+ データを開く
データを開く
- 基本情報
基本情報
| 登録情報 | データベース: PDB / ID: 8sik | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| タイトル | KCNQ1 with voltage sensor in the up conformation | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 要素 要素 |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 キーワード キーワード | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / voltage-gated potassium channel | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 機能・相同性 |  機能・相同性情報 機能・相同性情報gastrin-induced gastric acid secretion / corticosterone secretion / voltage-gated potassium channel activity involved in atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential repolarization / basolateral part of cell / lumenal side of membrane / negative regulation of voltage-gated potassium channel activity / rhythmic behavior / stomach development / iodide transport / regulation of gastric acid secretion ...gastrin-induced gastric acid secretion / corticosterone secretion / voltage-gated potassium channel activity involved in atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential repolarization / basolateral part of cell / lumenal side of membrane / negative regulation of voltage-gated potassium channel activity / rhythmic behavior / stomach development / iodide transport / regulation of gastric acid secretion / voltage-gated potassium channel activity involved in cardiac muscle cell action potential repolarization / Phase 3 - rapid repolarisation / membrane repolarization during atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential / membrane repolarization during action potential / Phase 2 - plateau phase / regulation of atrial cardiac muscle cell membrane repolarization / intracellular chloride ion homeostasis / membrane repolarization during ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential / membrane repolarization during cardiac muscle cell action potential / negative regulation of delayed rectifier potassium channel activity / potassium ion export across plasma membrane / renal sodium ion absorption / voltage-gated potassium channel activity involved in ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential repolarization / atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential / auditory receptor cell development / regulation of membrane repolarization / protein phosphatase 1 binding / detection of mechanical stimulus involved in sensory perception of sound / delayed rectifier potassium channel activity / ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential / potassium ion homeostasis / Voltage gated Potassium channels / positive regulation of potassium ion transmembrane transport / regulation of ventricular cardiac muscle cell membrane repolarization / non-motile cilium assembly / outward rectifier potassium channel activity / cardiac muscle cell contraction / CaM pathway / Cam-PDE 1 activation / intestinal absorption / Sodium/Calcium exchangers / Calmodulin induced events / Reduction of cytosolic Ca++ levels / Activation of Ca-permeable Kainate Receptor / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of CaMKII/CaMKK/CaMKIV cascasde / Loss of phosphorylation of MECP2 at T308 / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of Adenylate Cyclase / inner ear morphogenesis / CaMK IV-mediated phosphorylation of CREB / PKA activation / negative regulation of high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / Glycogen breakdown (glycogenolysis) / CLEC7A (Dectin-1) induces NFAT activation / Activation of RAC1 downstream of NMDARs / negative regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / organelle localization by membrane tethering / adrenergic receptor signaling pathway / mitochondrion-endoplasmic reticulum membrane tethering / autophagosome membrane docking / negative regulation of calcium ion export across plasma membrane / regulation of cardiac muscle cell action potential / ciliary base / renal absorption / regulation of heart contraction / presynaptic endocytosis / protein kinase A regulatory subunit binding / Synthesis of IP3 and IP4 in the cytosol / protein kinase A catalytic subunit binding / regulation of cell communication by electrical coupling involved in cardiac conduction / Phase 0 - rapid depolarisation / potassium ion import across plasma membrane / calcineurin-mediated signaling / Negative regulation of NMDA receptor-mediated neuronal transmission / Unblocking of NMDA receptors, glutamate binding and activation / inner ear development / RHO GTPases activate PAKs / regulation of heart rate by cardiac conduction / Ion transport by P-type ATPases / Uptake and function of anthrax toxins / action potential / regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / protein phosphatase activator activity / Long-term potentiation / cochlea development / Calcineurin activates NFAT / Regulation of MECP2 expression and activity / social behavior / DARPP-32 events / voltage-gated potassium channel activity / catalytic complex / Smooth Muscle Contraction / monoatomic ion channel complex / detection of calcium ion / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction by regulation of the release of sequestered calcium ion / positive regulation of heart rate / cellular response to interferon-beta / Protein methylation / calcium channel inhibitor activity 類似検索 - 分子機能 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 生物種 |  Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 手法 | 電子顕微鏡法 / 単粒子再構成法 / クライオ電子顕微鏡法 / 解像度: 2.9 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 データ登録者 データ登録者 | Mandala, V.S. / MacKinnon, R. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 資金援助 |  米国, 1件 米国, 1件
