+ データを開く
データを開く
- 基本情報
基本情報
| 登録情報 | データベース: PDB / ID: 8efi | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| タイトル | Helical reconstruction of the human cardiac actin-tropomyosin-myosin complex in the rigor form | ||||||
 要素 要素 |
| ||||||
 キーワード キーワード | MOTOR PROTEIN / actin / tropomyosin / myosin / cardiac | ||||||
| 機能・相同性 |  機能・相同性情報 機能・相同性情報regulation of slow-twitch skeletal muscle fiber contraction / regulation of the force of skeletal muscle contraction / positive regulation of heart rate by epinephrine / muscle thin filament tropomyosin / bleb / actin-myosin filament sliding / muscle myosin complex / regulation of muscle contraction / regulation of the force of heart contraction / transition between fast and slow fiber ...regulation of slow-twitch skeletal muscle fiber contraction / regulation of the force of skeletal muscle contraction / positive regulation of heart rate by epinephrine / muscle thin filament tropomyosin / bleb / actin-myosin filament sliding / muscle myosin complex / regulation of muscle contraction / regulation of the force of heart contraction / transition between fast and slow fiber / myosin filament / ruffle organization / adult heart development / Striated Muscle Contraction / cardiac muscle hypertrophy in response to stress / muscle filament sliding / myosin complex / myosin II complex / structural constituent of muscle / sarcomere organization / ventricular cardiac muscle tissue morphogenesis / microfilament motor activity / heart contraction / myosin binding / regulation of heart contraction / negative regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell migration / myofibril / mesenchyme migration / negative regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell proliferation / Smooth Muscle Contraction / skeletal muscle contraction / striated muscle contraction / ATP metabolic process / cytoskeletal protein binding / cardiac muscle contraction / stress fiber / positive regulation of stress fiber assembly / cytoskeleton organization / positive regulation of cell adhesion / muscle contraction / regulation of heart rate / actin filament organization / negative regulation of cell migration / sarcomere / cellular response to reactive oxygen species / filopodium / actin filament / wound healing / structural constituent of cytoskeleton / ruffle membrane / Z disc / actin filament binding / regulation of cell shape / lamellipodium / actin cytoskeleton / actin binding / cell body / cytoskeleton / calmodulin binding / protein heterodimerization activity / positive regulation of gene expression / protein homodimerization activity / ATP binding / identical protein binding / cytoplasm / cytosol 類似検索 - 分子機能 | ||||||
| 生物種 |  Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト) | ||||||
| 手法 | 電子顕微鏡法 / らせん対称体再構成法 / クライオ電子顕微鏡法 / 解像度: 3.4 Å | ||||||
 データ登録者 データ登録者 | Doran, M.H. / Lehman, W. / Rynkiewicz, M.J. | ||||||
| 資金援助 |  米国, 1件 米国, 1件
| ||||||
 引用 引用 |  ジャーナル: J Gen Physiol / 年: 2023 ジャーナル: J Gen Physiol / 年: 2023タイトル: Myosin loop-4 is critical for optimal tropomyosin repositioning on actin during muscle activation and relaxation. 著者: Matthew H Doran / Michael J Rynkiewicz / Elumalai Pavadai / Skylar M L Bodt / David Rasicci / Jeffrey R Moore / Christopher M Yengo / Esther Bullitt / William Lehman /  要旨: During force-generating steps of the muscle crossbridge cycle, the tip of the myosin motor, specifically loop-4, contacts the tropomyosin cable of actin filaments. In the current study, we determined ...During force-generating steps of the muscle crossbridge cycle, the tip of the myosin motor, specifically loop-4, contacts the tropomyosin cable of actin filaments. In the current study, we determined the corresponding effect of myosin loop-4 on the regulatory positioning of tropomyosin on actin. To accomplish this, we compared high-resolution cryo-EM structures of myosin S1-decorated thin filaments containing either wild-type or a loop-4 mutant construct, where the seven-residue portion of myosin loop-4 that contacts tropomyosin was replaced by glycine residues, thus removing polar side chains from residues 366-372. Cryo-EM analysis of fully decorated actin-tropomyosin filaments with wild-type and mutant S1, yielded 3.4-3.6 Å resolution reconstructions, with even higher definition at the actin-myosin interface. Loop-4 densities both in wild-type and mutant S1 were clearly identified, and side chains were resolved in the wild-type structure. Aside from loop-4, actin and myosin structural domains were indistinguishable from each other when filaments were decorated with either mutant or wild-type S1. In marked contrast, the position of tropomyosin on actin in the two reconstructions differed by 3 to 4 Å. In maps of filaments containing the mutant, tropomyosin was located closer to the myosin-head and thus moved in the direction of the C-state conformation adopted by myosin-free thin filaments. Complementary interaction energy measurements showed that tropomyosin in the mutant thin filaments sits on actin in a local energy minimum, whereas tropomyosin is positioned by wild-type S1 in an energetically unfavorable location. We propose that the high potential energy associated with tropomyosin positioning in wild-type filaments favors an effective transition to B- and C-states following release of myosin from the thin filaments during relaxation. | ||||||
