+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7zc1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
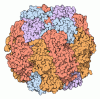
| Title | Subtomogram averaging of Rubisco from Cyanobium carboxysome | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | UNKNOWN FUNCTION / Rubisco / alpha carboxysomes | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationphotorespiration / carboxysome / ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase / ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase activity / reductive pentose-phosphate cycle / monooxygenase activity / magnesium ion binding Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Cyanobium sp. PCC 7001 (bacteria) Cyanobium sp. PCC 7001 (bacteria) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / subtomogram averaging / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.8 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Ni, T. / Zhu, Y. / Seaton-Burn, W. / Zhang, P. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, European Union, 3items United Kingdom, European Union, 3items
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022Title: Structure and assembly of cargo Rubisco in two native α-carboxysomes. Authors: Tao Ni / Yaqi Sun / Will Burn / Monsour M J Al-Hazeem / Yanan Zhu / Xiulian Yu / Lu-Ning Liu / Peijun Zhang /   Abstract: Carboxysomes are a family of bacterial microcompartments in cyanobacteria and chemoautotrophs. They encapsulate Ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (Rubisco) and carbonic anhydrase ...Carboxysomes are a family of bacterial microcompartments in cyanobacteria and chemoautotrophs. They encapsulate Ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (Rubisco) and carbonic anhydrase catalyzing carbon fixation inside a proteinaceous shell. How Rubisco complexes pack within the carboxysomes is unknown. Using cryo-electron tomography, we determine the distinct 3D organization of Rubisco inside two distant α-carboxysomes from a marine α-cyanobacterium Cyanobium sp. PCC 7001 where Rubiscos are organized in three concentric layers, and from a chemoautotrophic bacterium Halothiobacillus neapolitanus where they form intertwining spirals. We further resolve the structures of native Rubisco as well as its higher-order assembly at near-atomic resolutions by subtomogram averaging. The structures surprisingly reveal that the authentic intrinsically disordered linker protein CsoS2 interacts with Rubiscos in native carboxysomes but functions distinctively in the two α-carboxysomes. In contrast to the uniform Rubisco-CsoS2 association in the Cyanobium α-carboxysome, CsoS2 binds only to the Rubiscos close to the shell in the Halo α-carboxysome. Our findings provide critical knowledge of the assembly principles of α-carboxysomes, which may aid in the rational design and repurposing of carboxysome structures for new functions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7zc1.cif.gz 7zc1.cif.gz | 733.4 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7zc1.ent.gz pdb7zc1.ent.gz | 618.1 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7zc1.json.gz 7zc1.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/zc/7zc1 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/zc/7zc1 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/zc/7zc1 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/zc/7zc1 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  14617MC  7zbtC C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 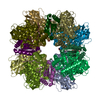
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 52526.531 Da / Num. of mol.: 8 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Cyanobium sp. PCC 7001 (bacteria) / Gene: rbcL, cbbL, CPCC7001_1083 / Production host: Cyanobium sp. PCC 7001 (bacteria) / Gene: rbcL, cbbL, CPCC7001_1083 / Production host:  Cyanobium sp. PCC 7001 (bacteria) Cyanobium sp. PCC 7001 (bacteria)References: UniProt: A5CKD0, ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase #2: Protein | Mass: 12967.611 Da / Num. of mol.: 8 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Cyanobium sp. PCC 7001 (bacteria) / Gene: CPCC7001_1801 / Production host: Cyanobium sp. PCC 7001 (bacteria) / Gene: CPCC7001_1801 / Production host:  Cyanobium sp. PCC 7001 (bacteria) / References: UniProt: B5ILN2 Cyanobium sp. PCC 7001 (bacteria) / References: UniProt: B5ILN2Has protein modification | N | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: subtomogram averaging |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Structure of Rubisco within Cyanobium carboxysome / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Cyanobium sp. PCC 7001 (bacteria) Cyanobium sp. PCC 7001 (bacteria) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 5000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 2500 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 3.65 e/Å2 / Avg electron dose per subtomogram: 150 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.20_4459: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: D4 (2x4 fold dihedral) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.8 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 152317 / Algorithm: FOURIER SPACE / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EM volume selection | Num. of tomograms: 139 / Num. of volumes extracted: 152317 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: AB INITIO MODEL / Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller










 PDBj
PDBj