[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
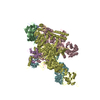
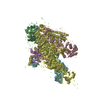
Yorodumi- PDB-6m6b: Cryo-EM structure of Thermus thermophilus Mfd in complex with RNA... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6m6b | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of Thermus thermophilus Mfd in complex with RNA polymerase and ATP-gamma-S | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSCRIPTION / RNA polymerase / DNA repair / Mfd | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationtranscription-coupled nucleotide-excision repair, DNA damage recognition / DNA-directed RNA polymerase complex / DNA helicase activity / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / ribonucleoside binding / DNA-directed RNA polymerase / DNA-directed RNA polymerase activity / damaged DNA binding / protein dimerization activity / hydrolase activity ...transcription-coupled nucleotide-excision repair, DNA damage recognition / DNA-directed RNA polymerase complex / DNA helicase activity / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / ribonucleoside binding / DNA-directed RNA polymerase / DNA-directed RNA polymerase activity / damaged DNA binding / protein dimerization activity / hydrolase activity / DNA-templated transcription / regulation of DNA-templated transcription / magnesium ion binding / DNA binding / zinc ion binding / ATP binding / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.1 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Shi, J. / Wen, A. / Feng, Y. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 1items China, 1items
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nucleic Acids Res / Year: 2020 Journal: Nucleic Acids Res / Year: 2020Title: Structural basis of Mfd-dependent transcription termination. Authors: Jing Shi / Aijia Wen / Minxing Zhao / Sha Jin / Linlin You / Yue Shi / Shuling Dong / Xiaoting Hua / Yu Zhang / Yu Feng /  Abstract: Mfd-dependent transcription termination plays an important role in transcription-coupled DNA repair, transcription-replication conflict resolution, and antimicrobial resistance development. Despite ...Mfd-dependent transcription termination plays an important role in transcription-coupled DNA repair, transcription-replication conflict resolution, and antimicrobial resistance development. Despite extensive studies, the molecular mechanism of Mfd-dependent transcription termination in bacteria remains unclear, with several long-standing puzzles. How Mfd is activated by stalled RNA polymerase (RNAP) and how activated Mfd translocates along the DNA are unknown. Here, we report the single-particle cryo-electron microscopy structures of T. thermophilus Mfd-RNAP complex with and without ATPγS. The structures reveal that Mfd undergoes profound conformational changes upon activation, contacts the RNAP β1 domain and its clamp, and pries open the RNAP clamp. These structures provide a foundation for future studies aimed at dissecting the precise mechanism of Mfd-dependent transcription termination and pave the way for rational drug design targeting Mfd for the purpose of tackling the antimicrobial resistance crisis. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6m6b.cif.gz 6m6b.cif.gz | 654.1 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6m6b.ent.gz pdb6m6b.ent.gz | 512.8 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6m6b.json.gz 6m6b.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/m6/6m6b https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/m6/6m6b ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/m6/6m6b ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/m6/6m6b | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  30118MC  6m6aC  6m6cC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit ... , 4 types, 5 molecules ABCDE
| #1: Protein | Mass: 35056.164 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)   Thermus thermophilus (strain HB8 / ATCC 27634 / DSM 579) (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus (strain HB8 / ATCC 27634 / DSM 579) (bacteria)Strain: HB8 / ATCC 27634 / DSM 579 / References: UniProt: Q5SHR6, DNA-directed RNA polymerase #2: Protein | | Mass: 125436.539 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)   Thermus thermophilus (strain HB8 / ATCC 27634 / DSM 579) (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus (strain HB8 / ATCC 27634 / DSM 579) (bacteria)Strain: HB8 / ATCC 27634 / DSM 579 / References: UniProt: Q8RQE9, DNA-directed RNA polymerase #3: Protein | | Mass: 170997.391 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)   Thermus thermophilus (strain HB8 / ATCC 27634 / DSM 579) (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus (strain HB8 / ATCC 27634 / DSM 579) (bacteria)Strain: HB8 / ATCC 27634 / DSM 579 / References: UniProt: Q8RQE8, DNA-directed RNA polymerase #4: Protein | | Mass: 11533.316 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)   Thermus thermophilus (strain HB8 / ATCC 27634 / DSM 579) (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus (strain HB8 / ATCC 27634 / DSM 579) (bacteria)Strain: HB8 / ATCC 27634 / DSM 579 / References: UniProt: Q8RQE7, DNA-directed RNA polymerase |
|---|
-Protein , 1 types, 1 molecules M
| #5: Protein | Mass: 109874.047 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Thermus thermophilus (strain HB27 / ATCC BAA-163 / DSM 7039) (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus (strain HB27 / ATCC BAA-163 / DSM 7039) (bacteria)Strain: HB27 / ATCC BAA-163 / DSM 7039 / Gene: mfd, TT_C0533 / Production host:  References: UniProt: Q72KB4, Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement |
|---|
-DNA chain , 2 types, 2 molecules TN
| #6: DNA chain | Mass: 19290.348 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)   Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) |
|---|---|
| #7: DNA chain | Mass: 19366.436 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)   Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) |
-Non-polymers , 3 types, 4 molecules 




| #8: Chemical | | #9: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / | #10: Chemical | ChemComp-AGS / | |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | N |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Thermus thermophilus transcription-repair coupling complex Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#7 / Source: MULTIPLE SOURCES |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.9 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 59 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.16_3549: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software | Name: PHENIX / Category: model refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 4.1 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 60650 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 PDBj
PDBj









































