[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-7vhq: Structural insights into the membrane microdomain organization by... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7vhq | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structural insights into the membrane microdomain organization by SPFH family proteins | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / membrane microdomain organization | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationHydrolases; Acting on peptide bonds (peptidases); Metalloendopeptidases / ATP-dependent peptidase activity / membrane => GO:0016020 / protein catabolic process / metalloendopeptidase activity / peptidase activity / cell division / proteolysis / zinc ion binding / ATP binding ...Hydrolases; Acting on peptide bonds (peptidases); Metalloendopeptidases / ATP-dependent peptidase activity / membrane => GO:0016020 / protein catabolic process / metalloendopeptidase activity / peptidase activity / cell division / proteolysis / zinc ion binding / ATP binding / membrane / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.27 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Ma, C.Y. / Wang, C.K. / Luo, D.Y. / Yan, L. / Yang, W.X. / Li, N.N. / Gao, N. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support | 1items
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
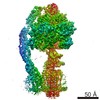
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell Res / Year: 2022 Journal: Cell Res / Year: 2022Title: Structural insights into the membrane microdomain organization by SPFH family proteins. Authors: Chengying Ma / Chengkun Wang / Dingyi Luo / Lu Yan / Wenxian Yang / Ningning Li / Ning Gao /  Abstract: The lateral segregation of membrane constituents into functional microdomains, conceptually known as lipid raft, is a universal organization principle for cellular membranes in both prokaryotes and ...The lateral segregation of membrane constituents into functional microdomains, conceptually known as lipid raft, is a universal organization principle for cellular membranes in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. The widespread Stomatin, Prohibitin, Flotillin, and HflK/C (SPFH) family proteins are enriched in functional membrane microdomains at various subcellular locations, and therefore were hypothesized to play a scaffolding role in microdomain formation. In addition, many SPFH proteins are also implicated in highly specific processes occurring on the membrane. However, none of these functions is understood at the molecular level. Here we report the structure of a supramolecular complex that is isolated from bacterial membrane microdomains and contains two SPFH proteins (HflK and HflC) and a membrane-anchored AAA+ protease FtsH. HflK and HflC form a circular 24-mer assembly, featuring a laterally segregated membrane microdomain (20 nm in diameter) bordered by transmembrane domains of HflK/C and a completely sealed periplasmic vault. Four FtsH hexamers are embedded inside this microdomain through interactions with the inner surface of the vault. These observations provide a mechanistic explanation for the role of HflK/C and their mitochondrial homologs prohibitins in regulating membrane-bound AAA+ proteases, and suggest a general model for the organization and functionalization of membrane microdomains by SPFH proteins. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7vhq.cif.gz 7vhq.cif.gz | 363.5 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7vhq.ent.gz pdb7vhq.ent.gz | 298.6 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7vhq.json.gz 7vhq.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vh/7vhq https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vh/7vhq ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vh/7vhq ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vh/7vhq | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  32003MC  7vhpC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 7345.267 Da / Num. of mol.: 6 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   References: UniProt: A0A376T6B9, Hydrolases; Acting on peptide bonds (peptidases); Metalloendopeptidases #2: Protein | Mass: 30164.129 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   #3: Protein | Mass: 37176.293 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Has protein modification | N | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: KCF complex / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 60 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.19.2_4158: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software | Name: PHENIX / Category: model refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: NONE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.27 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 274457 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller









 PDBj
PDBj



