li Wei Hung / Swati Jain / Airlie J McCoy / Nigel W Moriarty ...Authors: Dorothee Liebschner / Pavel V Afonine / Matthew L Baker / Gábor Bunkóczi / Vincent B Chen / Tristan I Croll / Bradley Hintze / Li Wei Hung / Swati Jain / Airlie J McCoy / Nigel W Moriarty / Robert D Oeffner / Billy K Poon / Michael G Prisant / Randy J Read / Jane S Richardson / David C Richardson / Massimo D Sammito / Oleg V Sobolev / Duncan H Stockwell / Thomas C Terwilliger / Alexandre G Urzhumtsev / Lizbeth L Videau / Christopher J Williams / Paul D Adams /    Abstract: Diffraction (X-ray, neutron and electron) and electron cryo-microscopy are powerful methods to determine three-dimensional macromolecular structures, which are required to understand biological ...Diffraction (X-ray, neutron and electron) and electron cryo-microscopy are powerful methods to determine three-dimensional macromolecular structures, which are required to understand biological processes and to develop new therapeutics against diseases. The overall structure-solution workflow is similar for these techniques, but nuances exist because the properties of the reduced experimental data are different. Software tools for structure determination should therefore be tailored for each method. Phenix is a comprehensive software package for macromolecular structure determination that handles data from any of these techniques. Tasks performed with Phenix include data-quality assessment, map improvement, model building, the validation/rebuilding/refinement cycle and deposition. Each tool caters to the type of experimental data. The design of Phenix emphasizes the automation of procedures, where possible, to minimize repetitive and time-consuming manual tasks, while default parameters are chosen to encourage best practice. A graphical user interface provides access to many command-line features of Phenix and streamlines the transition between programs, project tracking and re-running of previous tasks. #2:  Journal: Nat Methods / Year: 2019 Journal: Nat Methods / Year: 2019Title: Real-time cryo-electron microscopy data preprocessing with Warp. Authors: Dimitry Tegunov / Patrick Cramer /  Abstract: The acquisition of cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) data from biological specimens must be tightly coupled to data preprocessing to ensure the best data quality and microscope usage. Here we ...The acquisition of cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) data from biological specimens must be tightly coupled to data preprocessing to ensure the best data quality and microscope usage. Here we describe Warp, a software that automates all preprocessing steps of cryo-EM data acquisition and enables real-time evaluation. Warp corrects micrographs for global and local motion, estimates the local defocus and monitors key parameters for each recorded micrograph or tomographic tilt series in real time. The software further includes deep-learning-based models for accurate particle picking and image denoising. The output from Warp can be fed into established programs for particle classification and 3D-map refinement. Our benchmarks show improvement in the nominal resolution, which went from 3.9 Å to 3.2 Å, of a published cryo-EM data set for influenza virus hemagglutinin. Warp is easy to install from http://github.com/cramerlab/warp and computationally inexpensive, and has an intuitive, streamlined user interface. #3: Journal: Nat Methods / Year: 2020 Title: Non-uniform refinement: adaptive regularization improves single-particle cryo-EM reconstruction. Authors: Ali Punjani / Haowei Zhang / David J Fleet /  Abstract: Cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM) is widely used to study biological macromolecules that comprise regions with disorder, flexibility or partial occupancy. For example, membrane proteins are ...Cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM) is widely used to study biological macromolecules that comprise regions with disorder, flexibility or partial occupancy. For example, membrane proteins are often kept in solution with detergent micelles and lipid nanodiscs that are locally disordered. Such spatial variability negatively impacts computational three-dimensional (3D) reconstruction with existing iterative refinement algorithms that assume rigidity. We introduce non-uniform refinement, an algorithm based on cross-validation optimization, which automatically regularizes 3D density maps during refinement to account for spatial variability. Unlike common shift-invariant regularizers, non-uniform refinement systematically removes noise from disordered regions, while retaining signal useful for aligning particle images, yielding dramatically improved resolution and 3D map quality in many cases. We obtain high-resolution reconstructions for multiple membrane proteins as small as 100 kDa, demonstrating increased effectiveness of cryo-EM for this class of targets critical in structural biology and drug discovery. Non-uniform refinement is implemented in the cryoSPARC software package. | ||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8tua.cif.gz 8tua.cif.gz | 548.4 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8tua.ent.gz pdb8tua.ent.gz | 371 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8tua.json.gz 8tua.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tu/8tua https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tu/8tua ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tu/8tua ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tu/8tua | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  41621MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
| Experimental dataset #1 | Data reference:  10.6019/EMPIAR-11967 / Data set type: EMPIAR 10.6019/EMPIAR-11967 / Data set type: EMPIAR |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 183459.484 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Details: Inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate / Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PREX1 / Cell line (production host): 293 Freestyle / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PREX1 / Cell line (production host): 293 Freestyle / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q8TCU6 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q8TCU6 |
|---|---|
| #2: Chemical | ChemComp-4IP / |
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Complex of full-length Phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate (PIP3)-dependent Rac exchanger 1 (P-Rex1) bound to inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate (IP4) Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1 / Source: RECOMBINANT | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.183 MDa / Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) / Strain: HEK293 Freestyle Homo sapiens (human) / Strain: HEK293 Freestyle | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.56 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 81000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 200 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 57.8 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.21_5207 / Category: model refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 2426612 Details: 806,067 particles untilted and 1,620,545 particles tilted | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 4.1 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 187734 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT / Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | 3D fitting-ID: 1 / Chain-ID: A / Pdb chain-ID: A / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Cross valid method: NONE Stereochemistry target values: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 103.39 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


 PDBj
PDBj