Entry Database : PDB / ID : 5z12Title A structure of FXR/RXR (Peptide from Nuclear receptor coactivator ...) x 2 Bile acid receptor Retinoic acid receptor RXR-alpha Keywords / Function / homology Function Domain/homology Component
/ / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / Biological species Homo sapiens (human)Method / / / Resolution : 2.75 Å Authors Lu, Y. / Li, Y. Journal : J. Biol. Chem. / Year : 2018Title : Structural insights into the heterodimeric complex of the nuclear receptors FXR and RXRAuthors : Zheng, W. / Lu, Y. / Tian, S. / Ma, F. / Wei, Y. / Xu, S. / Li, Y. History Deposition Dec 23, 2017 Deposition site / Processing site Revision 1.0 Jul 4, 2018 Provider / Type Revision 1.1 Jul 25, 2018 Group / Database references / Category / citation_authorItem _citation.journal_abbrev / _citation.pdbx_database_id_DOI ... _citation.journal_abbrev / _citation.pdbx_database_id_DOI / _citation.pdbx_database_id_PubMed / _citation_author.name Revision 1.2 Aug 22, 2018 Group / Database references / Category / citation_authorItem _citation.journal_volume / _citation.page_first ... _citation.journal_volume / _citation.page_first / _citation.page_last / _citation_author.identifier_ORCID Revision 1.3 Dec 25, 2019 Group / Refinement description / Category / refine_histItem / _refine_hist.d_res_lowRevision 1.4 Mar 27, 2024 Group / Database references / Category / chem_comp_bond / database_2Item / _database_2.pdbx_database_accession
Show all Show less
 Open data
Open data Basic information
Basic information Components
Components Keywords
Keywords Function and homology information
Function and homology information Homo sapiens (human)
Homo sapiens (human) X-RAY DIFFRACTION /
X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON /
SYNCHROTRON /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 2.75 Å
MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 2.75 Å  Authors
Authors Citation
Citation Journal: J. Biol. Chem. / Year: 2018
Journal: J. Biol. Chem. / Year: 2018 Structure visualization
Structure visualization Molmil
Molmil Jmol/JSmol
Jmol/JSmol Downloads & links
Downloads & links Download
Download 5z12.cif.gz
5z12.cif.gz PDBx/mmCIF format
PDBx/mmCIF format pdb5z12.ent.gz
pdb5z12.ent.gz PDB format
PDB format 5z12.json.gz
5z12.json.gz PDBx/mmJSON format
PDBx/mmJSON format Other downloads
Other downloads 5z12_validation.pdf.gz
5z12_validation.pdf.gz wwPDB validaton report
wwPDB validaton report 5z12_full_validation.pdf.gz
5z12_full_validation.pdf.gz 5z12_validation.xml.gz
5z12_validation.xml.gz 5z12_validation.cif.gz
5z12_validation.cif.gz https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/z1/5z12
https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/z1/5z12 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/z1/5z12
ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/z1/5z12 Links
Links Assembly
Assembly
 Components
Components Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: NR1H4, BAR, FXR, HRR1, RIP14 / Production host:
Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: NR1H4, BAR, FXR, HRR1, RIP14 / Production host: 
 Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: RXRA, NR2B1 / Production host:
Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: RXRA, NR2B1 / Production host: 
 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q15596*PLUS
Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q15596*PLUS Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q15596*PLUS
Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q15596*PLUS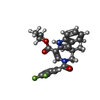




 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1
X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1  Sample preparation
Sample preparation SYNCHROTRON / Site:
SYNCHROTRON / Site:  SSRF
SSRF  / Beamline: BL19U1 / Wavelength: 0.97 Å
/ Beamline: BL19U1 / Wavelength: 0.97 Å Processing
Processing MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 2.75→50 Å / Cor.coef. Fo:Fc: 0.903 / Cor.coef. Fo:Fc free: 0.858 / SU B: 20.894 / SU ML: 0.409 / Cross valid method: THROUGHOUT / σ(F): 0 / ESU R Free: 0.586 / Stereochemistry target values: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD
MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 2.75→50 Å / Cor.coef. Fo:Fc: 0.903 / Cor.coef. Fo:Fc free: 0.858 / SU B: 20.894 / SU ML: 0.409 / Cross valid method: THROUGHOUT / σ(F): 0 / ESU R Free: 0.586 / Stereochemistry target values: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



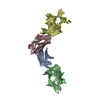
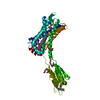

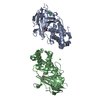


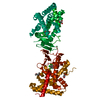
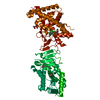
 PDBj
PDBj