+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6pvk | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
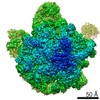
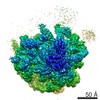
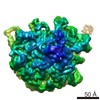
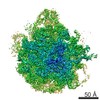
| Title | Bacterial 45SRbgA ribosomal particle class A | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | RIBOSOME / Ribosome assembly / 50S subunit / RbgA / YlqF | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpositive regulation of rRNA processing / nucleoid / rRNA processing / large ribosomal subunit / transferase activity / ribosomal large subunit assembly / large ribosomal subunit rRNA binding / cytosolic large ribosomal subunit / cytoplasmic translation / negative regulation of translation ...positive regulation of rRNA processing / nucleoid / rRNA processing / large ribosomal subunit / transferase activity / ribosomal large subunit assembly / large ribosomal subunit rRNA binding / cytosolic large ribosomal subunit / cytoplasmic translation / negative regulation of translation / rRNA binding / structural constituent of ribosome / ribosome / translation / ribonucleoprotein complex / mRNA binding / DNA binding / RNA binding / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.4 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Ortega, J. / Seffouh, A. / Jain, N. / Jahagirdar, D. / Basu, K. / Razi, A. / Ni, X. / Guarne, A. / Britton, R.A. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Canada, Canada,  United States, 2items United States, 2items
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nucleic Acids Res / Year: 2019 Journal: Nucleic Acids Res / Year: 2019Title: Structural consequences of the interaction of RbgA with a 50S ribosomal subunit assembly intermediate. Authors: Amal Seffouh / Nikhil Jain / Dushyant Jahagirdar / Kaustuv Basu / Aida Razi / Xiaodan Ni / Alba Guarné / Robert A Britton / Joaquin Ortega /   Abstract: Bacteria harbor a number GTPases that function in the assembly of the ribosome and are essential for growth. RbgA is one of these GTPases and is required for the assembly of the 50S subunit in most ...Bacteria harbor a number GTPases that function in the assembly of the ribosome and are essential for growth. RbgA is one of these GTPases and is required for the assembly of the 50S subunit in most bacteria. Homologs of this protein are also implicated in the assembly of the large subunit of the mitochondrial and eukaryotic ribosome. We present here the cryo-electron microscopy structure of RbgA bound to a Bacillus subtilis 50S subunit assembly intermediate (45SRbgA particle) that accumulates in cells upon RbgA depletion. Binding of RbgA at the P site of the immature particle stabilizes functionally important rRNA helices in the A and P-sites, prior to the completion of the maturation process of the subunit. The structure also reveals the location of the highly conserved N-terminal end of RbgA containing the catalytic residue Histidine 9. The derived model supports a mechanism of GTP hydrolysis, and it shows that upon interaction of RbgA with the 45SRbgA particle, Histidine 9 positions itself near the nucleotide potentially acting as the catalytic residue with minimal rearrangements. This structure represents the first visualization of the conformational changes induced by an assembly factor in a bacterial subunit intermediate. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6pvk.cif.gz 6pvk.cif.gz | 1.3 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6pvk.ent.gz pdb6pvk.ent.gz | 1 MB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6pvk.json.gz 6pvk.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pv/6pvk https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pv/6pvk ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pv/6pvk ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pv/6pvk | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 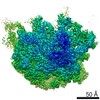 20491MC  6ppfC  6ppkC C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-50S ribosomal protein ... , 16 types, 16 molecules CDEJKLNPQRSTUbYd
| #2: Protein | Mass: 30335.125 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|---|
| #3: Protein | Mass: 22723.348 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #4: Protein | Mass: 22424.951 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #5: Protein | Mass: 16407.104 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #6: Protein | Mass: 13175.288 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #7: Protein | Mass: 15297.536 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #8: Protein | Mass: 13774.806 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #9: Protein | Mass: 13416.853 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #10: Protein | Mass: 13537.993 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #11: Protein | Mass: 11296.081 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #12: Protein | Mass: 12481.608 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #13: Protein | Mass: 10978.813 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #14: Protein | Mass: 11166.120 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #15: Protein | Mass: 6745.073 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #16: Protein | Mass: 7728.029 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #17: Protein/peptide | Mass: 5271.332 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
-RNA chain / Non-polymers , 2 types, 3 molecules A

| #18: Water | ChemComp-HOH / |
|---|---|
| #1: RNA chain | Mass: 949340.125 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
-Details
| Has protein modification | N |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: 45SRbgA ribosomal assembly intermediate Class A / Type: RIBOSOME Details: 50S subunit assembly intermediate generated by RbgA depletion in cells. Entity ID: #1-#17 / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 Details: 20mM Tris-HCl pH 7.5, 10mM MgCl2, 50mM NH4Cl, 1mM DTT |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Details: unspecified |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % Details: Cryo-EM grids were prepared by applying a 3.6 microliters volume of the diluted samples to holey carbon grids (c-flat CF-2/2-2C-T) with a freshly applied additional layer of continuous thin ...Details: Cryo-EM grids were prepared by applying a 3.6 microliters volume of the diluted samples to holey carbon grids (c-flat CF-2/2-2C-T) with a freshly applied additional layer of continuous thin carbon (5-10nm). Grids were blotted for 3 seconds and with a blot force +1 |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 1 sec. / Electron dose: 40 e/Å2 / Detector mode: INTEGRATING / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON II (4k x 4k) / Num. of real images: 8950 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.14_3260: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 1339712 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.4 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 574260 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: OTHER / Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | PDB-ID: 3J9W Accession code: 3J9W / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj






