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 引用 引用 |  ジャーナル: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / 年: 2023 ジャーナル: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / 年: 2023タイトル: The membrane electric field regulates the PIP-binding site to gate the KCNQ1 channel. 著者: Venkata Shiva Mandala / Roderick MacKinnon /  要旨: Voltage-dependent ion channels underlie the propagation of action potentials and other forms of electrical activity in cells. In these proteins, voltage sensor domains (VSDs) regulate opening and ...Voltage-dependent ion channels underlie the propagation of action potentials and other forms of electrical activity in cells. In these proteins, voltage sensor domains (VSDs) regulate opening and closing of the pore through the displacement of their positive-charged S4 helix in response to the membrane voltage. The movement of S4 at hyperpolarizing membrane voltages in some channels is thought to directly clamp the pore shut through the S4-S5 linker helix. The KCNQ1 channel (also known as K7.1), which is important for heart rhythm, is regulated not only by membrane voltage but also by the signaling lipid phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP). KCNQ1 requires PIP to open and to couple the movement of S4 in the VSD to the pore. To understand the mechanism of this voltage regulation, we use cryogenic electron microscopy to visualize the movement of S4 in the human KCNQ1 channel in lipid membrane vesicles with a voltage difference across the membrane, i.e., an applied electric field in the membrane. Hyperpolarizing voltages displace S4 in such a manner as to sterically occlude the PIP-binding site. Thus, in KCNQ1, the voltage sensor acts primarily as a regulator of PIP binding. The voltage sensors' influence on the channel's gate is indirect through the reaction sequence: voltage sensor movement → alter PIP ligand affinity → alter pore opening. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 履歴 |
|
- 構造の表示
構造の表示
| 構造ビューア | 分子:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- ダウンロードとリンク
ダウンロードとリンク
- ダウンロード
ダウンロード
| PDBx/mmCIF形式 |  8sik.cif.gz 8sik.cif.gz | 400.3 KB | 表示 |  PDBx/mmCIF形式 PDBx/mmCIF形式 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB形式 |  pdb8sik.ent.gz pdb8sik.ent.gz | 320.3 KB | 表示 |  PDB形式 PDB形式 |
| PDBx/mmJSON形式 |  8sik.json.gz 8sik.json.gz | ツリー表示 |  PDBx/mmJSON形式 PDBx/mmJSON形式 | |
| その他 |  その他のダウンロード その他のダウンロード |
-検証レポート
| 文書・要旨 |  8sik_validation.pdf.gz 8sik_validation.pdf.gz | 1.4 MB | 表示 |  wwPDB検証レポート wwPDB検証レポート |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 文書・詳細版 |  8sik_full_validation.pdf.gz 8sik_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.4 MB | 表示 | |
| XML形式データ |  8sik_validation.xml.gz 8sik_validation.xml.gz | 59.7 KB | 表示 | |
| CIF形式データ |  8sik_validation.cif.gz 8sik_validation.cif.gz | 89.5 KB | 表示 | |
| アーカイブディレクトリ |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/si/8sik https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/si/8sik ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/si/8sik ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/si/8sik | HTTPS FTP |
-関連構造データ
| 関連構造データ |  40508MC  8simC  8sinC M: このデータのモデリングに利用したマップデータ C: 同じ文献を引用 ( |
|---|---|
| 類似構造データ | 類似検索 - 機能・相同性  F&H 検索 F&H 検索 |
- リンク
リンク
- 集合体
集合体
| 登録構造単位 | 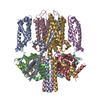
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- 要素
要素
| #1: タンパク質 | 分子量: 16852.545 Da / 分子数: 4 / 由来タイプ: 組換発現 / 由来: (組換発現)  Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: CALM1, CALM, CAM, CAM1 / 発現宿主: Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: CALM1, CALM, CAM, CAM1 / 発現宿主:  Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 参照: UniProt: P0DP23 Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 参照: UniProt: P0DP23#2: タンパク質 | 分子量: 63258.574 Da / 分子数: 4 / 由来タイプ: 組換発現 / 由来: (組換発現)  Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: KCNQ1, KCNA8, KCNA9, KVLQT1 / 発現宿主: Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: KCNQ1, KCNA8, KCNA9, KVLQT1 / 発現宿主:  Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 参照: UniProt: P51787 Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 参照: UniProt: P51787#3: 化合物 | ChemComp-CA / 研究の焦点であるリガンドがあるか | N | Has protein modification | N | |
|---|
-実験情報
-実験
| 実験 | 手法: 電子顕微鏡法 |
|---|---|
| EM実験 | 試料の集合状態: PARTICLE / 3次元再構成法: 単粒子再構成法 |
- 試料調製
試料調製
| 構成要素 | 名称: Complex of KCNQ1 (Kv7.1) channel bound to calmodulin-Ca2+ タイプ: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#2 / 由来: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| 分子量 | 実験値: NO |
| 由来(天然) | 生物種:  Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト) |
| 由来(組換発現) | 生物種:  Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト) |
| 緩衝液 | pH: 8 |
| 試料 | 濃度: 0.2 mg/ml / 包埋: NO / シャドウイング: NO / 染色: NO / 凍結: YES |
| 急速凍結 | 装置: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / 凍結剤: ETHANE / 湿度: 100 % / 凍結前の試料温度: 293 K |
- 電子顕微鏡撮影
電子顕微鏡撮影
| 実験機器 |  モデル: Titan Krios / 画像提供: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| 顕微鏡 | モデル: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| 電子銃 | 電子線源:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / 加速電圧: 300 kV / 照射モード: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / 加速電圧: 300 kV / 照射モード: FLOOD BEAM |
| 電子レンズ | モード: BRIGHT FIELD / 最大 デフォーカス(公称値): 2000 nm / 最小 デフォーカス(公称値): 1000 nm |
| 撮影 | 電子線照射量: 60 e/Å2 フィルム・検出器のモデル: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) |
- 解析
解析
| ソフトウェア | 名称: PHENIX / バージョン: 1.20.1_4487: / 分類: 精密化 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EMソフトウェア | 名称: PHENIX / カテゴリ: モデル精密化 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF補正 | タイプ: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 対称性 | 点対称性: C4 (4回回転対称) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3次元再構成 | 解像度: 2.9 Å / 解像度の算出法: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / 粒子像の数: 200862 / 対称性のタイプ: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 拘束条件 |
|
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー





 PDBj
PDBj






