| 履歴 |
|
- 構造の表示
構造の表示
| 構造ビューア | 分子:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- ダウンロードとリンク
ダウンロードとリンク
- ダウンロード
ダウンロード
| PDBx/mmCIF形式 |  8efi.cif.gz 8efi.cif.gz | 535.9 KB | 表示 |  PDBx/mmCIF形式 PDBx/mmCIF形式 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB形式 |  pdb8efi.ent.gz pdb8efi.ent.gz | 425 KB | 表示 |  PDB形式 PDB形式 |
| PDBx/mmJSON形式 |  8efi.json.gz 8efi.json.gz | ツリー表示 |  PDBx/mmJSON形式 PDBx/mmJSON形式 | |
| その他 |  その他のダウンロード その他のダウンロード |
-検証レポート
| 文書・要旨 |  8efi_validation.pdf.gz 8efi_validation.pdf.gz | 1.5 MB | 表示 |  wwPDB検証レポート wwPDB検証レポート |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 文書・詳細版 |  8efi_full_validation.pdf.gz 8efi_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.5 MB | 表示 | |
| XML形式データ |  8efi_validation.xml.gz 8efi_validation.xml.gz | 91.3 KB | 表示 | |
| CIF形式データ |  8efi_validation.cif.gz 8efi_validation.cif.gz | 136.9 KB | 表示 | |
| アーカイブディレクトリ |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ef/8efi https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ef/8efi ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ef/8efi ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ef/8efi | HTTPS FTP |
-関連構造データ
| 関連構造データ |  28083MC 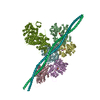 8encC M: このデータのモデリングに利用したマップデータ C: 同じ文献を引用 ( |
|---|---|
| 類似構造データ | 類似検索 - 機能・相同性  F&H 検索 F&H 検索 |
- リンク
リンク
- 集合体
集合体
| 登録構造単位 | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- 要素
要素
| #1: タンパク質 | 分子量: 223445.984 Da / 分子数: 1 / 由来タイプ: 組換発現 / 由来: (組換発現)  Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: MYH7, MYHCB / 発現宿主: Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: MYH7, MYHCB / 発現宿主:  | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #2: タンパク質 | 分子量: 42064.891 Da / 分子数: 5 / 由来タイプ: 天然 / 由来: (天然)  #3: タンパク質 | 分子量: 32763.621 Da / 分子数: 2 / 由来タイプ: 組換発現 / 由来: (組換発現)  Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: TPM1, C15orf13, TMSA / 発現宿主: Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: TPM1, C15orf13, TMSA / 発現宿主:  #4: 化合物 | ChemComp-ADP / #5: 化合物 | ChemComp-MG / 研究の焦点であるリガンドがあるか | N | Has protein modification | N | |
-実験情報
-実験
| 実験 | 手法: 電子顕微鏡法 |
|---|---|
| EM実験 | 試料の集合状態: FILAMENT / 3次元再構成法: らせん対称体再構成法 |
- 試料調製
試料調製
| 構成要素 |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 由来(天然) |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 由来(組換発現) |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 緩衝液 | pH: 7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 試料 | 濃度: 0.13 mg/ml / 包埋: NO / シャドウイング: NO / 染色: NO / 凍結: YES | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 試料支持 | グリッドの材料: GOLD / グリッドのサイズ: 200 divisions/in. / グリッドのタイプ: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 急速凍結 | 装置: FEI VITROBOT MARK III / 凍結剤: ETHANE / 湿度: 100 % / 凍結前の試料温度: 283 K |
- 電子顕微鏡撮影
電子顕微鏡撮影
| 実験機器 |  モデル: Titan Krios / 画像提供: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| 顕微鏡 | モデル: TFS KRIOS |
| 電子銃 | 電子線源:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / 加速電圧: 300 kV / 照射モード: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / 加速電圧: 300 kV / 照射モード: FLOOD BEAM |
| 電子レンズ | モード: BRIGHT FIELD / 倍率(公称値): 80000 X / 最大 デフォーカス(公称値): 2000 nm / 最小 デフォーカス(公称値): 700 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm |
| 試料ホルダ | 凍結剤: NITROGEN 試料ホルダーモデル: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| 撮影 | 平均露光時間: 3.12 sec. / 電子線照射量: 53.7 e/Å2 / フィルム・検出器のモデル: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / 撮影したグリッド数: 4 / 実像数: 3961 |
| 画像スキャン | 横: 539 / 縦: 539 |
- 解析
解析
| ソフトウェア | 名称: PHENIX / バージョン: 1.19.1_4122: / 分類: 精密化 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EMソフトウェア |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF補正 | タイプ: PHASE FLIPPING ONLY | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| らせん対称 | 回転角度/サブユニット: -166.4 ° / 軸方向距離/サブユニット: 27.9 Å / らせん対称軸の対称性: C1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 粒子像の選択 | 選択した粒子像数: 1045903 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3次元再構成 | 解像度: 3.4 Å / 解像度の算出法: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / 粒子像の数: 176178 / 対称性のタイプ: HELICAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 原子モデル構築 | プロトコル: OTHER / 空間: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 原子モデル構築 | PDB-ID: 6X5Z Accession code: 6X5Z / Source name: PDB / タイプ: experimental model | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 拘束条件 |
|
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー




 PDBj
PDBj
















