+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8czo | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of BCL10 CARD - MALT1 DD filament | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | IMMUNE SYSTEM / filament / CBM complex | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpositive regulation of lymphotoxin A production / polkadots / B-1 B cell differentiation / positive regulation of T-helper 17 cell differentiation / CBM complex / regulation of T cell receptor signaling pathway / protein kinase B binding / antifungal innate immune response / response to fungus / CARD domain binding ...positive regulation of lymphotoxin A production / polkadots / B-1 B cell differentiation / positive regulation of T-helper 17 cell differentiation / CBM complex / regulation of T cell receptor signaling pathway / protein kinase B binding / antifungal innate immune response / response to fungus / CARD domain binding / positive regulation of mast cell cytokine production / T cell apoptotic process / negative regulation of mature B cell apoptotic process / B cell apoptotic process / CLEC7A/inflammasome pathway / programmed cell death / nuclear export / non-canonical NF-kappaB signal transduction / positive regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway / response to food / toll-like receptor signaling pathway / small molecule binding / positive regulation of T cell receptor signaling pathway / immunoglobulin mediated immune response / B cell activation / immunological synapse / general transcription initiation factor binding / positive regulation of phosphorylation / NF-kappaB binding / cellular defense response / endopeptidase activator activity / T cell proliferation / cytoplasmic microtubule / signaling adaptor activity / positive regulation of interleukin-2 production / : / lipopolysaccharide-mediated signaling pathway / positive regulation of protein ubiquitination / positive regulation of interleukin-1 beta production / positive regulation of interleukin-8 production / neural tube closure / apoptotic signaling pathway / Activation of NF-kappaB in B cells / cellular response to mechanical stimulus / defense response / : / positive regulation of T cell cytokine production / protein homooligomerization / positive regulation of T cell activation / positive regulation of interleukin-6 production / CLEC7A (Dectin-1) signaling / FCERI mediated NF-kB activation / fibrillar center / ubiquitin-protein transferase activity / Downstream TCR signaling / peptidase activity / T cell receptor signaling pathway / E3 ubiquitin ligases ubiquitinate target proteins / cellular response to lipopolysaccharide / protease binding / endopeptidase activity / regulation of apoptotic process / protein-macromolecule adaptor activity / adaptive immune response / transcription coactivator activity / lysosome / Hydrolases; Acting on peptide bonds (peptidases); Cysteine endopeptidases / positive regulation of canonical NF-kappaB signal transduction / positive regulation of apoptotic process / membrane raft / innate immune response / cysteine-type endopeptidase activity / ubiquitin protein ligase binding / negative regulation of apoptotic process / positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription / protein-containing complex binding / perinuclear region of cytoplasm / protein-containing complex / proteolysis / nucleoplasm / identical protein binding / nucleus / cytosol / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / helical reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.3 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | David, L. / Wu, H. | ||||||
| Funding support | 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cancer Discov / Year: 2022 Journal: Cancer Discov / Year: 2022Title: BCL10 Mutations Define Distinct Dependencies Guiding Precision Therapy for DLBCL. Authors: Min Xia / Liron David / Matt Teater / Johana Gutierrez / Xiang Wang / Cem Meydan / Andrew Lytle / Graham W Slack / David W Scott / Ryan D Morin / Ozlem Onder / Kojo S J Elenitoba-Johnson / ...Authors: Min Xia / Liron David / Matt Teater / Johana Gutierrez / Xiang Wang / Cem Meydan / Andrew Lytle / Graham W Slack / David W Scott / Ryan D Morin / Ozlem Onder / Kojo S J Elenitoba-Johnson / Nahuel Zamponi / Leandro Cerchietti / Tianbao Lu / Ulrike Philippar / Lorena Fontan / Hao Wu / Ari M Melnick /    Abstract: Activated B cell-like diffuse large B-cell lymphomas (ABC-DLBCL) have unfavorable outcomes and chronic activation of CARD11-BCL10-MALT1 (CBM) signal amplification complexes that form due to ...Activated B cell-like diffuse large B-cell lymphomas (ABC-DLBCL) have unfavorable outcomes and chronic activation of CARD11-BCL10-MALT1 (CBM) signal amplification complexes that form due to polymerization of BCL10 subunits, which is affected by recurrent somatic mutations in ABC-DLBCLs. Herein, we show that BCL10 mutants fall into at least two functionally distinct classes: missense mutations of the