[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
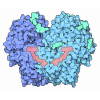
Yorodumi- PDB-8t1l: Atomic model of the mammalian mouse Mediator complex with CKM module -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8t1l | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Atomic model of the mammalian mouse Mediator complex with CKM module | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | GENE REGULATION / mouse mediator / CKM module | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpositive regulation of T cell extravasation / Nuclear Receptor transcription pathway / CKM complex / negative regulation of smooth muscle cell differentiation / enucleate erythrocyte development / positive regulation of type II interferon-mediated signaling pathway / regulation of RNA biosynthetic process / androgen biosynthetic process / positive regulation of G0 to G1 transition / Regulation of lipid metabolism by PPARalpha ...positive regulation of T cell extravasation / Nuclear Receptor transcription pathway / CKM complex / negative regulation of smooth muscle cell differentiation / enucleate erythrocyte development / positive regulation of type II interferon-mediated signaling pathway / regulation of RNA biosynthetic process / androgen biosynthetic process / positive regulation of G0 to G1 transition / Regulation of lipid metabolism by PPARalpha / retinal pigment epithelium development / G0 to G1 transition / thyroid hormone receptor signaling pathway / mammary gland branching involved in thelarche / Cytoprotection by HMOX1 / core mediator complex / Estrogen-dependent gene expression / regulation of vitamin D receptor signaling pathway / nuclear retinoic acid receptor binding / positive regulation of hepatocyte proliferation / ventricular trabecula myocardium morphogenesis / mediator complex / positive regulation of keratinocyte differentiation / thyroid hormone generation / camera-type eye development / peroxisome proliferator activated receptor binding / embryonic heart tube development / cellular response to thyroid hormone stimulus / nuclear vitamin D receptor binding / embryonic hindlimb morphogenesis / nuclear thyroid hormone receptor binding / lens development in camera-type eye / limb development / embryonic hemopoiesis / mammary gland epithelial cell proliferation / triglyceride homeostasis / megakaryocyte development / cellular response to hepatocyte growth factor stimulus / positive regulation of intracellular estrogen receptor signaling pathway / cortical actin cytoskeleton / negative regulation of neuron differentiation / epithelial cell proliferation involved in mammary gland duct elongation / histone acetyltransferase binding / LBD domain binding / erythrocyte development / fat cell differentiation / mammary gland branching involved in pregnancy / monocyte differentiation / general transcription initiation factor binding / skeletal muscle cell differentiation / somatic stem cell population maintenance / animal organ regeneration / blastocyst development / negative regulation of keratinocyte proliferation / hematopoietic stem cell differentiation / positive regulation of transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II / ubiquitin ligase complex / nuclear receptor-mediated steroid hormone signaling pathway / embryonic placenta development / nuclear retinoid X receptor binding / negative regulation of fibroblast proliferation / RNA polymerase II preinitiation complex assembly / keratinocyte differentiation / lactation / peroxisome proliferator activated receptor signaling pathway / positive regulation of erythrocyte differentiation / cholesterol homeostasis / cellular response to epidermal growth factor stimulus / animal organ morphogenesis / nuclear estrogen receptor binding / nuclear receptor binding / transcription coregulator activity / promoter-specific chromatin binding / positive regulation of transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / liver development / mRNA transcription by RNA polymerase II / protein-DNA complex / brain development / chromatin DNA binding / transcription coactivator binding / cell morphogenesis / protein import into nucleus / ubiquitin protein ligase activity / transcription corepressor activity / heart development / actin binding / angiogenesis / transcription regulator complex / in utero embryonic development / RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding / transcription by RNA polymerase II / transcription coactivator activity / cytoskeleton / nuclear body / protein ubiquitination / RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding / positive regulation of cell population proliferation / chromatin binding / positive regulation of gene expression / regulation of DNA-templated transcription Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.83 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Zhao, H. / Asturias, F. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2items United States, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2024 Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2024Title: An IDR-dependent mechanism for nuclear receptor control of Mediator interaction with RNA polymerase II. Authors: Haiyan Zhao / Jiaqin Li / Yufei Xiang / Sohail Malik / Supriya V Vartak / Giovana M B Veronezi / Natalie Young / McKayla Riney / Jens Kalchschmidt / Andrea Conte / Seol Kyoung Jung / ...Authors: Haiyan Zhao / Jiaqin Li / Yufei Xiang / Sohail Malik / Supriya V Vartak / Giovana M B Veronezi / Natalie Young / McKayla Riney / Jens Kalchschmidt / Andrea Conte / Seol Kyoung Jung / Srinivas Ramachandran / Robert G Roeder / Yi Shi / Rafael Casellas / Francisco J Asturias /  Abstract: The essential Mediator (MED) coactivator complex plays a well-understood role in regulation of basal transcription in all eukaryotes, but the mechanism underlying its role in activator-dependent ...The essential Mediator (MED) coactivator complex plays a well-understood role in regulation of basal transcription in all eukaryotes, but the mechanism underlying its role in activator-dependent transcription remains unknown. We investigated modulation of metazoan MED interaction with RNA polymerase II (RNA Pol II) by antagonistic effects of the MED26 subunit and the CDK8 kinase module (CKM). Biochemical analysis of CKM-MED showed that the CKM blocks binding of the RNA Pol II carboxy-terminal domain (CTD), preventing RNA Pol II interaction. This restriction is eliminated by nuclear receptor (NR) binding to CKM-MED, which enables CTD binding in a MED26-dependent manner. Cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM) and crosslinking-mass spectrometry (XL-MS) revealed that the structural basis for modulation of CTD interaction with MED relates to a large intrinsically disordered region (IDR) in CKM subunit MED13 that blocks MED26 and CTD interaction with MED but is repositioned upon NR binding. Hence, NRs can control transcription initiation by priming CKM-MED for MED26-dependent RNA Pol II interaction. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8t1l.cif.gz 8t1l.cif.gz | 1.3 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8t1l.ent.gz pdb8t1l.ent.gz | 958.1 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8t1l.json.gz 8t1l.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/t1/8t1l https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/t1/8t1l ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/t1/8t1l ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/t1/8t1l | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  40971MC  8t1iC  8t9dC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
+Mediator of RNA polymerase II transcription subunit ... , 25 types, 25 molecules EABCDFGHIJKLMOPQRSTVWXYZ9
-Protein/peptide , 1 types, 1 molecules a
| #25: Protein/peptide | Mass: 1720.111 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|
-Details
| Has protein modification | Y |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Mouse mediator complex / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 1.0 MDa / Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.9 |
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.1 mg/ml / Embedding applied: YES / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: EMS Lacey Carbon |
| EM embedding | Material: ice |
| Vitrification | Instrument: HOMEMADE PLUNGER / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Talos Arctica / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TALOS ARCTICA |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 36000 X / Calibrated magnification: 36000 X / Nominal defocus max: 3500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 700 nm / Calibrated defocus min: 700 nm / Calibrated defocus max: 3500 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 50 µm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Temperature (max): 70 K / Temperature (min): 70 K |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 22.5 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: NONE | ||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 4.83 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 111331 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj