[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
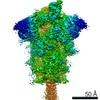
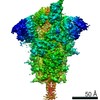
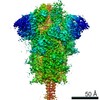
Yorodumi- PDB-7lyn: South African (B.1.351) SARS-CoV-2 spike protein variant (S-GSAS-... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7lyn | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
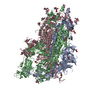
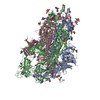
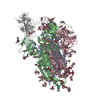
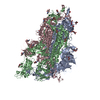
| Title | South African (B.1.351) SARS-CoV-2 spike protein variant (S-GSAS-B.1.351) in the 1-RBD-up conformation | |||||||||
 Components Components | Spike glycoprotein | |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | VIRAL PROTEIN / SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Trimer | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationMaturation of spike protein / viral translation / Translation of Structural Proteins / Virion Assembly and Release / host cell surface / host extracellular space / suppression by virus of host tetherin activity / Induction of Cell-Cell Fusion / structural constituent of virion / entry receptor-mediated virion attachment to host cell ...Maturation of spike protein / viral translation / Translation of Structural Proteins / Virion Assembly and Release / host cell surface / host extracellular space / suppression by virus of host tetherin activity / Induction of Cell-Cell Fusion / structural constituent of virion / entry receptor-mediated virion attachment to host cell / host cell endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane / receptor-mediated endocytosis of virus by host cell / membrane fusion / Attachment and Entry / positive regulation of viral entry into host cell / receptor-mediated virion attachment to host cell / receptor ligand activity / host cell surface receptor binding / symbiont-mediated suppression of host innate immune response / fusion of virus membrane with host plasma membrane / fusion of virus membrane with host endosome membrane / viral envelope / virion attachment to host cell / SARS-CoV-2 activates/modulates innate and adaptive immune responses / host cell plasma membrane / virion membrane / identical protein binding / membrane / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.32 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Gobeil, S. / Acharya, P. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Science / Year: 2021 Journal: Science / Year: 2021Title: Effect of natural mutations of SARS-CoV-2 on spike structure, conformation, and antigenicity. Authors: Sophie M-C Gobeil / Katarzyna Janowska / Shana McDowell / Katayoun Mansouri / Robert Parks / Victoria Stalls / Megan F Kopp / Kartik Manne / Dapeng Li / Kevin Wiehe / Kevin O Saunders / ...Authors: Sophie M-C Gobeil / Katarzyna Janowska / Shana McDowell / Katayoun Mansouri / Robert Parks / Victoria Stalls / Megan F Kopp / Kartik Manne / Dapeng Li / Kevin Wiehe / Kevin O Saunders / Robert J Edwards / Bette Korber / Barton F Haynes / Rory Henderson / Priyamvada Acharya /  Abstract: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) variants with multiple spike mutations enable increased transmission and antibody resistance. We combined cryo-electron microscopy (cryo- ...Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) variants with multiple spike mutations enable increased transmission and antibody resistance. We combined cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM), binding, and computational analyses to study variant spikes, including one that was involved in transmission between minks and humans, and others that originated and spread in human populations. All variants showed increased angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor binding and increased propensity for receptor binding domain (RBD)-up states. While adaptation to mink resulted in spike destabilization, the B.1.1.7 (UK) spike balanced stabilizing and destabilizing mutations. A local destabilizing effect of the RBD E484K mutation was implicated in resistance of the B.1.1.28/P.1 (Brazil) and B.1.351 (South Africa) variants to neutralizing antibodies. Our studies revealed allosteric effects of mutations and mechanistic differences that drive either interspecies transmission or escape from antibody neutralization. #1:  Journal: bioRxiv / Year: 2021 Journal: bioRxiv / Year: 2021Title: Effect of natural mutations of SARS-CoV-2 on spike structure, conformation and