+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6vm1 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
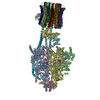
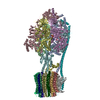
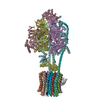
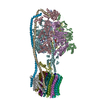
| Title | Chloroplast ATP synthase (C3, CF1FO) | ||||||
 Components Components | (ATP synthase ...) x 9 | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | PHOTOSYNTHESIS/TRANSLOCASE / CF1FO / ATP synthase / PHOTOSYNTHESIS / PHOTOSYNTHESIS-TRANSLOCASE complex | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationphotosynthetic electron transport in photosystem I / photosynthetic electron transport in photosystem II / chloroplast thylakoid membrane / proton-transporting ATP synthase complex / proton motive force-driven ATP synthesis / : / proton motive force-driven mitochondrial ATP synthesis / : / H+-transporting two-sector ATPase / proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism ...photosynthetic electron transport in photosystem I / photosynthetic electron transport in photosystem II / chloroplast thylakoid membrane / proton-transporting ATP synthase complex / proton motive force-driven ATP synthesis / : / proton motive force-driven mitochondrial ATP synthesis / : / H+-transporting two-sector ATPase / proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism / proton-transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism / ADP binding / lipid binding / ATP hydrolysis activity / mitochondrion / ATP binding / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Spinacia oleracea (spinach) Spinacia oleracea (spinach) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 7.9 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Yang, J.-H. / Williams, D. / Kandiah, E. / Fromme, P. / Chiu, P.-L. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Commun Biol / Year: 2020 Journal: Commun Biol / Year: 2020Title: Structural basis of redox modulation on chloroplast ATP synthase. Authors: Jay-How Yang / Dewight Williams / Eaazhisai Kandiah / Petra Fromme / Po-Lin Chiu /   Abstract: In higher plants, chloroplast ATP synthase has a unique redox switch on its γ subunit that modulates enzyme activity to limit ATP hydrolysis at night. To understand the molecular details of the ...In higher plants, chloroplast ATP synthase has a unique redox switch on its γ subunit that modulates enzyme activity to limit ATP hydrolysis at night. To understand the molecular details of the redox modulation, we used single-particle cryo-EM to determine the structures of spinach chloroplast ATP synthase in both reduced and oxidized states. The disulfide linkage of the oxidized γ subunit introduces a torsional constraint to stabilize the two β hairpin structures. Once reduced, free cysteines alleviate this constraint, resulting in a concerted motion of the enzyme complex and a smooth transition between rotary states to facilitate the ATP synthesis. We added an uncompetitive inhibitor, tentoxin, in the reduced sample to limit the flexibility of the enzyme and obtained high-resolution details. Our cryo-EM structures provide mechanistic insight into the redox modulation of the energy regulation activity of chloroplast ATP synthase. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6vm1.cif.gz 6vm1.cif.gz | 700.3 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6vm1.ent.gz pdb6vm1.ent.gz | 497.3 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6vm1.json.gz 6vm1.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vm/6vm1 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vm/6vm1 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vm/6vm1 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vm/6vm1 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  21235MC  6vm4C  6vmbC  6vmdC  6vmgC  6vofC  6vogC  6vohC  6voiC 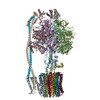 6vojC  6vokC  6volC  6vomC  6vonC  6vooC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 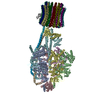
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-ATP synthase ... , 9 types, 26 molecules ABCDEFIJadegRQPONMZYXWVUTS
| #1: Protein | Mass: 55505.199 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Spinacia oleracea (spinach) Spinacia oleracea (spinach)References: UniProt: P06450, H+-transporting two-sector ATPase #2: Protein | Mass: 53797.367 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Spinacia oleracea (spinach) Spinacia oleracea (spinach)References: UniProt: P00825, H+-transporting two-sector ATPase #3: Protein | | Mass: 21013.904 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Spinacia oleracea (spinach) / References: UniProt: P06453 Spinacia oleracea (spinach) / References: UniProt: P06453#4: Protein | | Mass: 24487.596 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Spinacia oleracea (spinach) / References: UniProt: P31853 Spinacia oleracea (spinach) / References: UniProt: P31853#5: Protein | | Mass: 27102.680 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Spinacia oleracea (spinach) / References: UniProt: P06451 Spinacia oleracea (spinach) / References: UniProt: P06451#6: Protein | | Mass: 27708.582 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Spinacia oleracea (spinach) / References: UniProt: P11402 Spinacia oleracea (spinach) / References: UniProt: P11402#7: Protein | | Mass: 14715.707 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Spinacia oleracea (spinach) / References: UniProt: P00833 Spinacia oleracea (spinach) / References: UniProt: P00833#8: Protein | | Mass: 40119.066 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Spinacia oleracea (spinach) / References: UniProt: P05435 Spinacia oleracea (spinach) / References: UniProt: P05435#9: Protein | Mass: 7977.366 Da / Num. of mol.: 14 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Spinacia oleracea (spinach) / References: UniProt: P69447 Spinacia oleracea (spinach) / References: UniProt: P69447 |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Chloroplast ATP synthase / Type: COMPLEX / Details: Control rotary state 3 / Entity ID: all / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.59435 MDa / Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Spinacia oleracea (spinach) / Tissue: Leaves Spinacia oleracea (spinach) / Tissue: Leaves |
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 22500 X / Calibrated magnification: 48077 X / Nominal defocus max: -4000 nm / Nominal defocus min: -1500 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 70 µm / Alignment procedure: BASIC |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 43.5 e/Å2 / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 7.9 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 13947 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: BACKBONE TRACE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Cross valid method: NONE Stereochemistry target values: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 286 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller

















 PDBj
PDBj


