+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6tf9 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
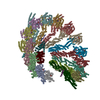
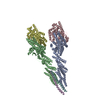
| Title | Structure of the vertebrate gamma-Tubulin Ring Complex | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | CELL CYCLE / gamma-Tubulin Ring Complex / microtubule nucleation | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationmicrotubule minus-end binding / microtubule nucleator activity / polar microtubule / gamma-tubulin complex / gamma-tubulin ring complex / mitotic spindle microtubule / meiotic spindle organization / microtubule nucleation / dense body / gamma-tubulin binding ...microtubule minus-end binding / microtubule nucleator activity / polar microtubule / gamma-tubulin complex / gamma-tubulin ring complex / mitotic spindle microtubule / meiotic spindle organization / microtubule nucleation / dense body / gamma-tubulin binding / mitotic sister chromatid segregation / spindle assembly / cytoplasmic microtubule organization / tubulin binding / mitotic spindle organization / meiotic cell cycle / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / spindle / spindle pole / mitotic cell cycle / actin cytoskeleton / microtubule / cytoskeleton / hydrolase activity / focal adhesion / centrosome / GTP binding / ATP binding / nucleus / plasma membrane / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species | |||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.8 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Zupa, E. / Pfeffer, S. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2020 Journal: Nature / Year: 2020Title: Insights into the assembly and activation of the microtubule nucleator γ-TuRC. Authors: Peng Liu / Erik Zupa / Annett Neuner / Anna Böhler / Justus Loerke / Dirk Flemming / Thomas Ruppert / Till Rudack / Christoph Peter / Christian Spahn / Oliver J Gruss / Stefan Pfeffer / Elmar Schiebel /  Abstract: Microtubules are dynamic polymers of α- and β-tubulin and have crucial roles in cell signalling, cell migration, intracellular transport and chromosome segregation. They assemble de novo from αβ- ...Microtubules are dynamic polymers of α- and β-tubulin and have crucial roles in cell signalling, cell migration, intracellular transport and chromosome segregation. They assemble de novo from αβ-tubulin dimers in an essential process termed microtubule nucleation. Complexes that contain the protein γ-tubulin serve as structural templates for the microtubule nucleation reaction. In vertebrates, microtubules are nucleated by the 2.2-megadalton γ-tubulin ring complex (γ-TuRC), which comprises γ-tubulin, five related γ-tubulin complex proteins (GCP2-GCP6) and additional factors. GCP6 is unique among the GCP proteins because it carries an extended insertion domain of unknown function. Our understanding of microtubule formation in cells and tissues is limited by a lack of high-resolution structural information on the γ-TuRC. Here we present the cryo-electron microscopy structure of γ-TuRC from Xenopus laevis at 4.8 Å global resolution, and identify a 14-spoked arrangement of GCP proteins and γ-tubulins in a partially flexible open left-handed spiral with a uniform sequence of GCP variants. By forming specific interactions with other GCP proteins, the GCP6-specific insertion domain acts as a scaffold for the assembly of the γ-TuRC. Unexpectedly, we identify actin as a bona fide structural component of the γ-TuRC with functional relevance in microtubule nucleation. The spiral geometry of γ-TuRC is suboptimal for microtubule nucleation and a controlled conformational rearrangement of the γ-TuRC is required for its activation. Collectively, our cryo-electron microscopy reconstructions provide detailed insights into the molecular organization, assembly and activation mechanism of vertebrate γ-TuRC, and will serve as a framework for the mechanistic understanding of fundamental biological processes associated with microtubule nucleation, such as meiotic and mitotic spindle formation and centriole biogenesis. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6tf9.cif.gz 6tf9.cif.gz | 2.6 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6tf9.ent.gz pdb6tf9.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6tf9.json.gz 6tf9.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tf/6tf9 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tf/6tf9 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tf/6tf9 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tf/6tf9 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  10491MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein/peptide , 6 types, 6 molecules AP1DP1EP1FP1MP1gP1
| #1: Protein/peptide | Mass: 2079.272 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural) |
|---|---|
| #3: Protein/peptide | Mass: 2221.427 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural) |
| #4: Protein/peptide | Mass: 1652.805 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural) |
| #5: Protein/peptide | Mass: 1297.416 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural) |
| #9: Protein/peptide | Mass: 1226.338 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural) |
| #16: Protein/peptide | Mass: 1368.494 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural) |
-Belt helices ... , 4 types, 13 molecules CP1HP1IP1XP1GP1LP1NP1JP1vP1KP1OP1PP1uP1
| #2: Protein/peptide | Mass: 942.027 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural) #6: Protein/peptide | Mass: 1084.182 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural) #7: Protein/peptide | Mass: 1013.105 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural) #8: Protein/peptide | Mass: 1155.260 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural) |
|---|
-Gamma-tubulin complex ... , 4 types, 13 molecules QP1cP1dP1eP1fP1RP1YP1ZP1aP1bP1UP1VP1WP1
| #10: Protein | Mass: 103789.352 Da / Num. of mol.: 5 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural) #11: Protein | Mass: 103468.312 Da / Num. of mol.: 5 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural) #14: Protein | | Mass: 117577.633 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural) #15: Protein | Mass: 76122.961 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural) |
|---|
-Protein , 3 types, 16 molecules SP1TP1hP1iP1kP1lP1mP1nP1oP1pP1qP1rP1sP1tP1wP1jP1
| #12: Protein | Mass: 184506.188 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| #13: Protein | Mass: 51226.719 Da / Num. of mol.: 14 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural) #17: Protein | | Mass: 41812.684 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural) |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Vertebrate gamma-Tubulin Ring Complex / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: NATURAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 2.2 MDa / Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.011 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 70 % / Chamber temperature: 295 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 42000 X / Nominal defocus max: 3500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 500 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 70 µm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 46 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 4 / Num. of real images: 9463 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 5482328 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 4.8 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 46096 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | PDB-ID: 3RIP Accession code: 3RIP / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Stereochemistry target values: CDL v1.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 PDBj
PDBj