antigenicity. Authors: Sophie M-C Gobeil / Katarzyna Janowska / Shana McDowell / Katayoun Mansouri / Robert Parks / Victoria Stalls / Megan F Kopp / Kartik Manne / Kevin Saunders / Robert J Edwards / Barton F ...Authors: Sophie M-C Gobeil / Katarzyna Janowska / Shana McDowell / Katayoun Mansouri / Robert Parks / Victoria Stalls / Megan F Kopp / Kartik Manne / Kevin Saunders / Robert J Edwards / Barton F Haynes / Rory C Henderson / Priyamvada Acharya Abstract: New SARS-CoV-2 variants that have accumulated multiple mutations in the spike (S) glycoprotein enable increased transmission and resistance to neutralizing antibodies. Here, we study the antigenic ...New SARS-CoV-2 variants that have accumulated multiple mutations in the spike (S) glycoprotein enable increased transmission and resistance to neutralizing antibodies. Here, we study the antigenic and structural impacts of the S protein mutations from four variants, one that was involved in transmission between minks and humans, and three that rapidly spread in human populations and originated in the United Kingdom, Brazil or South Africa. All variants either retained or improved binding to the ACE2 receptor. The B.1.1.7 (UK) and B.1.1.28 (Brazil) spike variants showed reduced binding to neutralizing NTD and RBD antibodies, respectively, while the B.1.351 (SA) variant showed reduced binding to both NTD- and RBD-directed antibodies. Cryo-EM structural analyses revealed allosteric effects of the mutations on spike conformations and revealed mechanistic differences that either drive inter-species transmission or promotes viral escape from dominant neutralizing epitopes. HIGHLIGHTS: Cryo-EM structures reveal changes in SARS-CoV-2 S protein during inter-species transmission or immune evasion.Adaptation to mink resulted in increased ACE2 binding and spike ...HIGHLIGHTS: Cryo-EM structures reveal changes in SARS-CoV-2 S protein during inter-species transmission or immune evasion.Adaptation to mink resulted in increased ACE2 binding and spike destabilization.B.1.1.7 S mutations reveal an intricate balance of stabilizing and destabilizing effects that impact receptor and antibody binding.E484K mutation in B.1.351 and B.1.1.28 S proteins drives immune evasion by altering RBD conformation.S protein uses different mechanisms to converge upon similar solutions for altering RBD up/down positioning. #2:  Journal: Science / Year: 2021 Journal: Science / Year: 2021Title: Effect of natural mutations of SARS-CoV-2 on spike structure, conformation, and antigenicity. Authors: Sophie M-C Gobeil / Katarzyna Janowska / Shana McDowell / Katayoun Mansouri / Robert Parks / Victoria Stalls / Megan F Kopp / Kartik Manne / Dapeng Li / Kevin Wiehe / Kevin O Saunders / ...Authors: Sophie M-C Gobeil / Katarzyna Janowska / Shana McDowell / Katayoun Mansouri / Robert Parks / Victoria Stalls / Megan F Kopp / Kartik Manne / Dapeng Li / Kevin Wiehe / Kevin O Saunders / Robert J Edwards / Bette Korber / Barton F Haynes / Rory Henderson / Priyamvada Acharya /  Abstract: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) variants with multiple spike mutations enable increased transmission and antibody resistance. We combined cryo-electron microscopy (cryo- ...Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) variants with multiple spike mutations enable increased transmission and antibody resistance. We combined cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM), binding, and computational analyses to study variant spikes, including one that was involved in transmission between minks and humans, and others that originated and spread in human populations. All variants showed increased angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor binding and increased propensity for receptor binding domain (RBD)-up states. While adaptation to mink resulted in spike destabilization, the B.1.1.7 (UK) spike balanced stabilizing and destabilizing mutations. A local destabilizing effect of the RBD E484K mutation was implicated in resistance of the B.1.1.28/P.1 (Brazil) and B.1.351 (South Africa) variants to neutralizing antibodies. Our studies revealed allosteric effects of mutations and mechanistic differences that drive either interspecies transmission or escape from antibody neutralization. #3:  Journal: bioRxiv / Year: 2021 Journal: bioRxiv / Year: 2021Title: Effect of natural mutations of SARS-CoV-2 on spike structure, conformation and antigenicity. Authors: Sophie M-C Gobeil / Katarzyna Janowska / Shana McDowell / Katayoun Mansouri / Robert