[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
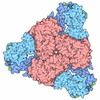
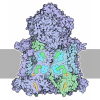
Yorodumi- PDB-8f3d: 3-methylcrotonyl-CoA carboxylase in filament, beta-subunit centered -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8f3d | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | 3-methylcrotonyl-CoA carboxylase in filament, beta-subunit centered | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | LIGASE / enzyme / multienzyme / multi-enzyme / biotin-dependent / leucine catabolism / PROTEIN FIBRIL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationmethylcrotonoyl-CoA carboxylase activity / mitochondrion / ATP binding / metal ion binding Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Leishmania tarentolae (eukaryote) Leishmania tarentolae (eukaryote) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.4 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Hu, J.J. / Lee, J.K.J. / Liu, Y.T. / Yu, C. / Huang, L. / Afasizheva, I. / Afasizhev, R. / Zhou, Z.H. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 7items United States, 7items
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Structure / Year: 2023 Journal: Structure / Year: 2023Title: Discovery, structure, and function of filamentous 3-methylcrotonyl-CoA carboxylase. Authors: Jason J Hu / Jane K J Lee / Yun-Tao Liu / Clinton Yu / Lan Huang / Inna Aphasizheva / Ruslan Aphasizhev / Z Hong Zhou /  Abstract: 3-methylcrotonyl-CoA carboxylase (MCC) is a biotin-dependent mitochondrial enzyme necessary for leucine catabolism in most organisms. While the crystal structure of recombinant bacterial MCC has been ...3-methylcrotonyl-CoA carboxylase (MCC) is a biotin-dependent mitochondrial enzyme necessary for leucine catabolism in most organisms. While the crystal structure of recombinant bacterial MCC has been characterized, the structure and potential polymerization of native MCC remain elusive. Here, we discovered that native MCC from Leishmania tarentolae (LtMCC) forms filaments, and determined the structures of different filament regions at 3.4, 3.9, and 7.3 Å resolution using cryoEM. αβ LtMCCs assemble in a twisted-stacks architecture, manifesting as supramolecular rods up to 400 nm. Filamentous LtMCCs bind biotin non-covalently and lack coenzyme A. Filaments elongate by stacking αβ LtMCCs onto the exterior α-trimer of the terminal LtMCC. This stacking immobilizes the biotin carboxylase domains, sequestering the enzyme in an inactive state. Our results support a new model for LtMCC catalysis, termed the dual-swinging-domains model, and cast new light on the function of polymerization in the carboxylase superfamily and beyond. #1:  Journal: To Be Published Journal: To Be PublishedTitle: Discovery, Structure, and Function of Filamentous 3-Methylcrotonyl-CoA Carboxylase Authors: Hu, J.J. / Lee, J.K.J. / Liu, Y.T. / Yu, C. / Huang, L. / Afasizheva, I. / Afasizhev, R. / Zhou, Z.H. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8f3d.cif.gz 8f3d.cif.gz | 1.2 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8f3d.ent.gz pdb8f3d.ent.gz | 1 MB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8f3d.json.gz 8f3d.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/f3/8f3d https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/f3/8f3d ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/f3/8f3d ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/f3/8f3d | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  28846MC  8f41C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
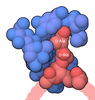
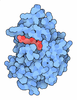
| #1: Protein | Mass: 76468.469 Da / Num. of mol.: 6 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Leishmania tarentolae (eukaryote) / Strain: TATII/UC / References: methylcrotonoyl-CoA carboxylase Leishmania tarentolae (eukaryote) / Strain: TATII/UC / References: methylcrotonoyl-CoA carboxylase#2: Protein | Mass: 76283.070 Da / Num. of mol.: 6 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Leishmania tarentolae (eukaryote) / Strain: TATII/UC / References: UniProt: A0A640KPA4 Leishmania tarentolae (eukaryote) / Strain: TATII/UC / References: UniProt: A0A640KPA4#3: Chemical | ChemComp-BTI / Has ligand of interest | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: FILAMENT / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: alpha6beta6 dodecamer in 3-methylcrotonyl-CoA filament Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#2 / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Leishmania tarentolae (eukaryote) / Strain: TATII/UC Leishmania tarentolae (eukaryote) / Strain: TATII/UC |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277.15 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1500 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 40 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
|---|---|
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.4 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 13250 / Symmetry type: POINT |
| Atomic model building | Protocol: AB INITIO MODEL / Space: REAL |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 PDBj
PDBj