+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6gua | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
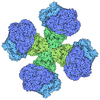
| Title | Xylulose 5-phosphate phosphoketolase from Lactococcus lactis | ||||||
 Components Components | Probable phosphoketolase | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | LYASE / THIAMINE DIPHOSPHATE-DEPENDENT ENZYME / ALPHA-BETA FOLD / HOMODIMER | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationLyases; Carbon-carbon lyases; Aldehyde-lyases / aldehyde-lyase activity / carbohydrate metabolic process Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis Il1403 (lactic acid bacteria) Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis Il1403 (lactic acid bacteria) | ||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SOLUTION SCATTERING / SOLUTION SCATTERING /  SYNCHROTRON / SYNCHROTRON /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 1.95 Å MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 1.95 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Scheidig, A.J. / Szedlacsek, S.E. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Struct Biol / Year: 2019 Journal: J Struct Biol / Year: 2019Title: Crystal structure of a xylulose 5-phosphate phosphoketolase. Insights into the substrate specificity for xylulose 5-phosphate. Authors: A J Scheidig / D Horvath / S E Szedlacsek /    Abstract: Phosphoketolases (PK) are TPP-dependent enzymes which play essential roles in carbohydrate metabolism of numerous bacteria. Depending on the substrate specificity PKs can be subdivided into xylulose ...Phosphoketolases (PK) are TPP-dependent enzymes which play essential roles in carbohydrate metabolism of numerous bacteria. Depending on the substrate specificity PKs can be subdivided into xylulose 5-phosphate (X5P) specific PKs (XPKs) and PKs which accept both X5P and fructose 6-phosphate (F6P) (XFPKs). Despite their key metabolic importance, so far only the crystal structures of two XFPKs have been reported. There are no reported structures for any XPKs and for any complexes between PK and substrate. One of the major unknowns concerning PKs mechanism of action is related to the structural determinants of PKs substrate specificity for X5P or F6P. We report here the crystal structure of XPK from Lactococcus lactis (XPK-Ll) at 2.1 Å resolution. Using small angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) we proved that XPK-Ll is a dimer in solution. Towards better understanding of PKs substrate specificity, we performed flexible docking of TPP-X5P and TPP-F6P on crystal structures of XPK-Ll, two XFPKs and transketolase (TK). Calculated structure-based binding energies consistently support XPK-Ll preference for X5P. Analysis of structural models thus obtained show that substrates adopt moderately different conformation in PKs active sites following distinct networks of polar interactions. Based on the here reported structure of XPK-Ll we propose the most probable amino acid residues involved in the catalytic steps of reaction mechanism. Altogether our results suggest that PKs substrate preference for X5P or F6P is the outcome of a fine balance between specific binding network and dissimilar catalytic residues depending on the enzyme (XPK or XFPK) - substrate (X5P or F6P) couples. #1: Journal: Acta Crystallogr. Sect. F Struct. Biol. Cryst. Commun. Year: 2010 Title: Preliminary X-ray crystallographic analysis of the D-xylulose 5-phosphate phosphoketolase from Lactococcus lactis. Authors: Petrareanu, G. / Balasu, M.C. / Zander, U. / Scheidig, A.J. / Szedlacsek, S.E. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6gua.cif.gz 6gua.cif.gz | 2.5 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6gua.ent.gz pdb6gua.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6gua.json.gz 6gua.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/gu/6gua https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/gu/6gua ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/gu/6gua ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/gu/6gua | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  1trkS S: Starting model for refinement C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
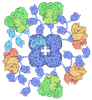
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 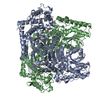
| ||||||||||||
| 2 | 
| ||||||||||||
| 3 | 
| ||||||||||||
| 4 | 
| ||||||||||||
| Unit cell |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 93474.992 Da / Num. of mol.: 8 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis Il1403 (lactic acid bacteria) Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis Il1403 (lactic acid bacteria)Gene: LL1502, L138230 / Production host:  References: UniProt: Q9CFH4, Lyases; Carbon-carbon lyases; Aldehyde-lyases #2: Chemical | ChemComp-TPP / #3: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / #4: Chemical | ChemComp-PO4 / #5: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment |
|
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 2.34 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 47.4 % |
|---|---|
| Crystal grow | Temperature: 291 K / Method: vapor diffusion, hanging drop / Details: 17 % (w/v) PEG-3350, 0.2 M sodium isothiocyanate, |
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 100 K |
|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  SYNCHROTRON / Site: SYNCHROTRON / Site:  ESRF ESRF  / Beamline: ID13 / Wavelength: 0.931 Å / Beamline: ID13 / Wavelength: 0.931 Å |
| Detector | Type: MAR CCD 130 mm / Detector: CCD / Date: May 21, 2005 |
| Radiation | Monochromator: mirror / Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray |
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength: 0.931 Å / Relative weight: 1 |
| Reflection | Resolution: 1.95→44.3 Å / Num. obs: 501022 / % possible obs: 97.3 % / Observed criterion σ(F): 0 / Observed criterion σ(I): 0 / Redundancy: 3.5 % / Biso Wilson estimate: 23.3 Å2 / CC1/2: 0.995 / Rpim(I) all: 0.079 / Rrim(I) all: 0.152 / Net I/σ(I): 6.79 |
| Reflection shell | Resolution: 1.95→2 Å / Redundancy: 2.5 % / Mean I/σ(I) obs: 1.27 / Num. unique obs: 44418 / CC1/2: 0.183 / Rpim(I) all: 0.548 / Rrim(I) all: 0.913 / % possible all: 86.6 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure:  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT MOLECULAR REPLACEMENTStarting model: 1TRK Resolution: 1.95→44.3 Å / Data cutoff high absF: 0 / Cross valid method: FREE R-VALUE / σ(F): 0
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 28.9 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST / Resolution: 1.95→44.3 Å
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell | Resolution: 1.95→2 Å
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller











 PDBj
PDBj