+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6z1u | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
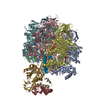
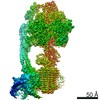
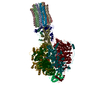
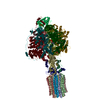
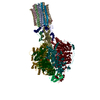
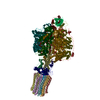
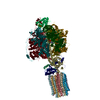
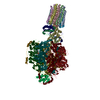
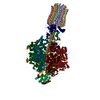
| Title | bovine ATP synthase F1c8-peripheral stalk domain, state 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | HYDROLASE / ATP synthase / mitochondria / mammalian / complex | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnegative regulation of mitochondrial ATP synthesis coupled proton transport / angiostatin binding / Formation of ATP by chemiosmotic coupling / Cristae formation / negative regulation of hydrolase activity / ATPase inhibitor activity / mitochondrial proton-transporting ATP synthase complex assembly / mitochondrial envelope / heme biosynthetic process / Mitochondrial protein degradation ...negative regulation of mitochondrial ATP synthesis coupled proton transport / angiostatin binding / Formation of ATP by chemiosmotic coupling / Cristae formation / negative regulation of hydrolase activity / ATPase inhibitor activity / mitochondrial proton-transporting ATP synthase complex assembly / mitochondrial envelope / heme biosynthetic process / Mitochondrial protein degradation / negative regulation of endothelial cell proliferation / proton transmembrane transporter activity / proton motive force-driven ATP synthesis / proton-transporting two-sector ATPase complex, proton-transporting domain / proton motive force-driven mitochondrial ATP synthesis / H+-transporting two-sector ATPase / proton-transporting ATP synthase complex / proton-transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism / proton transmembrane transport / aerobic respiration / erythrocyte differentiation / ADP binding / mitochondrial membrane / ATPase binding / protein homotetramerization / calmodulin binding / mitochondrial inner membrane / lipid binding / structural molecule activity / cell surface / protein homodimerization activity / ATP hydrolysis activity / protein-containing complex / mitochondrion / ATP binding / identical protein binding / plasma membrane / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.47 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Spikes, T. / Montgomery, M.G. / Walker, J.E. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 2items United Kingdom, 2items
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2020 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2020Title: Structure of the dimeric ATP synthase from bovine mitochondria. Authors: Tobias E Spikes / Martin G Montgomery / John E Walker /  Abstract: The structure of the dimeric ATP synthase from bovine mitochondria determined in three rotational states by electron cryo-microscopy provides evidence that the proton uptake from the mitochondrial ...The structure of the dimeric ATP synthase from bovine mitochondria determined in three rotational states by electron cryo-microscopy provides evidence that the proton uptake from the mitochondrial matrix via the proton inlet half channel proceeds via a Grotthus mechanism, and a similar mechanism may operate in the exit half channel. The structure has given information about the architecture and mechanical constitution and properties of the peripheral stalk, part of the membrane extrinsic region of the stator, and how the action of the peripheral stalk damps the side-to-side rocking motions that occur in the enzyme complex during the catalytic cycle. It also describes wedge structures in the membrane domains of each monomer, where the skeleton of each wedge is provided by three α-helices in the membrane domains of the b-subunit to which the supernumerary subunits e, f, and g and the membrane domain of subunit A6L are bound. Protein voids in the wedge are filled by three specifically bound cardiolipin molecules and two other phospholipids. The external surfaces of the wedges link the monomeric complexes together into the dimeric structures and provide a pivot to allow the monomer-monomer interfaces to change during catalysis and to accommodate other changes not related directly to catalysis in the monomer-monomer interface that occur in mitochondrial cristae. The structure of the bovine dimer also demonstrates that the structures of dimeric ATP synthases in a tetrameric porcine enzyme have been seriously misinterpreted in the membrane domains. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6z1u.cif.gz 6z1u.cif.gz | 1.3 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6z1u.ent.gz pdb6z1u.ent.gz | 1.1 MB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6z1u.json.gz 6z1u.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/z1/6z1u https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/z1/6z1u ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/z1/6z1u ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/z1/6z1u | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
