+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8k8e | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
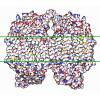
| Title | Human gamma-secretase in complex with a substrate mimetic | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / Complex / protease / substrate mimetic | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationCajal-Retzius cell differentiation / positive regulation of L-glutamate import across plasma membrane / amyloid precursor protein biosynthetic process / negative regulation of core promoter binding / Notch receptor processing / positive regulation of endopeptidase activity / gamma-secretase complex / short-term synaptic potentiation / aspartic endopeptidase activity, intramembrane cleaving / positive regulation of amyloid precursor protein biosynthetic process ...Cajal-Retzius cell differentiation / positive regulation of L-glutamate import across plasma membrane / amyloid precursor protein biosynthetic process / negative regulation of core promoter binding / Notch receptor processing / positive regulation of endopeptidase activity / gamma-secretase complex / short-term synaptic potentiation / aspartic endopeptidase activity, intramembrane cleaving / positive regulation of amyloid precursor protein biosynthetic process / smooth endoplasmic reticulum calcium ion homeostasis / Noncanonical activation of NOTCH3 / protein catabolic process at postsynapse / TGFBR3 PTM regulation / sequestering of calcium ion / synaptic vesicle targeting / positive regulation of coagulation / central nervous system myelination / negative regulation of axonogenesis / membrane protein intracellular domain proteolysis / skin morphogenesis / choline transport / T cell activation involved in immune response / NOTCH4 Activation and Transmission of Signal to the Nucleus / dorsal/ventral neural tube patterning / ciliary rootlet / Regulated proteolysis of p75NTR / neural retina development / regulation of resting membrane potential / L-glutamate import across plasma membrane / myeloid dendritic cell differentiation / regulation of phosphorylation / metanephros development / endoplasmic reticulum calcium ion homeostasis / brain morphogenesis / amyloid precursor protein metabolic process / regulation of synaptic vesicle cycle / locomotion / regulation of long-term synaptic potentiation / regulation of postsynapse organization / embryonic limb morphogenesis / cell fate specification / astrocyte activation involved in immune response / regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway / myeloid cell homeostasis / aggresome / growth factor receptor binding / skeletal system morphogenesis / Hydrolases; Acting on peptide bonds (peptidases); Aspartic endopeptidases / Golgi cisterna membrane / azurophil granule membrane / positive regulation of amyloid fibril formation / glutamate receptor signaling pathway / G protein-coupled dopamine receptor signaling pathway / amyloid precursor protein catabolic process / : / blood vessel development / amyloid-beta formation / mitochondrial transport / heart looping / regulation of neuron projection development / positive regulation of dendritic spine development / adult behavior / cerebral cortex cell migration / membrane protein ectodomain proteolysis / smooth endoplasmic reticulum / positive regulation of receptor recycling / nuclear outer membrane / negative regulation of apoptotic signaling pathway / EPH-ephrin mediated repulsion of cells / autophagosome assembly / negative regulation of ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / endopeptidase activator activity / neuron development / somitogenesis / Nuclear signaling by ERBB4 / T cell proliferation / hematopoietic progenitor cell differentiation / regulation of synaptic transmission, glutamatergic / calcium ion homeostasis / Notch signaling pathway / Degradation of the extracellular matrix / rough endoplasmic reticulum / neuron projection maintenance / astrocyte activation / NOTCH2 Activation and Transmission of Signal to the Nucleus / cellular response to calcium ion / NRIF signals cell death from the nucleus / Activated NOTCH1 Transmits Signal to the Nucleus / thymus development / cerebellum development / positive regulation of glycolytic process / epithelial cell proliferation / dendritic shaft / post-embryonic development / PDZ domain binding / neuromuscular junction / apoptotic signaling pathway / NOTCH3 Activation and Transmission of Signal to the Nucleus / cell-cell adhesion Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)synthetic construct (others) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.6 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Shi, Y.G. / Zhou, R. / Wolfe, M.S. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 1items China, 1items
