[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-6fox: The crystal structure of P.fluorescens Kynurenine 3-monooxygenase... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6fox | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | The crystal structure of P.fluorescens Kynurenine 3-monooxygenase (KMO) in complex with kynurenine | |||||||||||||||
 Components Components | Kynurenine 3-monooxygenase | |||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | OXIDOREDUCTASE / Substrate | |||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationkynurenine 3-monooxygenase / kynurenine 3-monooxygenase activity / kynurenine metabolic process / anthranilate metabolic process / NAD(P)H oxidase H2O2-forming activity / quinolinate biosynthetic process / L-tryptophan catabolic process / NAD+ biosynthetic process / NAD+ metabolic process / FAD binding Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Pseudomonas fluorescens (bacteria) Pseudomonas fluorescens (bacteria) | |||||||||||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON / SYNCHROTRON /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 1.9 Å MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 1.9 Å | |||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Levy, C.W. / Leys, D. | |||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 4items United Kingdom, 4items
| |||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Commun Biol / Year: 2019 Journal: Commun Biol / Year: 2019Title: A brain-permeable inhibitor of the neurodegenerative disease target kynurenine 3-monooxygenase prevents accumulation of neurotoxic metabolites. Authors: Zhang, S. / Sakuma, M. / Deora, G.S. / Levy, C.W. / Klausing, A. / Breda, C. / Read, K.D. / Edlin, C.D. / Ross, B.P. / Wright Muelas, M. / Day, P.J. / O'Hagan, S. / Kell, D.B. / Schwarcz, R. ...Authors: Zhang, S. / Sakuma, M. / Deora, G.S. / Levy, C.W. / Klausing, A. / Breda, C. / Read, K.D. / Edlin, C.D. / Ross, B.P. / Wright Muelas, M. / Day, P.J. / O'Hagan, S. / Kell, D.B. / Schwarcz, R. / Leys, D. / Heyes, D.J. / Giorgini, F. / Scrutton, N.S. #1: Journal: Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. / Year: 2012 Title: Towards automated crystallographic structure refinement with phenix.refine. Authors: Afonine, P.V. / Grosse-Kunstleve, R.W. / Echols, N. / Headd, J.J. / Moriarty, N.W. / Mustyakimov, M. / Terwilliger, T.C. / Urzhumtsev, A. / Zwart, P.H. / Adams, P.D. #2: Journal: Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr / Year: 2010 Title: PHENIX: a comprehensive Python-based system for macromolecular structure solution. Authors: Paul D Adams / Pavel V Afonine / Gábor Bunkóczi / Vincent B Chen / Ian W Davis / Nathaniel Echols / Jeffrey J Headd / Li-Wei Hung / Gary J Kapral / Ralf W Grosse-Kunstleve / Airlie J McCoy ...Authors: Paul D Adams / Pavel V Afonine / Gábor Bunkóczi / Vincent B Chen / Ian W Davis / Nathaniel Echols / Jeffrey J Headd / Li-Wei Hung / Gary J Kapral / Ralf W Grosse-Kunstleve / Airlie J McCoy / Nigel W Moriarty / Robert Oeffner / Randy J Read / David C Richardson / Jane S Richardson / Thomas C Terwilliger / Peter H Zwart /  Abstract: Macromolecular X-ray crystallography is routinely applied to understand biological processes at a molecular level. However, significant time and effort are still required to solve and complete many ...Macromolecular X-ray crystallography is routinely applied to understand biological processes at a molecular level. However, significant time and effort are still required to solve and complete many of these structures because of the need for manual interpretation of complex numerical data using many software packages and the repeated use of interactive three-dimensional graphics. PHENIX has been developed to provide a comprehensive system for macromolecular crystallographic structure solution with an emphasis on the automation of all procedures. This has relied on the development of algorithms that minimize or eliminate subjective input, the development of algorithms that automate procedures that are traditionally performed by hand and, finally, the development of a framework that allows a tight integration between the algorithms. | |||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
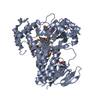
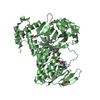
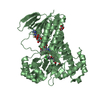
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6fox.cif.gz 6fox.cif.gz | 671.9 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6fox.ent.gz pdb6fox.ent.gz | 461.5 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6fox.json.gz 6fox.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fo/6fox https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fo/6fox ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fo/6fox ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fo/6fox | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 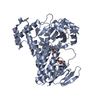
| ||||||||||||
| 2 | 
| ||||||||||||
| Unit cell |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 50608.324 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Pseudomonas fluorescens (bacteria) / Gene: kmo, qbsG / Plasmid: pET17b / Production host: Pseudomonas fluorescens (bacteria) / Gene: kmo, qbsG / Plasmid: pET17b / Production host:  #2: Chemical | #3: Chemical | ChemComp-CA / | #4: Chemical | ChemComp-KYN / ( | #5: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 2.45 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 49.83 % |
|---|---|
| Crystal grow | Temperature: 277 K / Method: vapor diffusion, sitting drop / pH: 6.5 Details: 0.2 M sodium acetate trihydrate, 0.1 M sodium cacodylate pH6.5, 18 % w/v PEG 8000 |
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 100 K |
|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  SYNCHROTRON / Site: SYNCHROTRON / Site:  Diamond Diamond  / Beamline: I03 / Wavelength: 0.98 Å / Beamline: I03 / Wavelength: 0.98 Å |
| Detector | Type: DECTRIS PILATUS 6M / Detector: PIXEL / Date: Jan 15, 2017 |
| Radiation | Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray |
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength: 0.98 Å / Relative weight: 1 |
| Reflection | Resolution: 1.899→44.02 Å / Num. obs: 74533 / % possible obs: 97.73 % / Redundancy: 4.1 % / Biso Wilson estimate: 19.56 Å2 / CC1/2: 0.997 / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.0617 / Rpim(I) all: 0.03467 / Net I/σ(I): 14.28 |
| Reflection shell | Resolution: 1.899→1.967 Å / Redundancy: 4 % / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.1846 / Mean I/σ(I) obs: 5.43 / Num. unique obs: 7153 / CC1/2: 0.957 / Rpim(I) all: 0.1034 / % possible all: 94.67 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure:  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT MOLECULAR REPLACEMENTStarting model: Inhouse Resolution: 1.9→44.02 Å / SU ML: 0.2401 / Cross valid method: FREE R-VALUE / σ(F): 1.48 / Phase error: 23.9234
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Shrinkage radii: 0.9 Å / VDW probe radii: 1.11 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 34.97 Å2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST / Resolution: 1.9→44.02 Å
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement TLS params. | Method: refined / Origin x: 111.60026503 Å / Origin y: 6.67181144148 Å / Origin z: -98.1626173491 Å
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement TLS group | Selection details: all |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





















 PDBj
PDBj