+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
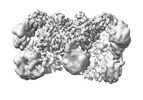
| Title | Composite map of the Hir complex with Asf1/H3/H4 | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | a composite map of the Hir with Asf1/H3/H4 | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Histone / Complex / Replication-Independent / CHAPERONE | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnegative regulation of chromatin organization / HIR complex / negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase III / Formation of Senescence-Associated Heterochromatin Foci (SAHF) / sexual sporulation resulting in formation of a cellular spore / cupric reductase (NADH) activity / HATs acetylate histones / global genome nucleotide-excision repair / RNA polymerase I upstream activating factor complex / Condensation of Prophase Chromosomes ...negative regulation of chromatin organization / HIR complex / negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase III / Formation of Senescence-Associated Heterochromatin Foci (SAHF) / sexual sporulation resulting in formation of a cellular spore / cupric reductase (NADH) activity / HATs acetylate histones / global genome nucleotide-excision repair / RNA polymerase I upstream activating factor complex / Condensation of Prophase Chromosomes / : / : / Assembly of the ORC complex at the origin of replication / regulation of chromatin organization / HDACs deacetylate histones / DNA replication-dependent chromatin assembly / Recruitment and ATM-mediated phosphorylation of repair and signaling proteins at DNA double strand breaks / Oxidative Stress Induced Senescence / RMTs methylate histone arginines / nucleosome disassembly / SUMOylation of chromatin organization proteins / transcription elongation-coupled chromatin remodeling / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Escape / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase I / nucleolar large rRNA transcription by RNA polymerase I / Estrogen-dependent gene expression / rRNA transcription / intracellular copper ion homeostasis / chromosome, centromeric region / CENP-A containing nucleosome / aerobic respiration / transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle / structural constituent of chromatin / transcription corepressor activity / nucleosome / nucleosome assembly / chromosome / chromatin organization / histone binding / chromatin remodeling / protein heterodimerization activity / regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / regulation of DNA-templated transcription / chromatin / negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / DNA binding / identical protein binding / nucleus / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.96 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Kim HJ / Murakami K | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2024 Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2024Title: Structure of the Hir histone chaperone complex. Authors: Hee Jong Kim / Mary R Szurgot / Trevor van Eeuwen / M Daniel Ricketts / Pratik Basnet / Athena L Zhang / Austin Vogt / Samah Sharmin / Craig D Kaplan / Benjamin A Garcia / Ronen Marmorstein / Kenji Murakami /  Abstract: The evolutionarily conserved HIRA/Hir histone chaperone complex and ASF1a/Asf1 co-chaperone cooperate to deposit histone (H3/H4) tetramers on DNA for replication-independent chromatin assembly. The ...The evolutionarily conserved HIRA/Hir histone chaperone complex and ASF1a/Asf1 co-chaperone cooperate to deposit histone (H3/H4) tetramers on DNA for replication-independent chromatin assembly. The molecular architecture of the HIRA/Hir complex and its mode of histone deposition have remained unknown. Here, we report the cryo-EM structure of the S. cerevisiae Hir complex with Asf1/H3/H4 at 2.9-6.8 Å resolution. We find that the Hir complex forms an arc-shaped dimer with a Hir1/Hir2/Hir3/Hpc2 stoichiometry of 2/4/2/4. The core of the complex containing two Hir1/Hir2/Hir2 trimers and N-terminal segments of Hir3 forms a central cavity containing two copies of Hpc2, with one engaged by Asf1/H3/H4, in a suitable position to accommodate a histone (H3/H4) tetramer, while the C-terminal segments of Hir3 harbor nucleic acid binding activity to wrap DNA around the Hpc2-assisted histone tetramer. The structure suggests a model for how the Hir/Asf1 complex promotes the formation of histone tetramers for their subsequent deposition onto DNA. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_40037.map.gz emd_40037.map.gz | 21.8 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-40037-v30.xml emd-40037-v30.xml emd-40037.xml emd-40037.xml | 9.5 KB 9.5 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_40037.png emd_40037.png | 74.9 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-40037.cif.gz emd-40037.cif.gz | 3.9 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-40037 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-40037 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-40037 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-40037 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8ghnMC  8ghaC  8ghlC  8ghmC  8gixC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_40037.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 512.5 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_40037.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 512.5 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | a composite map of the Hir with Asf1/H3/H4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. generated in cubic-lattice coordinate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.36 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : the yeast Hir complex with Asf1/H3/H4
| Entire | Name: the yeast Hir complex with Asf1/H3/H4 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: the yeast Hir complex with Asf1/H3/H4
| Supramolecule | Name: the yeast Hir complex with Asf1/H3/H4 / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 1.24 MDa |
-Supramolecule #2: the yeast Hir complex
| Supramolecule | Name: the yeast Hir complex / type: complex / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Supramolecule #3: Asf1/H3/H4
| Supramolecule | Name: Asf1/H3/H4 / type: complex / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.6 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 42.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 100.0 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 3.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: INSILICO MODEL |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 2.96 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 639000 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller













 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)




















