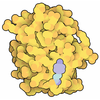
Entry Database : PDB / ID : 6a60Title Crystal structure of human FXR/RXR-LBD heterodimer bound to GW4064 and 9cRA and SRC1 Bile acid receptor Nuclear receptor coactivator 1 Retinoic acid receptor RXR-alpha Keywords / Function / homology Function Domain/homology Component
/ / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / Biological species Homo sapiens (human)Method / / / / Resolution : 3.05 Å Authors Wang, N. / Liu, J. Funding support Organization Grant number Country 31770817
Journal : J. Biol. Chem. / Year : 2018Title : Ligand binding and heterodimerization with retinoid X receptor alpha (RXR alpha ) induce farnesoid X receptor (FXR) conformational changes affecting coactivator bindingAuthors : Wang, N. / Zou, Q. / Xu, J. / Zhang, J. / Liu, J. History Deposition Jun 25, 2018 Deposition site / Processing site Revision 1.0 Oct 10, 2018 Provider / Type Revision 1.1 Oct 17, 2018 Group / Database references / Structure summaryCategory / citation_author / entityItem _citation.journal_abbrev / _citation.pdbx_database_id_DOI ... _citation.journal_abbrev / _citation.pdbx_database_id_DOI / _citation.pdbx_database_id_PubMed / _citation.title / _citation_author.identifier_ORCID / _entity.formula_weight Revision 1.2 Dec 5, 2018 Group / Database references / Category Item _citation.journal_volume / _citation.page_first ... _citation.journal_volume / _citation.page_first / _citation.page_last / _citation.title Revision 1.3 Mar 27, 2024 Group / Database references / Category / chem_comp_bond / database_2Item / _database_2.pdbx_database_accession
Show all Show less
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi Open data
Open data Basic information
Basic information Components
Components Keywords
Keywords Function and homology information
Function and homology information Homo sapiens (human)
Homo sapiens (human) X-RAY DIFFRACTION /
X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON /
SYNCHROTRON /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT /
MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT /  molecular replacement / Resolution: 3.05 Å
molecular replacement / Resolution: 3.05 Å  Authors
Authors China, 1items
China, 1items  Citation
Citation Journal: J. Biol. Chem. / Year: 2018
Journal: J. Biol. Chem. / Year: 2018 Structure visualization
Structure visualization Molmil
Molmil Jmol/JSmol
Jmol/JSmol Downloads & links
Downloads & links Download
Download 6a60.cif.gz
6a60.cif.gz PDBx/mmCIF format
PDBx/mmCIF format pdb6a60.ent.gz
pdb6a60.ent.gz PDB format
PDB format 6a60.json.gz
6a60.json.gz PDBx/mmJSON format
PDBx/mmJSON format Other downloads
Other downloads https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/a6/6a60
https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/a6/6a60 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/a6/6a60
ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/a6/6a60 Links
Links Assembly
Assembly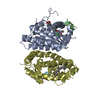
 Components
Components Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: NR1H4, BAR, FXR, HRR1, RIP14 / Production host:
Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: NR1H4, BAR, FXR, HRR1, RIP14 / Production host: 
 Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: RXRA, NR2B1 / Production host:
Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: RXRA, NR2B1 / Production host: 
 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: B5MCN7, UniProt: Q15788*PLUS
Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: B5MCN7, UniProt: Q15788*PLUS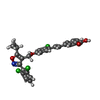




 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1
X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1  Sample preparation
Sample preparation SYNCHROTRON / Site:
SYNCHROTRON / Site:  SSRF
SSRF  / Beamline: BL19U1 / Wavelength: 0.9785 Å
/ Beamline: BL19U1 / Wavelength: 0.9785 Å molecular replacement
molecular replacement Processing
Processing MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 3.05→74.95 Å / Cor.coef. Fo:Fc: 0.935 / Cor.coef. Fo:Fc free: 0.937 / WRfactor Rfree: 0.2746 / WRfactor Rwork: 0.2104 / FOM work R set: 0.7548 / SU B: 24.502 / SU ML: 0.425 / SU Rfree: 0.5203 / Cross valid method: THROUGHOUT / σ(F): 0 / ESU R Free: 0.52 / Stereochemistry target values: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD
MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 3.05→74.95 Å / Cor.coef. Fo:Fc: 0.935 / Cor.coef. Fo:Fc free: 0.937 / WRfactor Rfree: 0.2746 / WRfactor Rwork: 0.2104 / FOM work R set: 0.7548 / SU B: 24.502 / SU ML: 0.425 / SU Rfree: 0.5203 / Cross valid method: THROUGHOUT / σ(F): 0 / ESU R Free: 0.52 / Stereochemistry target values: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






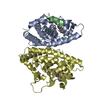





 PDBj
PDBj