+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
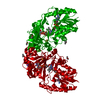
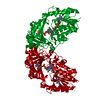
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6s8g | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of LptB2FGC in complex with AMP-PNP | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSPORT PROTEIN / lipopolysaccharide transporter / LPS / LptB2FGC / LptB / LptBFG / outer membrane / Gram-negative bacteria / ABC transporter / Inner membrane protein complex | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationTranslocases; Catalysing the translocation of carbohydrates and their derivatives; Linked to the hydrolysis of a nucleoside triphosphate / lipopolysaccharide transport / ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter complex / transmembrane transport / ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP binding / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Shigella flexneri (bacteria) Shigella flexneri (bacteria) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.5 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Tang, X.D. / Chang, S.H. / Luo, Q.H. / Zhang, Z.Y. / Qiao, W. / Xu, C.H. / Zhang, C.B. / Niu, Y. / Yang, W.X. / Wang, T. ...Tang, X.D. / Chang, S.H. / Luo, Q.H. / Zhang, Z.Y. / Qiao, W. / Xu, C.H. / Zhang, C.B. / Niu, Y. / Yang, W.X. / Wang, T. / Zhang, Z.B. / Zhu, X.F. / Dong, C.J. / Zhang, X. / Dong, H.H. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2019 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2019Title: Cryo-EM structures of lipopolysaccharide transporter LptBFGC in lipopolysaccharide or AMP-PNP-bound states reveal its transport mechanism. Authors: Xiaodi Tang / Shenghai Chang / Qinghua Luo / Zhengyu Zhang / Wen Qiao / Caihuang Xu / Changbin Zhang / Yang Niu / Wenxian Yang / Ting Wang / Zhibo Zhang / Xiaofeng Zhu / Xiawei Wei / ...Authors: Xiaodi Tang / Shenghai Chang / Qinghua Luo / Zhengyu Zhang / Wen Qiao / Caihuang Xu / Changbin Zhang / Yang Niu / Wenxian Yang / Ting Wang / Zhibo Zhang / Xiaofeng Zhu / Xiawei Wei / Changjiang Dong / Xing Zhang / Haohao Dong /   Abstract: Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) of Gram-negative bacteria are critical for the defence against cytotoxic substances and must be transported from the inner membrane (IM) to the outer membrane (OM) through ...Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) of Gram-negative bacteria are critical for the defence against cytotoxic substances and must be transported from the inner membrane (IM) to the outer membrane (OM) through a bridge formed by seven membrane proteins (LptBFGCADE). The IM component LptBFG powers the process through a yet unclarified mechanism. Here we report three high-resolution cryo-EM structures of LptBFG alone and complexed with LptC (LptBFGC), trapped in either the LPS- or AMP-PNP-bound state. The structures reveal conformational changes between these states and substrate binding with or without LptC. We identify two functional transmembrane arginine-containing loops interacting with the bound AMP-PNP and elucidate allosteric communications between the domains. AMP-PNP binding induces an inward rotation and shift of the transmembrane helices of LptFG and LptC to tighten the cavity, with the closure of two lateral gates, to eventually expel LPS into the bridge. Functional assays reveal the functionality of the LptF and LptG periplasmic domains. Our findings shed light on the LPS transport mechanism. #1:  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2019 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2019Title: Cryo-EM structures of lipopolysaccharide transporter LptBFGC in lipopolysaccharide or AMP-PNP-bound states reveal its transport mechanism. Authors: Xiaodi Tang / Shenghai Chang / Qinghua Luo / Zhengyu Zhang / Wen Qiao / Caihuang Xu / Changbin Zhang / Yang Niu / Wenxian Yang / Ting Wang / Zhibo Zhang / Xiaofeng Zhu / Xiawei Wei / ...Authors: Xiaodi Tang / Shenghai Chang / Qinghua Luo / Zhengyu Zhang / Wen Qiao / Caihuang Xu / Changbin Zhang / Yang Niu / Wenxian Yang / Ting Wang / Zhibo Zhang / Xiaofeng Zhu / Xiawei Wei / Changjiang Dong / Xing Zhang / Haohao Dong /   Abstract: Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) of Gram-negative bacteria are critical for the defence against cytotoxic substances and must be transported from the inner membrane (IM) to the outer membrane (OM) through ...Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) of Gram-negative bacteria are critical for the defence against cytotoxic substances and must be transported from the inner membrane (IM) to the outer membrane (OM) through a bridge formed by seven membrane proteins (LptBFGCADE). The IM component LptBFG powers the process through a yet unclarified mechanism. Here we report three high-resolution cryo-EM structures of LptBFG alone and complexed with LptC (LptBFGC), trapped in either the LPS- or AMP-PNP-bound state. The structures reveal conformational changes between these states and substrate binding with or without LptC. We identify two functional transmembrane arginine-containing loops interacting with the bound AMP-PNP and elucidate allosteric communications between the domains. AMP-PNP binding induces an inward rotation and shift of the transmembrane helices of LptFG and LptC to tighten the cavity, with the closure of two lateral gates, to eventually expel LPS into the bridge. Functional assays reveal the functionality of the LptF and LptG periplasmic domains. Our findings shed light on the LPS transport mechanism. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6s8g.cif.gz 6s8g.cif.gz | 209.6 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6s8g.ent.gz pdb6s8g.ent.gz | 158.5 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6s8g.json.gz 6s8g.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/s8/6s8g https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/s8/6s8g ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/s8/6s8g ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/s8/6s8g | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  10121MC  6s8hC  6s8nC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 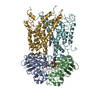
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 26837.668 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Shigella flexneri (bacteria) / Gene: SGF_01136 / Production host: Shigella flexneri (bacteria) / Gene: SGF_01136 / Production host:  #2: Protein | | Mass: 40453.520 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Shigella flexneri (bacteria) Shigella flexneri (bacteria)Gene: yjgP, CEG98_18960, CQA91_25115, DOU91_08970, NCTC9783_00310, SAMEA3710568_03583 Production host:  #3: Protein | | Mass: 39622.414 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Shigella flexneri (bacteria) Shigella flexneri (bacteria)Gene: yjgQ, S4488, CQA91_25110, NCTC9783_00309, SAMEA3710568_03584 Production host:  #4: Chemical | #5: Chemical | ChemComp-LMD / | Has ligand of interest | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: LptB2FGC / Type: COMPLEX / Details: LPS transporter LptB2FGC / Entity ID: #1-#3 / Source: RECOMBINANT | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Shigella flexneri (bacteria) Shigella flexneri (bacteria) | ||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  | ||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.8 | ||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 1 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK III / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 95 % / Chamber temperature: 298 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: DIFFRACTION |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 40 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING ONLY | ||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.5 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 149178 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller










 PDBj
PDBj