BCL10 CARD domain and truncation of its C-terminal tail. Truncating mutations abrogated a motif through which MALT1 inhibits BCL10 polymerization, trapping MALT1 in its activated filament-bound state. CARD missense mutations enhanced BCL10 filament formation, forming glutamine network structures that stabilize BCL10 filaments. Mutant forms of BCL10 were less dependent on upstream CARD11 activation and thus manifested resistance to BTK inhibitors, whereas BCL10 truncating but not CARD mutants were hypersensitive to MALT1 inhibitors. Therefore, BCL10 mutations are potential biomarkers for BTK inhibitor resistance in ABC-DLBCL, and further precision can be achieved by selecting therapy based on specific biochemical effects of distinct mutation classes. SIGNIFICANCE: ABC-DLBCLs feature frequent mutations of signaling mediators that converge on the CBM complex. We use structure-function approaches to reveal that BCL10 mutations fall into two distinct ...SIGNIFICANCE: ABC-DLBCLs feature frequent mutations of signaling mediators that converge on the CBM complex. We use structure-function approaches to reveal that BCL10 mutations fall into two distinct biochemical classes. Both classes confer resistance to BTK inhibitors, whereas BCL10 truncations confer hyperresponsiveness to MALT1 inhibitors, providing a road map for precision therapies in ABC-DLBCLs. See related commentary by Phelan and Oellerich, p. 1844. This article is highlighted in the In This Issue feature, p. 1825. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8czo.cif.gz 8czo.cif.gz | 721.5 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8czo.ent.gz pdb8czo.ent.gz | 613.8 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8czo.json.gz 8czo.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  8czo_validation.pdf.gz 8czo_validation.pdf.gz | 1.4 MB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  8czo_full_validation.pdf.gz 8czo_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.4 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  8czo_validation.xml.gz 8czo_validation.xml.gz | 81.5 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  8czo_validation.cif.gz 8czo_validation.cif.gz | 133.2 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/cz/8czo https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/cz/8czo ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/cz/8czo ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/cz/8czo | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  27100MC  8czdC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 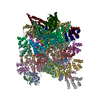
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 10615.389 Da / Num. of mol.: 22 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: MALT1, MLT / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: MALT1, MLT / Production host:  Escherichia phage EcSzw-2 (virus) Escherichia phage EcSzw-2 (virus)References: UniProt: Q9UDY8, Hydrolases; Acting on peptide bonds (peptidases); Cysteine endopeptidases #2: Protein | Mass: 12614.566 Da / Num. of mol.: 22 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: BCL10, CIPER, CLAP / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: BCL10, CIPER, CLAP / Production host:  Escherichia phage EcSzw-2 (virus) / References: UniProt: O95999 Escherichia phage EcSzw-2 (virus) / References: UniProt: O95999Has protein modification | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: FILAMENT / 3D reconstruction method: helical reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: filament / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: RECOMBINANT | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO | |||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Escherichia phage EcSzw-2 (virus) Escherichia phage EcSzw-2 (virus) | |||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 | |||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| |||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | |||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK III / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 47000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm / C2 aperture diameter: 2.7 µm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 55 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON II (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 700 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.18_3845: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software | Name: RELION / Version: 3.1 / Category: 3D reconstruction | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: NONE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Helical symmerty | Angular rotation/subunit: -100.8 ° / Axial rise/subunit: 5 Å / Axial symmetry: C1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 4.3 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 23000 / Symmetry type: HELICAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj








