[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-8fqb: GluA2 flip Q isoform of AMPA receptor in complex with gain-of-fun... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8fqb | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | GluA2 flip Q isoform of AMPA receptor in complex with gain-of-function TARP gamma2, with 10mM CaCl2, 140mM NMDG, 330uM CTZ, and 100mM L-glutamate (Open-Ca10) | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSPORT PROTEIN / Inotropic glutamate receptors / AMPA receptors / ligand gated ion channel / auxiliary subunit / TARP / stargazin / TARP gamma2 / glutamate / calcium / neurotransmitter receptor / synaptic transmission | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationPresynaptic depolarization and calcium channel opening / LGI-ADAM interactions / Trafficking of AMPA receptors / eye blink reflex / positive regulation of protein localization to basolateral plasma membrane / cerebellar mossy fiber / postsynaptic neurotransmitter receptor diffusion trapping / regulation of AMPA receptor activity / membrane hyperpolarization / nervous system process ...Presynaptic depolarization and calcium channel opening / LGI-ADAM interactions / Trafficking of AMPA receptors / eye blink reflex / positive regulation of protein localization to basolateral plasma membrane / cerebellar mossy fiber / postsynaptic neurotransmitter receptor diffusion trapping / regulation of AMPA receptor activity / membrane hyperpolarization / nervous system process / protein targeting to membrane / voltage-gated calcium channel complex / spine synapse / dendritic spine neck / dendritic spine head / cellular response to amine stimulus / neurotransmitter receptor localization to postsynaptic specialization membrane / perisynaptic space / ligand-gated monoatomic cation channel activity / Activation of AMPA receptors / neuromuscular junction development / AMPA glutamate receptor activity / response to lithium ion / Trafficking of GluR2-containing AMPA receptors / transmission of nerve impulse / kainate selective glutamate receptor activity / cellular response to glycine / extracellularly glutamate-gated ion channel activity / AMPA glutamate receptor complex / immunoglobulin binding / asymmetric synapse / ionotropic glutamate receptor complex / conditioned place preference / regulation of receptor recycling / membrane depolarization / glutamate receptor binding / Unblocking of NMDA receptors, glutamate binding and activation / positive regulation of synaptic transmission / regulation of synaptic transmission, glutamatergic / regulation of postsynaptic membrane neurotransmitter receptor levels / response to fungicide / voltage-gated calcium channel activity / glutamate-gated receptor activity / regulation of long-term synaptic depression / cytoskeletal protein binding / extracellular ligand-gated monoatomic ion channel activity / cellular response to brain-derived neurotrophic factor stimulus / glutamate-gated calcium ion channel activity / presynaptic active zone membrane / somatodendritic compartment / dendrite membrane / ionotropic glutamate receptor binding / ligand-gated monoatomic ion channel activity involved in regulation of presynaptic membrane potential / dendrite cytoplasm / ionotropic glutamate receptor signaling pathway / synaptic membrane / hippocampal mossy fiber to CA3 synapse / dendritic shaft / SNARE binding / PDZ domain binding / regulation of membrane potential / transmitter-gated monoatomic ion channel activity involved in regulation of postsynaptic membrane potential / synaptic transmission, glutamatergic / protein tetramerization / establishment of protein localization / response to calcium ion / postsynaptic density membrane / cerebral cortex development / modulation of chemical synaptic transmission / receptor internalization / Schaffer collateral - CA1 synapse / terminal bouton / synaptic vesicle / synaptic vesicle membrane / signaling receptor activity / presynapse / amyloid-beta binding / growth cone / presynaptic membrane / scaffold protein binding / perikaryon / dendritic spine / chemical synaptic transmission / postsynaptic membrane / neuron projection / postsynaptic density / axon / external side of plasma membrane / neuronal cell body / dendrite / synapse / protein kinase binding / protein-containing complex binding / glutamatergic synapse / cell surface / endoplasmic reticulum / protein-containing complex / identical protein binding / membrane / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |   | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.36 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Nakagawa, T. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2024 Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2024Title: The open gate of the AMPA receptor forms a Ca binding site critical in regulating ion transport. Authors: Terunaga Nakagawa / Xin-Tong Wang / Federico J Miguez-Cabello / Derek Bowie /   Abstract: Alpha-amino-3-hydroxyl-5-methyl-4-isoxazole-propionic acid receptors (AMPARs) are cation-selective ion channels that mediate most fast excitatory neurotransmission in the brain. Although their gating ...Alpha-amino-3-hydroxyl-5-methyl-4-isoxazole-propionic acid receptors (AMPARs) are cation-selective ion channels that mediate most fast excitatory neurotransmission in the brain. Although their gating mechanism has been studied extensively, understanding how cations traverse the pore has remained elusive. Here we investigated putative ion and water densities in the open pore of Ca-permeable AMPARs (rat GRIA2 flip-Q isoform) at 2.3-2.6 Å resolution. We show that the ion permeation pathway attains an extracellular Ca binding site (site-G) when the channel gate moves into the open configuration. Site-G is highly selective for Ca over Na, favoring the movement of Ca into the selectivity filter of the pore. Seizure-related N619K mutation, adjacent to site-G, promotes channel opening but attenuates Ca binding and thus diminishes Ca permeability. Our work identifies the importance of site-G, which coordinates with the Q/R site of the selectivity filter to ensure the preferential transport of Ca through the channel pore. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8fqb.cif.gz 8fqb.cif.gz | 333.1 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8fqb.ent.gz pdb8fqb.ent.gz | 233.5 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8fqb.json.gz 8fqb.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fq/8fqb https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fq/8fqb ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fq/8fqb ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fq/8fqb | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  29382MC  8fp4C  8fp9C  8fpcC  8fpgC  8fphC  8fpkC  8fplC  8fpsC  8fpvC  8fpyC  8fpzC  8fq1C  8fq2C  8fq3C  8fq5C  8fq6C  8fq8C  8fqaC  8fqdC  8fqeC  8fqfC  8fqgC  8fqhC 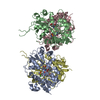 8fr0C C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 99559.461 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Fragment: DYKDDDDK near the C-terminal is a FLAG epitope tag used for purification Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P19491 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P19491#2: Protein | Mass: 37109.809 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Mutation: K52E, K53E Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: O88602 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: O88602#3: Chemical | ChemComp-CA / | #4: Chemical | #5: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | Has ligand of interest | Y | Has protein modification | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Homotetrameric assembly of GluA2 flip-Q isoform in complex with TARP gamma2 (K52E, K53E). Dimer-of-dimers assembly. Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#2 / Source: RECOMBINANT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.5 MDa / Experimental value: NO | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) / Cell: HEK Homo sapiens (human) / Cell: HEK | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 Details: L-glutamic acid (100mM) and cyclothiazide (CTZ, 0.33mM) was added before freezing. The 1M L-glutamic acid stock solution is adjusted to pH 7.4 using NaOH. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 10 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277.15 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 130000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 800 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 50 µm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 53 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 28505 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C2 (2 fold cyclic) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.36 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 986075 / Algorithm: FOURIER SPACE / Num. of class averages: 1 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




















 PDBj
PDBj









