+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8ghn | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Composite model of the yeast Hir Complex with Asf1/H3/H4 | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | CHAPERONE / Histone / Complex / Replication-Independent | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationHIR complex / negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase III / Formation of Senescence-Associated Heterochromatin Foci (SAHF) / sexual sporulation resulting in formation of a cellular spore / cupric reductase (NADH) activity / HATs acetylate histones / global genome nucleotide-excision repair / RNA polymerase I upstream activating factor complex / Condensation of Prophase Chromosomes / : ...HIR complex / negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase III / Formation of Senescence-Associated Heterochromatin Foci (SAHF) / sexual sporulation resulting in formation of a cellular spore / cupric reductase (NADH) activity / HATs acetylate histones / global genome nucleotide-excision repair / RNA polymerase I upstream activating factor complex / Condensation of Prophase Chromosomes / : / : / Assembly of the ORC complex at the origin of replication / regulation of chromatin organization / HDACs deacetylate histones / DNA replication-dependent chromatin assembly / Recruitment and ATM-mediated phosphorylation of repair and signaling proteins at DNA double strand breaks / Oxidative Stress Induced Senescence / RMTs methylate histone arginines / nucleosome disassembly / SUMOylation of chromatin organization proteins / transcription elongation-coupled chromatin remodeling / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Escape / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase I / nucleolar large rRNA transcription by RNA polymerase I / Estrogen-dependent gene expression / rRNA transcription / intracellular copper ion homeostasis / chromosome, centromeric region / CENP-A containing nucleosome / aerobic respiration / transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle / structural constituent of chromatin / transcription corepressor activity / nucleosome / nucleosome assembly / chromosome / chromatin organization / histone binding / chromatin remodeling / protein heterodimerization activity / regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / regulation of DNA-templated transcription / chromatin / negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / DNA binding / identical protein binding / nucleus / cytosol Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.96 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Kim, H.J. / Murakami, K. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| ||||||
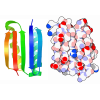
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2024 Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2024Title: Structure of the Hir histone chaperone complex. Authors: Hee Jong Kim / Mary R Szurgot / Trevor van Eeuwen / M Daniel Ricketts / Pratik Basnet / Athena L Zhang / Austin Vogt / Samah Sharmin / Craig D Kaplan / Benjamin A Garcia / Ronen Marmorstein / Kenji Murakami /  Abstract: The evolutionarily conserved HIRA/Hir histone chaperone complex and ASF1a/Asf1 co-chaperone cooperate to deposit histone (H3/H4) tetramers on DNA for replication-independent chromatin assembly. The ...The evolutionarily conserved HIRA/Hir histone chaperone complex and ASF1a/Asf1 co-chaperone cooperate to deposit histone (H3/H4) tetramers on DNA for replication-independent chromatin assembly. The molecular architecture of the HIRA/Hir complex and its mode of histone deposition have remained unknown. Here, we report the cryo-EM structure of the S. cerevisiae Hir complex with Asf1/H3/H4 at 2.9-6.8 Å resolution. We find that the Hir complex forms an arc-shaped dimer with a Hir1/Hir2/Hir3/Hpc2 stoichiometry of 2/4/2/4. The core of the complex containing two Hir1/Hir2/Hir2 trimers and N-terminal segments of Hir3 forms a central cavity containing two copies of Hpc2, with one engaged by Asf1/H3/H4, in a suitable position to accommodate a histone (H3/H4) tetramer, while the C-terminal segments of Hir3 harbor nucleic acid binding activity to wrap DNA around the Hpc2-assisted histone tetramer. The structure suggests a model for how the Hir/Asf1 complex promotes the formation of histone tetramers for their subsequent deposition onto DNA. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8ghn.cif.gz 8ghn.cif.gz | 1.3 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8ghn.ent.gz pdb8ghn.ent.gz | 1.1 MB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8ghn.json.gz 8ghn.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/gh/8ghn https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/gh/8ghn ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/gh/8ghn ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/gh/8ghn | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  40037MC  8ghaC  8ghlC  8ghmC  8gixC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 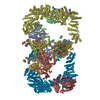
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 7 types, 15 molecules AGBCHIDJEFKLMNO
| #1: Protein | Mass: 93983.688 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #2: Protein | Mass: 98553.625 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #3: Protein | Mass: 191915.188 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #4: Protein | Mass: 67877.391 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #5: Protein | | Mass: 15391.007 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: HHT1, YBR010W, YBR0201, HHT2, SIN2, YNL031C, N2749 / Production host:  #6: Protein | | Mass: 11395.390 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: HHF1, YBR009C, YBR0122, HHF2, YNL030W, N2752 / Production host:  #7: Protein | | Mass: 31629.260 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: ASF1, GI527_G0003133 / Production host:  |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 1.24 MDa / Experimental value: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid type: Quantifoil R2/2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 3000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 42 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.21_5207: / Category: model refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.96 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 639629 / Algorithm: FOURIER SPACE / Details: A composite map from Maps 1-3 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 PDBj
PDBj