+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7sid | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
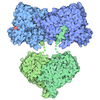
| Title | Human ATM Dimer Bound to Nbs1 | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | SIGNALING PROTEIN / Kinase | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationtelomere maintenance via telomere trimming / chromosomal region / telomeric 3' overhang formation / Mre11 complex / establishment of RNA localization to telomere / positive regulation of telomerase catalytic core complex assembly / cellular response to nitrosative stress / negative regulation of telomere capping / blastocyst growth / BRCA1-C complex ...telomere maintenance via telomere trimming / chromosomal region / telomeric 3' overhang formation / Mre11 complex / establishment of RNA localization to telomere / positive regulation of telomerase catalytic core complex assembly / cellular response to nitrosative stress / negative regulation of telomere capping / blastocyst growth / BRCA1-C complex / establishment of protein-containing complex localization to telomere / Sensing of DNA Double Strand Breaks / peptidyl-serine autophosphorylation / protection from non-homologous end joining at telomere / R-loop processing / positive regulation of telomere maintenance via telomere lengthening / meiotic telomere clustering / pre-B cell allelic exclusion / phosphorylation-dependent protein binding / DNA-dependent protein kinase activity / male meiotic nuclear division / extrinsic component of synaptic vesicle membrane / histone mRNA catabolic process / histone H2AXS139 kinase activity / regulation of telomere maintenance via telomerase / female meiotic nuclear division / t-circle formation / DNA strand resection involved in replication fork processing / homologous recombination / nuclear inclusion body / lipoprotein catabolic process / DNA double-strand break processing / regulation of autophagosome assembly / V(D)J recombination / pexophagy / oocyte development / cellular response to X-ray / double-strand break repair via alternative nonhomologous end joining / Impaired BRCA2 binding to PALB2 / mitotic G2/M transition checkpoint / isotype switching / HDR through MMEJ (alt-NHEJ) / protein localization to site of double-strand break / chromatin-protein adaptor activity / DNA repair complex / reciprocal meiotic recombination / regulation of DNA-templated DNA replication initiation / positive regulation of DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator / 1-phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase activity / Homologous DNA Pairing and Strand Exchange / Defective homologous recombination repair (HRR) due to BRCA1 loss of function / Defective HDR through Homologous Recombination Repair (HRR) due to PALB2 loss of BRCA1 binding function / Defective HDR through Homologous Recombination Repair (HRR) due to PALB2 loss of BRCA2/RAD51/RAD51C binding function / Resolution of D-loop Structures through Synthesis-Dependent Strand Annealing (SDSA) / neuromuscular process controlling balance / Resolution of D-loop Structures through Holliday Junction Intermediates / HDR through Single Strand Annealing (SSA) / negative regulation of B cell proliferation / TP53 Regulates Transcription of Caspase Activators and Caspases / cellular response to stress / mitotic spindle assembly checkpoint signaling / positive regulation of double-strand break repair / response to ionizing radiation / Impaired BRCA2 binding to RAD51 / mitotic G2 DNA damage checkpoint signaling / TP53 Regulates Transcription of Genes Involved in Cytochrome C Release / peroxisomal matrix / telomere maintenance in response to DNA damage / positive regulation of telomere maintenance / Presynaptic phase of homologous DNA pairing and strand exchange / replicative senescence / neuroblast proliferation / Regulation of HSF1-mediated heat shock response / protein K63-linked ubiquitination / somitogenesis / ovarian follicle development / regulation of cellular response to heat / positive regulation of double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / signal transduction in response to DNA damage / cellular response to retinoic acid / positive regulation of telomere maintenance via telomerase / negative regulation of TORC1 signaling / positive regulation of cell adhesion / intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway / telomere maintenance / Pexophagy / thymus development / DNA damage checkpoint signaling / regulation of signal transduction by p53 class mediator / replication fork / protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity / determination of adult lifespan / post-embryonic development / meiotic cell cycle / TP53 Regulates Transcription of DNA Repair Genes / cellular response to reactive oxygen species / DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator / Stabilization of p53 / Nonhomologous End-Joining (NHEJ) / Autodegradation of the E3 ubiquitin ligase COP1 Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
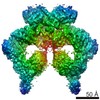
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.53 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Warren, C. / Pavletich, N.P. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2items United States, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Elife / Year: 2022 Journal: Elife / Year: 2022Title: Structure of the human ATM kinase and mechanism of Nbs1 binding. Authors: Christopher Warren / Nikola P Pavletich /  Abstract: DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) can lead to mutations, chromosomal rearrangements, genome instability, and cancer. Central to the sensing of DSBs is the ATM (Ataxia-telangiectasia mutated) kinase, ...DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) can lead to mutations, chromosomal rearrangements, genome instability, and cancer. Central to the sensing of DSBs is the ATM (Ataxia-telangiectasia mutated) kinase, which belongs to the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-related protein kinase (PIKK) family. In response to DSBs, ATM is activated by the MRN (Mre11-Rad50-Nbs1) protein complex through a poorly understood process that also requires double-stranded DNA. Previous studies indicate that the FxF/Y motif of Nbs1 directly binds to ATM, and is required to retain active ATM at sites of DNA damage. Here, we report the 2.5 Å resolution cryo-EM structures of human ATM and its complex with the Nbs1 FxF/Y motif. In keeping with previous structures of ATM and its yeast homolog Tel1, the dimeric human ATM kinase adopts a symmetric, butterfly-shaped structure. The conformation of the ATM kinase domain is most similar to the inactive states of other PIKKs, suggesting that activation may involve an analogous realigning of the N and C lobes along with relieving the blockage of the substrate-binding site. We also show that the Nbs1 FxF/Y motif binds to a conserved hydrophobic cleft within the Spiral domain of ATM, suggesting an allosteric mechanism of activation. We evaluate the importance of these structural findings with mutagenesis and biochemical assays. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7sid.cif.gz 7sid.cif.gz | 976.3 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7sid.ent.gz pdb7sid.ent.gz | 795.2 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7sid.json.gz 7sid.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/si/7sid https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/si/7sid ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/si/7sid ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/si/7sid | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  25141MC  7sicC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 351127.688 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ATM / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ATM / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)References: UniProt: Q13315, non-specific serine/threonine protein kinase #2: Protein/peptide | Mass: 3514.947 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Details: C-terminal 28aa of Human Nbs1 / Source: (synth.)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: O60934 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: O60934#3: Chemical | #4: Chemical | Has ligand of interest | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Human ATM Dimer Bound to Nbs1 / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#2 / Source: MULTIPLE SOURCES |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 |
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.42 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: UltrAuFoil R1.2/1.3 |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 51.6 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.19.2_4158: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.53 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 224367 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller









 PDBj
PDBj