+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8bhi | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
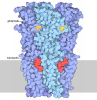
| Title | GABA-A receptor a5 homomer - a5V3 - RO5211223 | ||||||
 Components Components | Gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor subunit alpha-5 | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / pLGIC GABA Neurotransmission | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationGABA receptor binding / GABA receptor activation / inner ear receptor cell development / inhibitory synapse assembly / GABA-A receptor activity / GABA-gated chloride ion channel activity / GABA-A receptor complex / innervation / postsynaptic specialization membrane / neuronal cell body membrane ...GABA receptor binding / GABA receptor activation / inner ear receptor cell development / inhibitory synapse assembly / GABA-A receptor activity / GABA-gated chloride ion channel activity / GABA-A receptor complex / innervation / postsynaptic specialization membrane / neuronal cell body membrane / gamma-aminobutyric acid signaling pathway / synaptic transmission, GABAergic / associative learning / cochlea development / chloride channel complex / behavioral fear response / dendrite membrane / ligand-gated monoatomic ion channel activity involved in regulation of presynaptic membrane potential / chloride transmembrane transport / transmitter-gated monoatomic ion channel activity involved in regulation of postsynaptic membrane potential / GABA-ergic synapse / signaling receptor activity / presynaptic membrane / postsynapse / signal transduction / nucleoplasm / plasma membrane / cytosol Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.67 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Miller, P.S. / Malinauskas, T.M. / Hardwick, S.W. / Chirgadze, D.Y. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 1items United Kingdom, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2023 Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2023Title: The molecular basis of drug selectivity for α5 subunit-containing GABA receptors. Authors: Vikram Babu Kasaragod / Tomas Malinauskas / Ayla A Wahid / Judith Lengyel / Frederic Knoflach / Steven W Hardwick / Charlotte F Jones / Wan-Na Chen / Xavier Lucas / Kamel El Omari / Dimitri ...Authors: Vikram Babu Kasaragod / Tomas Malinauskas / Ayla A Wahid / Judith Lengyel / Frederic Knoflach / Steven W Hardwick / Charlotte F Jones / Wan-Na Chen / Xavier Lucas / Kamel El Omari / Dimitri Y Chirgadze / A Radu Aricescu / Giuseppe Cecere / Maria-Clemencia Hernandez / Paul S Miller /   Abstract: α5 subunit-containing γ-aminobutyric acid type A (GABA) receptors represent a promising drug target for neurological and neuropsychiatric disorders. Altered expression and function contributes to ...α5 subunit-containing γ-aminobutyric acid type A (GABA) receptors represent a promising drug target for neurological and neuropsychiatric disorders. Altered expression and function contributes to neurodevelopmental disorders such as Dup15q and Angelman syndromes, developmental epilepsy and autism. Effective drug action without side effects is dependent on both α5-subtype selectivity and the strength of the positive or negative allosteric modulation (PAM or NAM). Here we solve structures of drugs bound to the α5 subunit. These define the molecular basis of binding and α5 selectivity of the β-carboline, methyl 6,7-dimethoxy-4-ethyl-β-carboline-3-carboxylate (DMCM), type II benzodiazepine NAMs, and a series of isoxazole NAMs and PAMs. For the isoxazole series, each molecule appears as an 'upper' and 'lower' moiety in the pocket. Structural data and radioligand binding data reveal a positional displacement of the upper moiety containing the isoxazole between the NAMs and PAMs. Using a hybrid molecule we directly measure the functional contribution of the upper moiety to NAM versus PAM activity. Overall, these structures provide a framework by which to understand distinct modulator binding modes and their basis of α5-subtype selectivity, appreciate structure-activity relationships, and empower future structure-based drug design campaigns. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8bhi.cif.gz 8bhi.cif.gz | 635 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8bhi.ent.gz pdb8bhi.ent.gz | 539.7 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8bhi.json.gz 8bhi.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  8bhi_validation.pdf.gz 8bhi_validation.pdf.gz | 1.9 MB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  8bhi_full_validation.pdf.gz 8bhi_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.9 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  8bhi_validation.xml.gz 8bhi_validation.xml.gz | 67.9 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  8bhi_validation.cif.gz 8bhi_validation.cif.gz | 98 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/bh/8bhi https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/bh/8bhi ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/bh/8bhi ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/bh/8bhi | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  16055MC  8bejC  8bgiC  8bhaC  8bhbC  8bhgC  8bhkC  8bhmC  8bhoC  8bhqC  8bhrC  8bhsC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
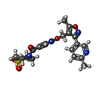
| #1: Protein | Mass: 41057.910 Da / Num. of mol.: 5 Mutation: I79M,T82N,V98I,R101A,S103T,I142F,N145W,K151R,L152M,L155I,E156W,D157N,T160R,L161V,M165L,Q176D,A184E,H185Q,A186N,P287A,I336L,T340F,F344I,V335I Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GABRA5 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GABRA5 / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P31644 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P31644#2: Sugar | ChemComp-NAG / #3: Chemical | ChemComp-QKF / [ Has ligand of interest | Y | Has protein modification | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: GABA-A receptor a5 homomer - a5V3 - RO5211223 / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.205 MDa / Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 |
| Specimen | Conc.: 1.5 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN |
| Electron lens | Mode: DIFFRACTION / Nominal defocus max: 2500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 1.45 sec. / Electron dose: 49.27 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
|---|---|
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.67 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 15289 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller












 PDBj
PDBj