+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7v3u | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of MCM double hexamer with structured Mcm4-NSD | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | CELL CYCLE / DNA replication initiation / Complex / Replicative helicase / Replication | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationMCM core complex / Assembly of the pre-replicative complex / Switching of origins to a post-replicative state / MCM complex binding / nuclear DNA replication / premeiotic DNA replication / replication fork protection complex / pre-replicative complex assembly involved in nuclear cell cycle DNA replication / Activation of the pre-replicative complex / mitotic DNA replication ...MCM core complex / Assembly of the pre-replicative complex / Switching of origins to a post-replicative state / MCM complex binding / nuclear DNA replication / premeiotic DNA replication / replication fork protection complex / pre-replicative complex assembly involved in nuclear cell cycle DNA replication / Activation of the pre-replicative complex / mitotic DNA replication / CMG complex / nuclear pre-replicative complex / DNA replication preinitiation complex / Activation of ATR in response to replication stress / MCM complex / double-strand break repair via break-induced replication / mitotic DNA replication initiation / single-stranded DNA helicase activity / silent mating-type cassette heterochromatin formation / regulation of DNA-templated DNA replication initiation / DNA strand elongation involved in DNA replication / nuclear replication fork / DNA replication origin binding / DNA replication initiation / subtelomeric heterochromatin formation / DNA helicase activity / transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / helicase activity / heterochromatin formation / single-stranded DNA binding / DNA helicase / DNA replication / chromosome, telomeric region / DNA damage response / chromatin binding / ATP hydrolysis activity / zinc ion binding / nucleoplasm / ATP binding / nucleus / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.2 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Cheng, J. / Li, N. / Huo, Y. / Dang, S. / Tye, B. / Gao, N. / Zhai, Y. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 1items China, 1items
| |||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022Title: Structural Insight into the MCM double hexamer activation by Dbf4-Cdc7 kinase. Authors: Jiaxuan Cheng / Ningning Li / Yunjing Huo / Shangyu Dang / Bik-Kwoon Tye / Ning Gao / Yuanliang Zhai /   Abstract: The Dbf4-dependent kinase Cdc7 (DDK) regulates DNA replication initiation by phosphorylation of the MCM double hexamer (MCM-DH) to promote helicase activation. Here, we determine a series of cryo ...The Dbf4-dependent kinase Cdc7 (DDK) regulates DNA replication initiation by phosphorylation of the MCM double hexamer (MCM-DH) to promote helicase activation. Here, we determine a series of cryo electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures of yeast DDK bound to the MCM-DH. These structures, occupied by one or two DDKs, differ primarily in the conformations of the kinase core. The interactions of DDK with the MCM-DH are mediated exclusively by subunit Dbf4 straddling across the hexamer interface on the three N-terminal domains (NTDs) of subunits Mcm2, Mcm6, and Mcm4. This arrangement brings Cdc7 close to its only essential substrate, the N-terminal serine/threonine-rich domain (NSD) of Mcm4. Dbf4 further displaces the NSD from its binding site on Mcm4-NTD, facilitating an immediate targeting of this motif by Cdc7. Moreover, the active center of Cdc7 is occupied by a unique Dbf4 inhibitory loop, which is disengaged when the kinase core assumes wobbling conformations. This study elucidates the versatility of Dbf4 in regulating the ordered multisite phosphorylation of the MCM-DH by Cdc7 kinase during helicase activation. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7v3u.cif.gz 7v3u.cif.gz | 1.4 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7v3u.ent.gz pdb7v3u.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7v3u.json.gz 7v3u.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/v3/7v3u https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/v3/7v3u ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/v3/7v3u ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/v3/7v3u | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  31684MC  7v3vC  7w8gC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 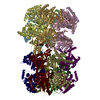
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-DNA replication licensing factor ... , 5 types, 10 molecules 2B3C4D6F7G
| #1: Protein | Mass: 98911.539 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #2: Protein | Mass: 107653.508 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #3: Protein | Mass: 105138.375 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #5: Protein | Mass: 113110.211 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #6: Protein | Mass: 95049.875 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|
-Protein , 1 types, 2 molecules 5E
| #4: Protein | Mass: 86505.734 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 4 types, 34 molecules 






| #7: Chemical | ChemComp-AGS / #8: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / #9: Chemical | ChemComp-ZN / #10: Chemical | |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: MCM double hexamer (DH) / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#6 / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.6 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: YES / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| EM embedding | Material: Ice |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 3500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 46 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.19.2_4158: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software | Name: PHENIX / Category: model refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.2 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 150000 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller

















 PDBj
PDBj





