[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-7zdz: Cryo-EM structure of the human inward-rectifier potassium 2.1 cha... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7zdz | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the human inward-rectifier potassium 2.1 channel (Kir2.1) | ||||||||||||
 Components Components | Inward rectifier potassium channel 2 | ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / Potassium channel / Inward-rectifier channel / inward rectification | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationSensory perception of sour taste / Classical Kir channels / regulation of skeletal muscle contraction via regulation of action potential / relaxation of skeletal muscle / magnesium ion transport / voltage-gated potassium channel activity involved in cardiac muscle cell action potential repolarization / Phase 4 - resting membrane potential / membrane repolarization during action potential / membrane repolarization during cardiac muscle cell action potential / regulation of membrane repolarization ...Sensory perception of sour taste / Classical Kir channels / regulation of skeletal muscle contraction via regulation of action potential / relaxation of skeletal muscle / magnesium ion transport / voltage-gated potassium channel activity involved in cardiac muscle cell action potential repolarization / Phase 4 - resting membrane potential / membrane repolarization during action potential / membrane repolarization during cardiac muscle cell action potential / regulation of membrane repolarization / membrane depolarization during cardiac muscle cell action potential / regulation of resting membrane potential / regulation of monoatomic ion transmembrane transport / inward rectifier potassium channel activity / positive regulation of potassium ion transmembrane transport / cardiac muscle cell action potential involved in contraction / regulation of cardiac muscle cell contraction / relaxation of cardiac muscle / potassium ion import across plasma membrane / intracellular potassium ion homeostasis / regulation of heart rate by cardiac conduction / intercalated disc / phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate binding / voltage-gated potassium channel complex / potassium ion transmembrane transport / T-tubule / cellular response to mechanical stimulus / potassium ion transport / Activation of G protein gated Potassium channels / Inhibition of voltage gated Ca2+ channels via Gbeta/gamma subunits / protein homotetramerization / dendritic spine / postsynaptic membrane / neuronal cell body / glutamatergic synapse / identical protein binding / membrane / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.3 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Fernandes, C.A.H. / Venien-Bryan, C. / Fagnen, C. / Zuniga, D. | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  France, 3items France, 3items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2022 Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2022Title: Cryo-electron microscopy unveils unique structural features of the human Kir2.1 channel. Authors: Carlos A H Fernandes / Dania Zuniga / Charline Fagnen / Valérie Kugler / Rosa Scala / Gérard Péhau-Arnaudet / Renaud Wagner / David Perahia / Saïd Bendahhou / Catherine Vénien-Bryan /  Abstract: We present the first structure of the human Kir2.1 channel containing both transmembrane domain (TMD) and cytoplasmic domain (CTD). Kir2.1 channels are strongly inward-rectifying potassium channels ...We present the first structure of the human Kir2.1 channel containing both transmembrane domain (TMD) and cytoplasmic domain (CTD). Kir2.1 channels are strongly inward-rectifying potassium channels that play a key role in maintaining resting membrane potential. Their gating is modulated by phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP). Genetically inherited defects in Kir2.1 channels are responsible for several rare human diseases, including Andersen's syndrome. The structural analysis (cryo-electron microscopy), surface plasmon resonance, and electrophysiological experiments revealed a well-connected network of interactions between the PIP-binding site and the G-loop through residues R312 and H221. In addition, molecular dynamics simulations and normal mode analysis showed the intrinsic tendency of the CTD to tether to the TMD and a movement of the secondary anionic binding site to the membrane even without PIP. Our results revealed structural features unique to human Kir2.1 and provided insights into the connection between G-loop and gating and the pathological mechanisms associated with this channel. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7zdz.cif.gz 7zdz.cif.gz | 241 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7zdz.ent.gz pdb7zdz.ent.gz | 192.4 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7zdz.json.gz 7zdz.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  7zdz_validation.pdf.gz 7zdz_validation.pdf.gz | 1.2 MB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  7zdz_full_validation.pdf.gz 7zdz_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.2 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  7zdz_validation.xml.gz 7zdz_validation.xml.gz | 46.4 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  7zdz_validation.cif.gz 7zdz_validation.cif.gz | 67.1 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/zd/7zdz https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/zd/7zdz ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/zd/7zdz ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/zd/7zdz | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  14678MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 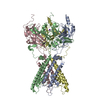
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 48344.141 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: KCNJ2, IRK1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: KCNJ2, IRK1 / Production host:  Komagataella pastoris (fungus) / References: UniProt: P63252 Komagataella pastoris (fungus) / References: UniProt: P63252#2: Chemical | ChemComp-K / | #3: Chemical | Has ligand of interest | Y | Has protein modification | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Human inward-rectifier potassium channel 2.1 (Kir2.1) / Type: ORGANELLE OR CELLULAR COMPONENT / Entity ID: #1 / Source: RECOMBINANT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 50 kDa/nm / Experimental value: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Komagataella pastoris (fungus) Komagataella pastoris (fungus) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.6 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK III / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 105000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2800 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1200 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 100 µm / Alignment procedure: BASIC |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 4 sec. / Electron dose: 61.7 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON III (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 9895 |
| Image scans | Sampling size: 10 µm / Width: 5760 / Height: 4092 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.19.2_4158: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 1031472 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C4 (4 fold cyclic) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 4.3 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 63584 / Num. of class averages: 1 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | B value: 404.73 / Protocol: OTHER / Space: REAL / Target criteria: Correlation coefficient Details: For structural fitting, it was used dock-in-map (available at PHENIX) that uses both SSM and convolution-based shape searches to find a part of a map that is similar to a model. An initial ...Details: For structural fitting, it was used dock-in-map (available at PHENIX) that uses both SSM and convolution-based shape searches to find a part of a map that is similar to a model. An initial in silico homology model of human Kir2.1 was generated using I-TASSER using the crystal structure of chicken Kir2.2 channel (PDB ID 3JYC) as a template. For building and refinement of the atomic model, the transmembrane domain (TMD, 55-184 region) of this in silico model was placed into the final sharpened cryo-EM map using the Dock in Map tool available in PHENIX. For the cytoplasmic domain (CTD; 188-367 region), the crystal structure of the CTD from mice Kir2.1 channel (PDB ID 1U4F) was placed into the final cryo-EM map using the same approach. Once the models were placed in the electron density, the loops that connect the two domains (185-187 region) and a N-terminal loop (41-54 region) absent in the in silico model were manually built using Coot. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | PDB-ID: 1U4F Accession code: 1U4F / Pdb chain residue range: 188-367 / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


 PDBj
PDBj