+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7plh | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
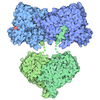
| Title | Scytonema hofmannii TnsC bound to AMPPNP and DNA | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | DNA BINDING PROTEIN / TnsC / Transposition protein / AAA+ ATPase / Tn7 / CRISPR | |||||||||
| Function / homology | P-loop containing nucleotide triphosphate hydrolases / Rossmann fold / 3-Layer(aba) Sandwich / Alpha Beta / PHOSPHOAMINOPHOSPHONIC ACID-ADENYLATE ESTER / DNA / DNA (> 10) Function and homology information Function and homology information | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Scytonema hofmannii (bacteria) Scytonema hofmannii (bacteria)synthetic construct (others) | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / helical reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.57 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Querques, I. / Jinek, M. | |||||||||
| Funding support | European Union, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2021 Journal: Nature / Year: 2021Title: Target site selection and remodelling by type V CRISPR-transposon systems. Authors: Irma Querques / Michael Schmitz / Seraina Oberli / Christelle Chanez / Martin Jinek /  Abstract: Canonical CRISPR-Cas systems provide adaptive immunity against mobile genetic elements. However, type I-F, I-B and V-K systems have been adopted by Tn7-like transposons to direct RNA-guided ...Canonical CRISPR-Cas systems provide adaptive immunity against mobile genetic elements. However, type I-F, I-B and V-K systems have been adopted by Tn7-like transposons to direct RNA-guided transposon insertion. Type V-K CRISPR-associated transposons rely on the pseudonuclease Cas12k, the transposase TnsB, the AAA+ ATPase TnsC and the zinc-finger protein TniQ, but the molecular mechanism of RNA-directed DNA transposition has remained elusive. Here we report cryo-electron microscopic structures of a Cas12k-guide RNA-target DNA complex and a DNA-bound, polymeric TnsC filament from the CRISPR-associated transposon system of the photosynthetic cyanobacterium Scytonema hofmanni. The Cas12k complex structure reveals an intricate guide RNA architecture and critical interactions mediating RNA-guided target DNA recognition. TnsC helical filament assembly is ATP-dependent and accompanied by structural remodelling of the bound DNA duplex. In vivo transposition assays corroborate key features of the structures, and biochemical experiments show that TniQ restricts TnsC polymerization, while TnsB interacts directly with TnsC filaments to trigger their disassembly upon ATP hydrolysis. Together, these results suggest that RNA-directed target selection by Cas12k primes TnsC polymerization and DNA remodelling, generating a recruitment platform for TnsB to catalyse site-specific transposon insertion. Insights from this work will inform the development of CRISPR-associated transposons as programmable site-specific gene insertion tools. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7plh.cif.gz 7plh.cif.gz | 342.6 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7plh.ent.gz pdb7plh.ent.gz | 279.8 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7plh.json.gz 7plh.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pl/7plh https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pl/7plh ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pl/7plh ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pl/7plh | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 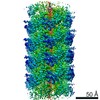 13489MC  7oxdC  7plaC  9go0C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
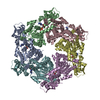
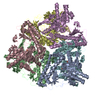
| Deposited unit | 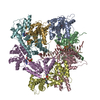
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 31444.617 Da / Num. of mol.: 7 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Scytonema hofmannii (bacteria) / Production host: Scytonema hofmannii (bacteria) / Production host:  #2: DNA chain | Mass: 6746.438 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) #3: Chemical | ChemComp-ANP / #4: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / Has ligand of interest | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: FILAMENT / 3D reconstruction method: helical reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Complex of ShTnsC with AMPPNP and dsDNA / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#2 / Source: MULTIPLE SOURCES |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 66.39 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
|---|---|
| Helical symmerty | Angular rotation/subunit: 59.72 ° / Axial rise/subunit: 6.78 Å / Axial symmetry: C1 |
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.57 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 77544 / Symmetry type: HELICAL |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj