[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-6z1f: CryoEM structure of Rubisco Activase with its substrate Rubisco f... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6z1f | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
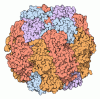
| Title | CryoEM structure of Rubisco Activase with its substrate Rubisco from Nostoc sp. (strain PCC7120) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | CHAPERONE / AAA+ / beta barrel | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationphotorespiration / carboxysome / ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase / ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase activity / reductive pentose-phosphate cycle / monooxygenase activity / magnesium ion binding / ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP binding Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Nostoc sp. (bacteria) Nostoc sp. (bacteria) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.86 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Wang, H. / Bracher, A. / Flecken, M. / Popilka, L. / Hartl, F.U. / Hayer-Hartl, M. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell / Year: 2020 Journal: Cell / Year: 2020Title: Dual Functions of a Rubisco Activase in Metabolic Repair and Recruitment to Carboxysomes. Authors: Mirkko Flecken / Huping Wang / Leonhard Popilka / F Ulrich Hartl / Andreas Bracher / Manajit Hayer-Hartl /  Abstract: Rubisco, the key enzyme of CO fixation in photosynthesis, is prone to inactivation by inhibitory sugar phosphates. Inhibited Rubisco undergoes conformational repair by the hexameric AAA+ chaperone ...Rubisco, the key enzyme of CO fixation in photosynthesis, is prone to inactivation by inhibitory sugar phosphates. Inhibited Rubisco undergoes conformational repair by the hexameric AAA+ chaperone Rubisco activase (Rca) in a process that is not well understood. Here, we performed a structural and mechanistic analysis of cyanobacterial Rca, a close homolog of plant Rca. In the Rca:Rubisco complex, Rca is positioned over the Rubisco catalytic site under repair and pulls the N-terminal tail of the large Rubisco subunit (RbcL) into the hexamer pore. Simultaneous displacement of the C terminus of the adjacent RbcL opens the catalytic site for inhibitor release. An alternative interaction of Rca with Rubisco is mediated by C-terminal domains that resemble the small Rubisco subunit. These domains, together with the N-terminal AAA+ hexamer, ensure that Rca is packaged with Rubisco into carboxysomes. The cyanobacterial Rca is a dual-purpose protein with functions in Rubisco repair and carboxysome organization. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6z1f.cif.gz 6z1f.cif.gz | 1.2 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6z1f.ent.gz pdb6z1f.ent.gz | 989.2 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6z1f.json.gz 6z1f.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/z1/6z1f https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/z1/6z1f ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/z1/6z1f ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/z1/6z1f | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  11028MC  6hasC  6z1dC  6z1eC  6z1gC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 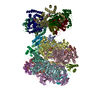
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase ... , 2 types, 16 molecules ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOP
| #2: Protein | Mass: 53155.125 Da / Num. of mol.: 8 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Nostoc sp. (strain PCC 7120 / SAG 25.82 / UTEX 2576) (bacteria) Nostoc sp. (strain PCC 7120 / SAG 25.82 / UTEX 2576) (bacteria)Gene: cbbL, rbc, rbcA, rbcL, alr1524 / Plasmid: pET11a-NosGroSEL-H6ubi-NosLS / Cell line (production host): STAR / Production host:  References: UniProt: P00879, ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase #3: Protein | Mass: 12840.725 Da / Num. of mol.: 8 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Nostoc sp. (strain PCC 7120 / SAG 25.82 / UTEX 2576) (bacteria) Nostoc sp. (strain PCC 7120 / SAG 25.82 / UTEX 2576) (bacteria)Gene: cbbS, rbcS, alr1526 / Plasmid: pET11a-NosGroSEL-H6ubi-NosLS / Cell line (production host): STAR / Production host:  References: UniProt: P06514, ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase |
|---|
-Protein / Sugars , 2 types, 13 molecules 123456

| #1: Protein | Mass: 32773.316 Da / Num. of mol.: 6 / Fragment: AAA+ domain Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Nostoc sp. (strain PCC 7120 / SAG 25.82 / UTEX 2576) (bacteria) Nostoc sp. (strain PCC 7120 / SAG 25.82 / UTEX 2576) (bacteria)Gene: rca, alr1533 / Plasmid: pHUE / Cell line (production host): pBAD33-EcGroSEL / Production host:  #7: Sugar | ChemComp-CAP / |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 3 types, 18 molecules 




| #4: Chemical | ChemComp-ADP / | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| #5: Chemical | ChemComp-AGS / #6: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / |
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | N |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 8.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 2.2 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES Details: NosRubisco (1 uM) was incubated with NaHCO3 (10 mM) at 298 K for 10 min followed by addition of CABP (8 uM). CABP-inhibited NosRubisco (0.5 uM) was then incubated with NosRcaDC (10 uM) in ...Details: NosRubisco (1 uM) was incubated with NaHCO3 (10 mM) at 298 K for 10 min followed by addition of CABP (8 uM). CABP-inhibited NosRubisco (0.5 uM) was then incubated with NosRcaDC (10 uM) in the presence of ATP (2 mM) for 10 s, followed by the addition of ATP-gammaS (2 mM), and incubated at 298 K for another 10 min before preparing the cryo-grids. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R2/1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 90 % / Chamber temperature: 298 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 2.8 sec. / Electron dose: 60 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 9042 / Details: 31 frames per image |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 519151 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.86 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 21149 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: OTHER / Space: RECIPROCAL |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 PDBj
PDBj