+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8b5r | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
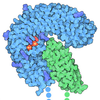
| Title | p97-p37-SPI substrate complex | ||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | CHAPERONE / AAA+ ATPase / p97 / VCP / Cdc48 / unfoldase / protein phosphatase-1 / protein maturation | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnegative regulation of protein localization to centrosome / positive regulation of mitotic centrosome separation / PTW/PP1 phosphatase complex / regulation of nucleocytoplasmic transport / protein phosphatase 1 binding / nuclear membrane reassembly / lamin binding / protein phosphatase regulator activity / spindle pole centrosome / : ...negative regulation of protein localization to centrosome / positive regulation of mitotic centrosome separation / PTW/PP1 phosphatase complex / regulation of nucleocytoplasmic transport / protein phosphatase 1 binding / nuclear membrane reassembly / lamin binding / protein phosphatase regulator activity / spindle pole centrosome / : / flavin adenine dinucleotide catabolic process / VCP-NSFL1C complex / endosome to lysosome transport via multivesicular body sorting pathway / endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced pre-emptive quality control / BAT3 complex binding / cellular response to arsenite ion / protein-DNA covalent cross-linking repair / SHOC2 M1731 mutant abolishes MRAS complex function / Gain-of-function MRAS complexes activate RAF signaling / Derlin-1 retrotranslocation complex / positive regulation of protein K63-linked deubiquitination / cytoplasm protein quality control / positive regulation of oxidative phosphorylation / : / aggresome assembly / deubiquitinase activator activity / mitotic spindle disassembly / ubiquitin-modified protein reader activity / regulation of protein localization to chromatin / VCP-NPL4-UFD1 AAA ATPase complex / cellular response to misfolded protein / negative regulation of protein localization to chromatin / positive regulation of mitochondrial membrane potential / vesicle-fusing ATPase / K48-linked polyubiquitin modification-dependent protein binding / regulation of aerobic respiration / retrograde protein transport, ER to cytosol / stress granule disassembly / glycogen metabolic process / entrainment of circadian clock by photoperiod / protein-serine/threonine phosphatase / ATPase complex / Triglyceride catabolism / regulation of synapse organization / ubiquitin-specific protease binding / Golgi organization / protein serine/threonine phosphatase activity / phosphatase activity / positive regulation of ATP biosynthetic process / MHC class I protein binding / Maturation of hRSV A proteins / microtubule organizing center / cleavage furrow / ubiquitin-like protein ligase binding / establishment of mitotic spindle orientation / phosphoprotein phosphatase activity / mitotic sister chromatid segregation / RHOH GTPase cycle / positive regulation of glial cell proliferation / polyubiquitin modification-dependent protein binding / autophagosome maturation / autophagosome assembly / blastocyst development / endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi vesicle-mediated transport / negative regulation of hippo signaling / HSF1 activation / translesion synthesis / interstrand cross-link repair / protein dephosphorylation / ATP metabolic process / endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response / proteasomal protein catabolic process / Protein methylation / enzyme regulator activity / Attachment and Entry / ERAD pathway / lipid droplet / Amplification of signal from unattached kinetochores via a MAD2 inhibitory signal / Mitotic Prometaphase / EML4 and NUDC in mitotic spindle formation / proteasome complex / viral genome replication / Resolution of Sister Chromatid Cohesion / ubiquitin binding / Josephin domain DUBs / Downregulation of TGF-beta receptor signaling / N-glycan trimming in the ER and Calnexin/Calreticulin cycle / negative regulation of smoothened signaling pathway / macroautophagy / circadian regulation of gene expression / establishment of protein localization / Hh mutants are degraded by ERAD / positive regulation of protein-containing complex assembly / RAF activation / Hedgehog ligand biogenesis / Defective CFTR causes cystic fibrosis / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / positive regulation of non-canonical NF-kappaB signal transduction / Translesion Synthesis by POLH / ADP binding Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 6.1 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | van den Boom, J. / Marini, G. / Meyer, H. / Saibil, H. | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 3items United Kingdom, 3items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: EMBO J / Year: 2023 Journal: EMBO J / Year: 2023Title: Structural basis of ubiquitin-independent PP1 complex disassembly by p97. Authors: Johannes van den Boom / Guendalina Marini / Hemmo Meyer / Helen R Saibil /   Abstract: The AAA+-ATPase p97 (also called VCP or Cdc48) unfolds proteins and disassembles protein complexes in numerous cellular processes, but how substrate complexes are loaded onto p97 and disassembled is ...The AAA+-ATPase p97 (also called VCP or Cdc48) unfolds proteins and disassembles protein complexes in numerous cellular processes, but how substrate complexes are loaded onto p97 and disassembled is unclear. Here, we present cryo-EM structures of p97 in the process of disassembling a protein phosphatase-1 (PP1) complex by extracting an inhibitory subunit from PP1. We show that PP1 and its partners SDS22 and inhibitor-3 (I3) are loaded tightly onto p97, surprisingly via a direct contact of SDS22 with the p97 N-domain. Loading is assisted by the p37 adapter that bridges two adjacent p97 N-domains underneath the substrate complex. A stretch of I3 is threaded into the central channel of the spiral-shaped p97 hexamer, while other elements of I3 are still attached to PP1. Thus, our data show how p97 arranges a protein complex between the p97 N-domain and central channel, suggesting a hold-and-extract mechanism for p97-mediated disassembly. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8b5r.cif.gz 8b5r.cif.gz | 679 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8b5r.ent.gz pdb8b5r.ent.gz | 458.2 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8b5r.json.gz 8b5r.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/b5/8b5r https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/b5/8b5r ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/b5/8b5r ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/b5/8b5r | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  15861MC C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 3 types, 8 molecules ABCDEFPS
| #1: Protein | Mass: 90265.695 Da / Num. of mol.: 6 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: VCP / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: VCP / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P55072, vesicle-fusing ATPase Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P55072, vesicle-fusing ATPase#3: Protein | | Mass: 37030.777 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PPP1CC / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PPP1CC / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper)References: UniProt: P36873, protein-serine/threonine phosphatase #4: Protein | | Mass: 41616.129 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PPP1R7, SDS22 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PPP1R7, SDS22 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q15435 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q15435 |
|---|
-Protein/peptide , 1 types, 1 molecules I
| #2: Protein/peptide | Mass: 1890.321 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) |
|---|
-UBX domain-containing protein ... , 2 types, 2 molecules XY
| #5: Protein/peptide | Mass: 1123.238 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: UBXN2B Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: UBXN2BProduction host:  References: UniProt: Q14CS0 |
|---|---|
| #6: Protein | Mass: 9759.220 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: UBXN2B Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: UBXN2BProduction host:  References: UniProt: Q14CS0 |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: p97 complex with p37 adaptor and SPI substrate / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#4, #6, #5 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: C-flat-1.2/1.3 |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 85 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 81000 X / Nominal defocus max: 3300 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1800 nm / Alignment procedure: BASIC |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 3 sec. / Electron dose: 48 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter name: GIF Bioquantum / Energyfilter slit width: 20 eV |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.20.1_4487: / Category: model refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 6.1 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 191477 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj