+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7l7i | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of Hsp90:FKBP51:p23 closed-state complex | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | ISOMERASE/CHAPERONE / ISOMERASE-CHAPERONE complex | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationprostaglandin-E synthase / prostaglandin-E synthase activity / prostanoid biosynthetic process / Aryl hydrocarbon receptor signalling / telomerase activity / Synthesis of Prostaglandins (PG) and Thromboxanes (TX) / telomerase holoenzyme complex / Modulation of host responses by IFN-stimulated genes / prostaglandin biosynthetic process / response to alcohol ...prostaglandin-E synthase / prostaglandin-E synthase activity / prostanoid biosynthetic process / Aryl hydrocarbon receptor signalling / telomerase activity / Synthesis of Prostaglandins (PG) and Thromboxanes (TX) / telomerase holoenzyme complex / Modulation of host responses by IFN-stimulated genes / prostaglandin biosynthetic process / response to alcohol / sperm mitochondrial sheath / sulfonylurea receptor binding / dATP binding / CTP binding / positive regulation of protein polymerization / Scavenging by Class F Receptors / vRNP Assembly / UTP binding / chaperone-mediated autophagy / sperm plasma membrane / FK506 binding / Respiratory syncytial virus genome replication / Rho GDP-dissociation inhibitor binding / telomerase holoenzyme complex assembly / mitochondrial transport / Drug-mediated inhibition of ERBB2 signaling / Resistance of ERBB2 KD mutants to trastuzumab / Resistance of ERBB2 KD mutants to sapitinib / Resistance of ERBB2 KD mutants to tesevatinib / Resistance of ERBB2 KD mutants to neratinib / Resistance of ERBB2 KD mutants to osimertinib / Resistance of ERBB2 KD mutants to afatinib / Resistance of ERBB2 KD mutants to AEE788 / Resistance of ERBB2 KD mutants to lapatinib / Drug resistance in ERBB2 TMD/JMD mutants / : / Uptake and function of diphtheria toxin / protein import into mitochondrial matrix / TPR domain binding / dendritic growth cone / : / PIWI-interacting RNA (piRNA) biogenesis / Assembly and release of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) virions / non-chaperonin molecular chaperone ATPase / protein unfolding / Sema3A PAK dependent Axon repulsion / regulation of protein ubiquitination / positive regulation of cell size / HSF1-dependent transactivation / protein folding chaperone complex / enzyme-substrate adaptor activity / response to unfolded protein / regulation of protein-containing complex assembly / HSF1 activation / Attenuation phase / chaperone-mediated protein complex assembly / neurofibrillary tangle assembly / RHOBTB2 GTPase cycle / regulation of postsynaptic membrane neurotransmitter receptor levels / telomere maintenance via telomerase / axonal growth cone / skeletal muscle contraction / positive regulation of lamellipodium assembly / MECP2 regulates neuronal receptors and channels / nitric oxide metabolic process / positive regulation of defense response to virus by host / heat shock protein binding / response to salt stress / eNOS activation / DNA polymerase binding / positive regulation of telomere maintenance via telomerase / Signaling by ERBB2 / Tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) synthesis, recycling, salvage and regulation / cardiac muscle cell apoptotic process / endocytic vesicle lumen / positive regulation of cardiac muscle contraction / Loss of Nlp from mitotic centrosomes / Loss of proteins required for interphase microtubule organization from the centrosome / Recruitment of mitotic centrosome proteins and complexes / Recruitment of NuMA to mitotic centrosomes / activation of innate immune response / Anchoring of the basal body to the plasma membrane / lysosomal lumen / ESR-mediated signaling / positive regulation of interferon-beta production / HSP90 chaperone cycle for steroid hormone receptors (SHR) in the presence of ligand / telomere maintenance / Constitutive Signaling by Overexpressed ERBB2 / protein tyrosine kinase binding / response to cold / AURKA Activation by TPX2 / nitric-oxide synthase regulator activity / VEGFR2 mediated vascular permeability / response to cocaine / peptidylprolyl isomerase / response to bacterium / peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase activity / ATP-dependent protein folding chaperone / brush border membrane / Signaling by ERBB2 TMD/JMD mutants Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.3 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Lee, K. / Thwin, A.C. / Tse, E. / Gates, S.N. / Southworth, D.R. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2items United States, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2021 Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2021Title: The structure of an Hsp90-immunophilin complex reveals cochaperone recognition of the client maturation state. Authors: Kanghyun Lee / Aye C Thwin / Cory M Nadel / Eric Tse / Stephanie N Gates / Jason E Gestwicki / Daniel R Southworth /  Abstract: The Hsp90 chaperone promotes folding and activation of hundreds of client proteins in the cell through an ATP-dependent conformational cycle guided by distinct cochaperone regulators. The FKBP51 ...The Hsp90 chaperone promotes folding and activation of hundreds of client proteins in the cell through an ATP-dependent conformational cycle guided by distinct cochaperone regulators. The FKBP51 immunophilin binds Hsp90 with its tetratricopeptide repeat (TPR) domain and catalyzes peptidyl-prolyl isomerase (PPIase) activity during folding of kinases, nuclear receptors, and tau. Here we determined the cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM) structure of the human Hsp90:FKBP51:p23 complex to 3.3 Å, which, together with mutagenesis and crosslinking analyses, reveals the basis for cochaperone binding to Hsp90 during client maturation. A helix extension in the TPR functions as a key recognition element, interacting across the Hsp90 C-terminal dimer interface presented in the closed, ATP conformation. The PPIase domain is positioned along the middle domain, adjacent to Hsp90 client binding sites, whereas a single p23 makes stabilizing interactions with the N-terminal dimer. With this architecture, FKBP51 is positioned to act on specific client residues presented during Hsp90-catalyzed remodeling. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7l7i.cif.gz 7l7i.cif.gz | 318.9 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7l7i.ent.gz pdb7l7i.ent.gz | 247.6 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7l7i.json.gz 7l7i.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/l7/7l7i https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/l7/7l7i ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/l7/7l7i ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/l7/7l7i | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 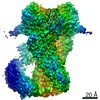 23213MC  7l7jC C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 51290.191 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: FKBP5, AIG6, FKBP51 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: FKBP5, AIG6, FKBP51 / Production host:  | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 84781.727 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: HSP90AA1, HSP90A, HSPC1, HSPCA / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: HSP90AA1, HSP90A, HSPC1, HSPCA / Production host:  #3: Protein | | Mass: 18720.395 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PTGES3, P23, TEBP / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PTGES3, P23, TEBP / Production host:  #4: Chemical | Has ligand of interest | N | |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Hsp90:FKBP51:p23 closed-state complex / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#3 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS | ||||||||||||
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM | ||||||||||||
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD | ||||||||||||
| Image recording |
|
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 576169 | ||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.3 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 121882 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller










 PDBj
PDBj