Parks / Victoria Stalls / Megan F Kopp / Kartik Manne / Kevin Saunders / Robert J Edwards / Barton F ...Authors: Sophie M-C Gobeil / Katarzyna Janowska / Shana McDowell / Katayoun Mansouri / Robert Parks / Victoria Stalls / Megan F Kopp / Kartik Manne / Kevin Saunders / Robert J Edwards / Barton F Haynes / Rory C Henderson / Priyamvada Acharya Abstract: New SARS-CoV-2 variants that have accumulated multiple mutations in the spike (S) glycoprotein enable increased transmission and resistance to neutralizing antibodies. Here, we study the antigenic ...New SARS-CoV-2 variants that have accumulated multiple mutations in the spike (S) glycoprotein enable increased transmission and resistance to neutralizing antibodies. Here, we study the antigenic and structural impacts of the S protein mutations from four variants, one that was involved in transmission between minks and humans, and three that rapidly spread in human populations and originated in the United Kingdom, Brazil or South Africa. All variants either retained or improved binding to the ACE2 receptor. The B.1.1.7 (UK) and B.1.1.28 (Brazil) spike variants showed reduced binding to neutralizing NTD and RBD antibodies, respectively, while the B.1.351 (SA) variant showed reduced binding to both NTD- and RBD-directed antibodies. Cryo-EM structural analyses revealed allosteric effects of the mutations on spike conformations and revealed mechanistic differences that either drive inter-species transmission or promotes viral escape from dominant neutralizing epitopes. HIGHLIGHTS: Cryo-EM structures reveal changes in SARS-CoV-2 S protein during inter-species transmission or immune evasion.Adaptation to mink resulted in increased ACE2 binding and spike ...HIGHLIGHTS: Cryo-EM structures reveal changes in SARS-CoV-2 S protein during inter-species transmission or immune evasion.Adaptation to mink resulted in increased ACE2 binding and spike destabilization.B.1.1.7 S mutations reveal an intricate balance of stabilizing and destabilizing effects that impact receptor and antibody binding.E484K mutation in B.1.351 and B.1.1.28 S proteins drives immune evasion by altering RBD conformation.S protein uses different mechanisms to converge upon similar solutions for altering RBD up/down positioning. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7lyn.cif.gz 7lyn.cif.gz | 543.2 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7lyn.ent.gz pdb7lyn.ent.gz | 435.9 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7lyn.json.gz 7lyn.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  7lyn_validation.pdf.gz 7lyn_validation.pdf.gz | 891.8 KB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  7lyn_full_validation.pdf.gz 7lyn_full_validation.pdf.gz | 910.6 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  7lyn_validation.xml.gz 7lyn_validation.xml.gz | 73.7 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  7lyn_validation.cif.gz 7lyn_validation.cif.gz | 115.4 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ly/7lyn https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ly/7lyn ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ly/7lyn ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ly/7lyn | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 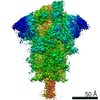 23596MC  7lwiC  7lwjC  7lwkC  7lwlC  7lwmC  7lwnC  7lwoC  7lwpC  7lwqC  7lwtC  7lwuC  7lwvC  7lwwC  7lykC  7lylC  7lymC  7lyoC  7lypC  7lyqC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 142325.469 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 Mutation: N501Y, K417N, E484K, L18F, D80A, D215G, R246I, A701V, D614G, R682G, R683S, R685S Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: S, 2 / Variant: South African (B.1.351) / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P0DTC2 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P0DTC2#2: Sugar | ChemComp-NAG / Has ligand of interest | N | Has protein modification | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: South African (B.1.351) SARS-CoV-2 spike protein variant (S-GSAS-B.1.351) Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 |
| Specimen | Conc.: 1.5 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 51.16 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.19.1_4122: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.32 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 404423 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: AB INITIO MODEL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 PDBj
PDBj