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell Rep / Year: 2024 Journal: Cell Rep / Year: 2024Title: Familial Alzheimer mutations stabilize synaptotoxic γ-secretase-substrate complexes. Authors: Sujan Devkota / Rui Zhou / Vaishnavi Nagarajan / Masato Maesako / Hung Do / Arshad Noorani / Caitlin Overmeyer / Sanjay Bhattarai / Justin T Douglas / Anita Saraf / Yinglong Miao / Brian D ...Authors: Sujan Devkota / Rui Zhou / Vaishnavi Nagarajan / Masato Maesako / Hung Do / Arshad Noorani / Caitlin Overmeyer / Sanjay Bhattarai / Justin T Douglas / Anita Saraf / Yinglong Miao / Brian D Ackley / Yigong Shi / Michael S Wolfe /   Abstract: Mutations that cause familial Alzheimer's disease (FAD) are found in amyloid precursor protein (APP) and presenilin, the catalytic component of γ-secretase, that together produce amyloid β-peptide ...Mutations that cause familial Alzheimer's disease (FAD) are found in amyloid precursor protein (APP) and presenilin, the catalytic component of γ-secretase, that together produce amyloid β-peptide (Aβ). Nevertheless, whether Aβ is the primary disease driver remains controversial. We report here that FAD mutations disrupt initial proteolytic events in the multistep processing of APP substrate C99 by γ-secretase. Cryoelectron microscopy reveals that a substrate mimetic traps γ-secretase during the transition state, and this structure aligns with activated enzyme-substrate complex captured by molecular dynamics simulations. In silico simulations and in cellulo fluorescence microscopy support stabilization of enzyme-substrate complexes by FAD mutations. Neuronal expression of C99 and/or presenilin-1 in Caenorhabditis elegans leads to synaptic loss only with FAD-mutant transgenes. Designed mutations that stabilize the enzyme-substrate complex and block Aβ production likewise led to synaptic loss. Collectively, these findings implicate the stalled process-not the products-of γ-secretase cleavage of substrates in FAD pathogenesis. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8k8e.cif.gz 8k8e.cif.gz | 285.7 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8k8e.ent.gz pdb8k8e.ent.gz | 221.7 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8k8e.json.gz 8k8e.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/k8/8k8e https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/k8/8k8e ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/k8/8k8e ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/k8/8k8e | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  36948MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 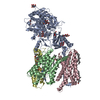
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 2 types, 2 molecules AB
| #1: Protein | Mass: 78483.570 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: NCSTN, KIAA0253, UNQ1874/PRO4317 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: NCSTN, KIAA0253, UNQ1874/PRO4317 / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q92542 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q92542 |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 52713.535 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PSEN1, AD3, PS1, PSNL1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PSEN1, AD3, PS1, PSNL1 / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)References: UniProt: P49768, Hydrolases; Acting on peptide bonds (peptidases); Aspartic endopeptidases |
-Gamma-secretase subunit ... , 2 types, 2 molecules CD
| #3: Protein | Mass: 29017.943 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: APH1A, PSF, CGI-78, UNQ579/PRO1141 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: APH1A, PSF, CGI-78, UNQ579/PRO1141 / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q96BI3 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q96BI3 |
|---|---|
| #4: Protein | Mass: 12038.029 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PSENEN, PEN2, MDS033 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PSENEN, PEN2, MDS033 / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9NZ42 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9NZ42 |
-Protein/peptide , 1 types, 1 molecules H
| #5: Protein/peptide | Mass: 1864.298 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) |
|---|
-Sugars , 3 types, 8 molecules 
| #6: Polysaccharide | 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose-(1-4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source |
|---|---|
| #7: Polysaccharide | beta-D-mannopyranose-(1-3)-[beta-D-mannopyranose-(1-6)]beta-D-mannopyranose Type: oligosaccharide / Mass: 504.438 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source |
| #8: Sugar | ChemComp-NAG / |
-Non-polymers , 2 types, 4 molecules 


| #9: Chemical | ChemComp-PC1 / |
|---|---|
| #10: Chemical |
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Human gamma-secretase / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#4 / Source: MULTIPLE SOURCES |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1800 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1500 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software | Name: PHENIX / Category: model refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: NONE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.6 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 349532 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 PDBj
PDBj