[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
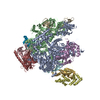
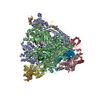
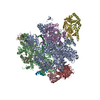
Yorodumi- PDB-6exv: Structure of mammalian RNA polymerase II elongation complex inhib... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6exv | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
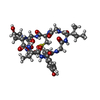
| Title | Structure of mammalian RNA polymerase II elongation complex inhibited by Alpha-amanitin | ||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSCRIPTION / Inhibitor / elongation / active site | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information: / B-WICH complex positively regulates rRNA expression / RNA Polymerase I Transcription Initiation / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Escape / RNA Polymerase I Transcription Termination / RNA Polymerase III Transcription Initiation From Type 1 Promoter / RNA Polymerase III Transcription Initiation From Type 2 Promoter / RNA Polymerase III Transcription Initiation From Type 3 Promoter / Formation of RNA Pol II elongation complex / Formation of the Early Elongation Complex ...: / B-WICH complex positively regulates rRNA expression / RNA Polymerase I Transcription Initiation / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Escape / RNA Polymerase I Transcription Termination / RNA Polymerase III Transcription Initiation From Type 1 Promoter / RNA Polymerase III Transcription Initiation From Type 2 Promoter / RNA Polymerase III Transcription Initiation From Type 3 Promoter / Formation of RNA Pol II elongation complex / Formation of the Early Elongation Complex / Transcriptional regulation by small RNAs / RNA Polymerase II Pre-transcription Events / TP53 Regulates Transcription of DNA Repair Genes / FGFR2 alternative splicing / RNA polymerase II transcribes snRNA genes / mRNA Capping / mRNA Splicing - Minor Pathway / Processing of Capped Intron-Containing Pre-mRNA / RNA Polymerase II Promoter Escape / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Pre-Initiation And Promoter Opening / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Initiation / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Elongation / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Initiation And Promoter Clearance / RNA Pol II CTD phosphorylation and interaction with CE / Estrogen-dependent gene expression / Formation of TC-NER Pre-Incision Complex / Dual incision in TC-NER / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in TC-NER / mRNA Splicing - Major Pathway / organelle membrane / maintenance of transcriptional fidelity during transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / positive regulation of nuclear-transcribed mRNA poly(A) tail shortening / RNA polymerase II activity / transcription elongation by RNA polymerase I / transcription-coupled nucleotide-excision repair / tRNA transcription by RNA polymerase III / RNA polymerase I complex / RNA polymerase III complex / positive regulation of translational initiation / RNA polymerase II, core complex / core promoter sequence-specific DNA binding / translation initiation factor binding / transcription initiation at RNA polymerase II promoter / P-body / euchromatin / ribonucleoside binding / fibrillar center / DNA-directed 5'-3' RNA polymerase activity / DNA-directed RNA polymerase / single-stranded DNA binding / toxin activity / transcription by RNA polymerase II / nucleic acid binding / chromosome, telomeric region / single-stranded RNA binding / protein dimerization activity / nuclear speck / RNA-dependent RNA polymerase activity / nucleotide binding / DNA-templated transcription / chromatin binding / nucleolus / DNA binding / zinc ion binding / nucleus / metal ion binding / cytosol Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |    Amanita phalloides (death cap) Amanita phalloides (death cap)synthetic construct (others) | ||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.6 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Liu, X. / Farnung, L. / Wigge, C. / Cramer, P. | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, 3items Germany, 3items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Biol Chem / Year: 2018 Journal: J Biol Chem / Year: 2018Title: Cryo-EM structure of a mammalian RNA polymerase II elongation complex inhibited by α-amanitin. Authors: Xiangyang Liu / Lucas Farnung / Christoph Wigge / Patrick Cramer /  Abstract: RNA polymerase II (Pol II) is the central enzyme that transcribes eukaryotic protein-coding genes to produce mRNA. The mushroom toxin α-amanitin binds Pol II and inhibits transcription at the step ...RNA polymerase II (Pol II) is the central enzyme that transcribes eukaryotic protein-coding genes to produce mRNA. The mushroom toxin α-amanitin binds Pol II and inhibits transcription at the step of RNA chain elongation. Pol II from yeast binds α-amanitin with micromolar affinity, whereas metazoan Pol II enzymes exhibit nanomolar affinities. Here, we present the high-resolution cryo-EM structure of α-amanitin bound to and inhibited by its natural target, the mammalian Pol II elongation complex. The structure revealed that the toxin is located in a pocket previously identified in yeast Pol II but forms additional contacts with metazoan-specific residues, which explains why its affinity to mammalian Pol II is ∼3000 times higher than for yeast Pol II. Our work provides the structural basis for the inhibition of mammalian Pol II by the natural toxin α-amanitin and highlights that cryo-EM is well suited to studying interactions of a small molecule with its macromolecular target. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6exv.cif.gz 6exv.cif.gz | 752.4 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6exv.ent.gz pdb6exv.ent.gz | 604.6 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6exv.json.gz 6exv.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  6exv_validation.pdf.gz 6exv_validation.pdf.gz | 1.2 MB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  6exv_full_validation.pdf.gz 6exv_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.2 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  6exv_validation.xml.gz 6exv_validation.xml.gz | 111.2 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  6exv_validation.cif.gz 6exv_validation.cif.gz | 174.3 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ex/6exv https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ex/6exv ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ex/6exv ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ex/6exv | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  3981MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
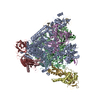
-DNA-DIRECTED RNA POLYMERASE II SUBUNIT ... , 6 types, 6 molecules ABCDGI
| #1: Protein | Mass: 217450.078 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 133201.625 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #3: Protein | Mass: 31439.074 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #4: Protein | Mass: 16331.255 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #7: Protein | Mass: 19314.283 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #9: Protein | Mass: 14541.221 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
-DNA-DIRECTED RNA POLYMERASES I, II, AND III SUBUNIT ... , 6 types, 6 molecules EFHJKL
| #5: Protein | Mass: 24644.318 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|---|
| #6: Protein | Mass: 14477.001 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #8: Protein | Mass: 17162.273 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #10: Protein | Mass: 7655.123 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #11: Protein | Mass: 13310.284 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #12: Protein | Mass: 7018.244 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
-DNA chain , 2 types, 2 molecules NT
| #14: DNA chain | Mass: 13303.563 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) |
|---|---|
| #16: DNA chain | Mass: 13178.483 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) |
-Protein/peptide / RNA chain , 2 types, 2 molecules MP
-Non-polymers , 2 types, 9 molecules 


| #17: Chemical | ChemComp-ZN / #18: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / | |
|---|
-Details
| Compound details | ALPHA-AMANITIN, AN AMATOXIN, IS A DI-CYCLIC PEPTIDE. HERE, ALPHA-AMANITIN IS REPRESENTED BY THE ...ALPHA-AMANITIN, AN AMATOXIN, IS A DI-CYCLIC PEPTIDE. HERE, ALPHA-AMANITIN IS REPRESENTE |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.607 MDa / Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism: synthetic construct (others) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.244 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R2/2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 130000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1500 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Residual tilt: 10 mradians |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 10 sec. / Electron dose: 35 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 2264 |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter name: GIF Quantum LS / Energyfilter upper: 20 eV / Energyfilter lower: 0 eV |
| Image scans | Width: 3710 / Height: 3838 / Movie frames/image: 40 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.11.1_2575: / Classification: refinement | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 207410 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.6 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 134512 / Symmetry type: POINT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | B value: 53.97 / Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Space: REAL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 PDBj
PDBj