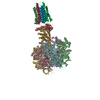
| Related structure data |  11040MC 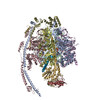 6yy0C  6z1rC  6zbbC  6zg7C  6zg8C  6zikC  6ziqC  6zitC  6ziuC  6zmrC 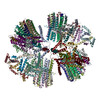 6znaC  6zpoC  6zqmC  6zqnC C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 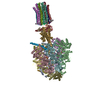
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-ATP synthase subunit ... , 6 types, 10 molecules ABCDEFGHIS
| #1: Protein | Mass: 55302.191 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Details: Chain ABC res 481: Residue 481 in chains A, B, and C in this structure should be GLY. There is no density to support a SER and negative density appears if you try SER. We have seen SER in ...Details: Chain ABC res 481: Residue 481 in chains A, B, and C in this structure should be GLY. There is no density to support a SER and negative density appears if you try SER. We have seen SER in some of our previous structures of bovine F1-ATPAse. We have used the following REMARK in other PDB files: REMARK 999 REFERENCE FOR THE ALPHA SUBUNIT J. E. WALKER, S. J. REMARK 999 POWELL,O. VINAS AND M. J. RUNSWICK, BIOCHEMISTRY,VOL 28,PP REMARK 999 4702-4708, 1989. REMARK 999 REMARK 999 SER 481 GLY IN CHAINS A, B AND C REMARK 999 WAS IDENTIFIED AS A GLY FROM THE PROTEIN REMARK 999 SEQUENCE. IN THE CDNA SEQUENCE, THE CODON FOR THIS REMARK 999 RESIDUE WAS AGC SER IN THREE CLONES WHILE IN TWO REMARK 999 OTHERS IT WAS GGC GLY. THE DIFFERENCE WAS THOUGHT TO REMARK 999 BE DUE TO A MUTATION OCCURRING DURING EITHER PROPAGATION REMARK 999 OF THE CLONES IN THE LIBRARY OR SUBCLONING INTO M13 REMARK 999 VECTORS. THE ELECTRON DENSITY SUGGESTS A GLY IN REMARK 999 THIS POSITION. Source: (natural)  #2: Protein | Mass: 51757.836 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  References: UniProt: P00829, H+-transporting two-sector ATPase #3: Protein | | Mass: 30300.760 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #4: Protein | | Mass: 15074.813 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #5: Protein/peptide | | Mass: 5662.693 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #8: Protein | | Mass: 20959.777 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|
-Protein , 2 types, 2 molecules Jh
| #6: Protein | Mass: 7462.098 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Details: ATP synthase inhibitor protein IF1 residues 1-60 with a 6HIS affinity tag Source: (gene. exp.)   |
|---|---|
| #10: Protein | Mass: 8971.079 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
-ATP synthase F(0) complex subunit ... , 2 types, 9 molecules KLMNPQROb
| #7: Protein | Mass: 7653.034 Da / Num. of mol.: 8 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Details: Trimethyl-lysine at position 43 / Source: (natural)  #9: Protein | | Mass: 24702.709 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 4 types, 28 molecules 






| #11: Chemical | | #12: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / #13: Chemical | #14: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | N |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 4.5 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES / Details: Nickel affinity purified filled by gel filtration | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 294 K Details: The sample was allowed to penetrate through the holey support and to distribute to both sides of the grid surface for ca. 15 sec. Then the grids were blotted with filter paper for 8-10 sec before blotting. |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 12 sec. / Electron dose: 4.6 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 QUANTUM (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C2 (2 fold cyclic) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.47 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 61458 / Symmetry type: POINT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT / Space: REAL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | 3D fitting-ID: 1 / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Cross valid method: NONE Stereochemistry target values: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 53.9 Å2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller











 PDBj
PDBj