+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7p37 | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
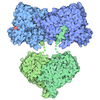
| Title | Streptomyces coelicolor ATP-loaded NrdR | ||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components | Transcriptional repressor NrdR | ||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | DNA BINDING PROTEIN / Repressor / Dodecamer / ATP-binding | ||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationdouble-stranded DNA binding / negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription / zinc ion binding / ATP binding Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species | Streptomyces coelicolor A3 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.96 Å | ||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Martinez-Carranza, M. / Stenmark, P. | ||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Sweden, 5items Sweden, 5items
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022Title: A nucleotide-sensing oligomerization mechanism that controls NrdR-dependent transcription of ribonucleotide reductases. Authors: Inna Rozman Grinberg / Markel Martínez-Carranza / Ornella Bimai / Ghada Nouaïria / Saher Shahid / Daniel Lundin / Derek T Logan / Britt-Marie Sjöberg / Pål Stenmark /  Abstract: Ribonucleotide reductase (RNR) is an essential enzyme that catalyzes the synthesis of DNA building blocks in virtually all living cells. NrdR, an RNR-specific repressor, controls the transcription of ...Ribonucleotide reductase (RNR) is an essential enzyme that catalyzes the synthesis of DNA building blocks in virtually all living cells. NrdR, an RNR-specific repressor, controls the transcription of RNR genes and, often, its own, in most bacteria and some archaea. NrdR senses the concentration of nucleotides through its ATP-cone, an evolutionarily mobile domain that also regulates the enzymatic activity of many RNRs, while a Zn-ribbon domain mediates binding to NrdR boxes upstream of and overlapping the transcription start site of RNR genes. Here, we combine biochemical and cryo-EM studies of NrdR from Streptomyces coelicolor to show, at atomic resolution, how NrdR binds to DNA. The suggested mechanism involves an initial dodecamer loaded with two ATP molecules that cannot bind to DNA. When dATP concentrations increase, an octamer forms that is loaded with one molecule each of dATP and ATP per monomer. A tetramer derived from this octamer then binds to DNA and represses transcription of RNR. In many bacteria - including well-known pathogens such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis - NrdR simultaneously controls multiple RNRs and hence DNA synthesis, making it an excellent target for novel antibiotics development. | ||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7p37.cif.gz 7p37.cif.gz | 324.3 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7p37.ent.gz pdb7p37.ent.gz | 268.4 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7p37.json.gz 7p37.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  7p37_validation.pdf.gz 7p37_validation.pdf.gz | 2.7 MB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  7p37_full_validation.pdf.gz 7p37_full_validation.pdf.gz | 2.7 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  7p37_validation.xml.gz 7p37_validation.xml.gz | 66.7 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  7p37_validation.cif.gz 7p37_validation.cif.gz | 84.1 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/p3/7p37 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/p3/7p37 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/p3/7p37 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/p3/7p37 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  13178MC  7p3fC  7p3qC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 21271.629 Da / Num. of mol.: 12 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) (bacteria) Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) (bacteria)Production host:  #2: Chemical | ChemComp-ATP / #3: Chemical | ChemComp-ZN / Has ligand of interest | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Homododecameric assembly of ATP-loaded NrdR. / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.247 MDa / Experimental value: YES |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) (bacteria) Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) (bacteria) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 |
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.4 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 298 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: TFS KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON III (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 2 / Num. of real images: 6317 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: D3 (2x3 fold dihedral) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.96 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 922502 / Num. of class averages: 1 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj