[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-8cmy: Structure of the Cyanobium sp. PCC 7001 determined with C1 symmetry -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8cmy | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
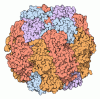
| Title | Structure of the Cyanobium sp. PCC 7001 determined with C1 symmetry | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | PHOTOSYNTHESIS / Carboxysome / Carbon fixation / cyanobacteria | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationphotorespiration / carboxysome / ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase / ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase activity / reductive pentose-phosphate cycle / monooxygenase activity / magnesium ion binding Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Cyanobium (bacteria) Cyanobium (bacteria) | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.79 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Evans, S.L. / Bergeron, J.R.C. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 1items United Kingdom, 1items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Structure / Year: 2023 Journal: Structure / Year: 2023Title: Single-particle cryo-EM analysis of the shell architecture and internal organization of an intact α-carboxysome. Authors: Sasha L Evans / Monsour M J Al-Hazeem / Daniel Mann / Nicolas Smetacek / Andrew J Beavil / Yaqi Sun / Taiyu Chen / Gregory F Dykes / Lu-Ning Liu / Julien R C Bergeron /    Abstract: Carboxysomes are proteinaceous bacterial microcompartments that sequester the key enzymes for carbon fixation in cyanobacteria and some proteobacteria. They consist of a virus-like icosahedral shell, ...Carboxysomes are proteinaceous bacterial microcompartments that sequester the key enzymes for carbon fixation in cyanobacteria and some proteobacteria. They consist of a virus-like icosahedral shell, encapsulating several enzymes, including ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (RuBisCO), responsible for the first step of the Calvin-Benson-Bassham cycle. Despite their significance in carbon fixation and great bioengineering potentials, the structural understanding of native carboxysomes is currently limited to low-resolution studies. Here, we report the characterization of a native α-carboxysome from a marine cyanobacterium by single-particle cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM). We have determined the structure of its RuBisCO enzyme, and obtained low-resolution maps of its icosahedral shell, and of its concentric interior organization. Using integrative modeling approaches, we have proposed a complete atomic model of an intact carboxysome, providing insight into its organization and assembly. This is critical for a better understanding of the carbon fixation mechanism and toward repurposing carboxysomes in synthetic biology for biotechnological applications. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8cmy.cif.gz 8cmy.cif.gz | 893 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8cmy.ent.gz pdb8cmy.ent.gz | 624.8 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8cmy.json.gz 8cmy.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/cm/8cmy https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/cm/8cmy ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/cm/8cmy ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/cm/8cmy | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7yyoC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 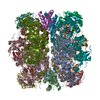
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 52526.531 Da / Num. of mol.: 8 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Cyanobium (bacteria) Cyanobium (bacteria)References: UniProt: A5CKD0, ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase #2: Protein | Mass: 12967.611 Da / Num. of mol.: 8 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Cyanobium (bacteria) Cyanobium (bacteria)References: UniProt: A0A182AM64, ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase #3: Sugar | ChemComp-CAP / #4: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / Has ligand of interest | N | Has protein modification | N | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Carboxysome / Type: ORGANELLE OR CELLULAR COMPONENT / Entity ID: #1-#2 / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Cyanobium (bacteria) Cyanobium (bacteria) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 500 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 30 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.79 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 131356 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Cross valid method: NONE Stereochemistry target values: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 81.81 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 PDBj
PDBj