[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-8b6z: CryoEM Structure of Extended eEF1A bound to the Ribosome in the C... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8b6z | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | CryoEM Structure of Extended eEF1A bound to the Ribosome in the Classical Pre State | ||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | RIBOSOME / translation / protein biogenesis / elongation factor | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpositive regulation of lipid kinase activity / cytoplasmic side of lysosomal membrane / Eukaryotic Translation Elongation / eukaryotic translation elongation factor 1 complex / regulation of chaperone-mediated autophagy / translation factor activity, RNA binding / translational elongation / translation elongation factor activity / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on GTP to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / positive regulation of apoptotic process ...positive regulation of lipid kinase activity / cytoplasmic side of lysosomal membrane / Eukaryotic Translation Elongation / eukaryotic translation elongation factor 1 complex / regulation of chaperone-mediated autophagy / translation factor activity, RNA binding / translational elongation / translation elongation factor activity / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on GTP to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / positive regulation of apoptotic process / translation / GTPase activity / synapse / protein kinase binding / endoplasmic reticulum membrane / GTP binding / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.9 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Gemmer, M. / Fedry, J.M.M. / Forster, F.G. | ||||||||||||
| Funding support | European Union,  Netherlands, 3items Netherlands, 3items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2023 Journal: Nature / Year: 2023Title: Visualization of translation and protein biogenesis at the ER membrane. Authors: Max Gemmer / Marten L Chaillet / Joyce van Loenhout / Rodrigo Cuevas Arenas / Dimitrios Vismpas / Mariska Gröllers-Mulderij / Fujiet A Koh / Pascal Albanese / Richard A Scheltema / Stuart C ...Authors: Max Gemmer / Marten L Chaillet / Joyce van Loenhout / Rodrigo Cuevas Arenas / Dimitrios Vismpas / Mariska Gröllers-Mulderij / Fujiet A Koh / Pascal Albanese / Richard A Scheltema / Stuart C Howes / Abhay Kotecha / Juliette Fedry / Friedrich Förster /  Abstract: The dynamic ribosome-translocon complex, which resides at the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane, produces a major fraction of the human proteome. It governs the synthesis, translocation, membrane ...The dynamic ribosome-translocon complex, which resides at the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane, produces a major fraction of the human proteome. It governs the synthesis, translocation, membrane insertion, N-glycosylation, folding and disulfide-bond formation of nascent proteins. Although individual components of this machinery have been studied at high resolution in isolation, insights into their interplay in the native membrane remain limited. Here we use cryo-electron tomography, extensive classification and molecular modelling to capture snapshots of mRNA translation and protein maturation at the ER membrane at molecular resolution. We identify a highly abundant classical pre-translocation intermediate with eukaryotic elongation factor 1a (eEF1a) in an extended conformation, suggesting that eEF1a may remain associated with the ribosome after GTP hydrolysis during proofreading. At the ER membrane, distinct polysomes bind to different ER translocons specialized in the synthesis of proteins with signal peptides or multipass transmembrane proteins with the translocon-associated protein complex (TRAP) present in both. The near-complete atomic model of the most abundant ER translocon variant comprising the protein-conducting channel SEC61, TRAP and the oligosaccharyltransferase complex A (OSTA) reveals specific interactions of TRAP with other translocon components. We observe stoichiometric and sub-stoichiometric cofactors associated with OSTA, which are likely to include protein isomerases. In sum, we visualize ER-bound polysomes with their coordinated downstream machinery. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8b6z.cif.gz 8b6z.cif.gz | 193.8 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8b6z.ent.gz pdb8b6z.ent.gz | 95.2 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8b6z.json.gz 8b6z.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/b6/8b6z https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/b6/8b6z ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/b6/8b6z ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/b6/8b6z | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  15893MC  8b6lC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 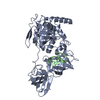
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 50545.102 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q05639 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q05639 |
|---|---|
| #2: RNA chain | Mass: 1640222.125 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: GenBank: 86475748 Homo sapiens (human) / References: GenBank: 86475748 |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Ribosome in the Classical Pre+ state / Type: RIBOSOME / Entity ID: all / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid type: Quantifoil R3.5/1 |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 200 nm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 40 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON IV (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.9 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 19046 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller














 PDBj
PDBj





























