Entry Database : PDB / ID : 7khtTitle The acyl chains of phosphoinositide PIP3 alter the structure and function of nuclear receptor Steroidogenic Factor-1 (SF-1) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha peptide Steroidogenic factor 1 Keywords / / / / / / / / Function / homology Function Domain/homology Component
/ / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / Biological species Homo sapiens (human)Method / / / Resolution : 2.504 Å Authors Blind, R.D. Funding support Organization Grant number Country American Cancer Society RSG-17-063-01 National Institutes of Health/National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIH/NIGMS) GM138873 National Institutes of Health/National Cancer Institute (NIH/NCI) CA243036 National Institutes of Health/National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Disease (NIH/NIDDK)
Journal : J.Lipid Res. / Year : 2021Title : The acyl chains of phosphoinositide PIP3 alter the structure and function of nuclear receptor steroidogenic factor-1.Authors : Bryant, J.M. / Malabanan, M.M. / Vanderloop, B.H. / Nichols, C.M. / Haratipour, Z. / Poon, K.T. / Sherrod, S.D. / McLean, J.A. / Blind, R.D. History Deposition Oct 22, 2020 Deposition site / Processing site Revision 1.0 May 19, 2021 Provider / Type Revision 1.1 Jun 9, 2021 Group / Category / Item / _citation.titleRevision 1.2 Oct 18, 2023 Group / Database references / Refinement descriptionCategory chem_comp_atom / chem_comp_bond ... chem_comp_atom / chem_comp_bond / database_2 / pdbx_initial_refinement_model Item / _database_2.pdbx_database_accession
Show all Show less
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi Open data
Open data Basic information
Basic information Components
Components Keywords
Keywords Function and homology information
Function and homology information Homo sapiens (human)
Homo sapiens (human) X-RAY DIFFRACTION /
X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON /
SYNCHROTRON /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 2.504 Å
MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 2.504 Å  Authors
Authors United States, 4items
United States, 4items  Citation
Citation Journal: J.Lipid Res. / Year: 2021
Journal: J.Lipid Res. / Year: 2021 Structure visualization
Structure visualization Molmil
Molmil Jmol/JSmol
Jmol/JSmol Downloads & links
Downloads & links Download
Download 7kht.cif.gz
7kht.cif.gz PDBx/mmCIF format
PDBx/mmCIF format pdb7kht.ent.gz
pdb7kht.ent.gz PDB format
PDB format 7kht.json.gz
7kht.json.gz PDBx/mmJSON format
PDBx/mmJSON format Other downloads
Other downloads 7kht_validation.pdf.gz
7kht_validation.pdf.gz wwPDB validaton report
wwPDB validaton report 7kht_full_validation.pdf.gz
7kht_full_validation.pdf.gz 7kht_validation.xml.gz
7kht_validation.xml.gz 7kht_validation.cif.gz
7kht_validation.cif.gz https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/kh/7kht
https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/kh/7kht ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/kh/7kht
ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/kh/7kht
 Links
Links Assembly
Assembly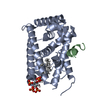
 Components
Components Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: NR5A1, AD4BP, FTZF1, SF1 / Production host:
Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: NR5A1, AD4BP, FTZF1, SF1 / Production host: 
 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9UBK2
Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9UBK2 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1
X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1  Sample preparation
Sample preparation SYNCHROTRON / Site:
SYNCHROTRON / Site:  APS
APS  / Beamline: 21-ID-F / Wavelength: 0.97857 Å
/ Beamline: 21-ID-F / Wavelength: 0.97857 Å Processing
Processing MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT
MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



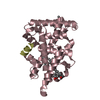



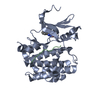



 PDBj
PDBj