[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-6flp: CryoEM structure of E.coli RNA polymerase paused elongation compl... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6flp | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
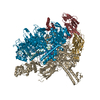
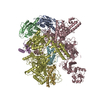
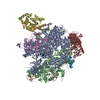
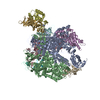
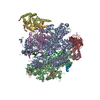
| Title | CryoEM structure of E.coli RNA polymerase paused elongation complex without RNA hairpin bound to NusA | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSCRIPTION / RNA polymerase / Transcriptional pausing / his pause / NusA | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationRNA polymerase complex / submerged biofilm formation / cellular response to cell envelope stress / regulation of DNA-templated transcription initiation / bacterial-type flagellum assembly / bacterial-type RNA polymerase core enzyme binding / cytosolic DNA-directed RNA polymerase complex / bacterial-type flagellum-dependent cell motility / nitrate assimilation / regulation of DNA-templated transcription elongation ...RNA polymerase complex / submerged biofilm formation / cellular response to cell envelope stress / regulation of DNA-templated transcription initiation / bacterial-type flagellum assembly / bacterial-type RNA polymerase core enzyme binding / cytosolic DNA-directed RNA polymerase complex / bacterial-type flagellum-dependent cell motility / nitrate assimilation / regulation of DNA-templated transcription elongation / transcription elongation factor complex / transcription antitermination / DNA-directed RNA polymerase complex / cell motility / DNA-templated transcription initiation / ribonucleoside binding / DNA-directed RNA polymerase / DNA-directed RNA polymerase activity / response to heat / protein-containing complex assembly / intracellular iron ion homeostasis / protein dimerization activity / response to antibiotic / DNA-templated transcription / magnesium ion binding / DNA binding / zinc ion binding / membrane / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  synthetic construct (others) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.1 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Guo, X. / Weixlbaumer, A. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  France, 1items France, 1items
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2018 Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2018Title: Structural Basis for NusA Stabilized Transcriptional Pausing. Authors: Xieyang Guo / Alexander G Myasnikov / James Chen / Corinne Crucifix / Gabor Papai / Maria Takacs / Patrick Schultz / Albert Weixlbaumer /   Abstract: Transcriptional pausing by RNA polymerases (RNAPs) is a key mechanism to regulate gene expression in all kingdoms of life and is a prerequisite for transcription termination. The essential bacterial ...Transcriptional pausing by RNA polymerases (RNAPs) is a key mechanism to regulate gene expression in all kingdoms of life and is a prerequisite for transcription termination. The essential bacterial transcription factor NusA stimulates both pausing and termination of transcription, thus playing a central role. Here, we report single-particle electron cryo-microscopy reconstructions of NusA bound to paused E. coli RNAP elongation complexes with and without a pause-enhancing hairpin in the RNA exit channel. The structures reveal four interactions between NusA and RNAP that suggest how NusA stimulates RNA folding, pausing, and termination. An asymmetric translocation intermediate of RNA and DNA converts the active site of the enzyme into an inactive state, providing a structural explanation for the inhibition of catalysis. Comparing RNAP at different stages of pausing provides insights on the dynamic nature of the process and the role of NusA as a regulatory factor. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6flp.cif.gz 6flp.cif.gz | 605.8 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6flp.ent.gz pdb6flp.ent.gz | 479.9 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6flp.json.gz 6flp.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fl/6flp https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fl/6flp ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fl/6flp ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fl/6flp | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  4274MC  4275C  6flqC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 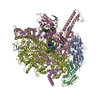
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit ... , 4 types, 5 molecules ABCDE
| #1: Protein | Mass: 36558.680 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Strain: K12 / Gene: rpoA, pez, phs, sez, b3295, JW3257 / Production host:  #2: Protein | | Mass: 150820.875 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Strain: K12 Gene: rpoB, groN, nitB, rif, ron, stl, stv, tabD, b3987, JW3950 Production host:  #3: Protein | | Mass: 155366.781 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Strain: K12 / Gene: rpoC, tabB, b3988, JW3951 / Production host:  #4: Protein | | Mass: 10249.547 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Strain: K12 / Gene: rpoZ, b3649, JW3624 / Production host:  |
|---|
-DNA chain , 2 types, 2 molecules NT
| #5: DNA chain | Mass: 9676.235 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) |
|---|---|
| #7: DNA chain | Mass: 11815.586 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) |
-RNA chain , 1 types, 1 molecules R
| #6: RNA chain | Mass: 3194.917 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 2 types, 3 molecules 


| #8: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / |
|---|---|
| #9: Chemical |
-Details
| Has protein modification | N |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source (natural) |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 400 divisions/in. / Grid type: C-flat-1.2/1.3 4C | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 95 % / Chamber temperature: 283.15 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 105000 X / Nominal defocus max: 3200 nm / Nominal defocus min: 800 nm / Cs: 0.001 mm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 8 sec. / Electron dose: 53 e/Å2 / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Num. of real images: 4957 |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter name: GIF Quantum ER / Energyfilter upper: 20 eV / Energyfilter lower: 0 eV |
| Image scans | Movie frames/image: 40 / Used frames/image: 3-40 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.12_2829: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 65966 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 4.1 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 65966 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT / Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj








































