+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 5w66 | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
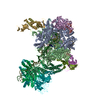
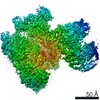
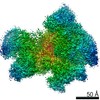
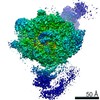
| Title | RNA polymerase I Initial Transcribing Complex State 3 | ||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSCRIPTION / RNA Polymerase I Core Factor Transcription | ||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationRNA polymerase I transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding / RNA polymerase I core factor complex / RNA polymerase I general transcription initiation factor activity / RNA polymerase I general transcription initiation factor binding / RNA polymerase I core promoter sequence-specific DNA binding / RNA polymerase I preinitiation complex assembly / RNA Polymerase I Transcription Initiation / Processing of Capped Intron-Containing Pre-mRNA / RNA Polymerase III Transcription Initiation From Type 2 Promoter / RNA Pol II CTD phosphorylation and interaction with CE ...RNA polymerase I transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding / RNA polymerase I core factor complex / RNA polymerase I general transcription initiation factor activity / RNA polymerase I general transcription initiation factor binding / RNA polymerase I core promoter sequence-specific DNA binding / RNA polymerase I preinitiation complex assembly / RNA Polymerase I Transcription Initiation / Processing of Capped Intron-Containing Pre-mRNA / RNA Polymerase III Transcription Initiation From Type 2 Promoter / RNA Pol II CTD phosphorylation and interaction with CE / Formation of the Early Elongation Complex / mRNA Capping / RNA polymerase II transcribes snRNA genes / TP53 Regulates Transcription of DNA Repair Genes / RNA Polymerase II Promoter Escape / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Pre-Initiation And Promoter Opening / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Initiation / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Initiation And Promoter Clearance / termination of RNA polymerase III transcription / RNA Polymerase II Pre-transcription Events / RNA-templated transcription / Formation of TC-NER Pre-Incision Complex / regulation of cell size / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Escape / transcription initiation at RNA polymerase III promoter / termination of RNA polymerase I transcription / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in TC-NER / nucleolar large rRNA transcription by RNA polymerase I / transcription initiation at RNA polymerase I promoter / Estrogen-dependent gene expression / transcription by RNA polymerase III / Dual incision in TC-NER / RNA polymerase I complex / RNA polymerase III complex / transcription elongation by RNA polymerase I / RNA polymerase II, core complex / tRNA transcription by RNA polymerase III / transcription by RNA polymerase I / TBP-class protein binding / transcription initiation at RNA polymerase II promoter / transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / promoter-specific chromatin binding / ribonucleoside binding / DNA-directed RNA polymerase / DNA-directed RNA polymerase activity / peroxisome / ribosome biogenesis / nucleic acid binding / transcription by RNA polymerase II / RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding / protein dimerization activity / nucleolus / negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / mitochondrion / DNA binding / zinc ion binding / nucleoplasm / metal ion binding / nucleus / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |   | ||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.9 Å | ||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Han, Y. / He, Y. | ||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 5items United States, 5items
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Elife / Year: 2017 Journal: Elife / Year: 2017Title: Structural mechanism of ATP-independent transcription initiation by RNA polymerase I. Authors: Yan Han / Chunli Yan / Thi Hoang Duong Nguyen / Ashleigh J Jackobel / Ivaylo Ivanov / Bruce A Knutson / Yuan He /  Abstract: Transcription initiation by RNA Polymerase I (Pol I) depends on the Core Factor (CF) complex to recognize the upstream promoter and assemble into a Pre-Initiation Complex (PIC). Here, we solve a ...Transcription initiation by RNA Polymerase I (Pol I) depends on the Core Factor (CF) complex to recognize the upstream promoter and assemble into a Pre-Initiation Complex (PIC). Here, we solve a structure of Pol I-CF-DNA to 3.8 Å resolution using single-particle cryo-electron microscopy. The structure reveals a bipartite architecture of Core Factor and its recognition of the promoter from -27 to -16. Core Factor's intrinsic mobility correlates well with different conformational states of the Pol I cleft, in addition to the stabilization of either Rrn7 N-terminal domain near Pol I wall or the tandem winged helix domain of A49 at a partially overlapping location. Comparison of the three states in this study with the Pol II system suggests that a ratchet motion of the Core Factor-DNA sub-complex at upstream facilitates promoter melting in an ATP-independent manner, distinct from a DNA translocase actively threading the downstream DNA in the Pol II PIC. | ||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  5w66.cif.gz 5w66.cif.gz | 1.1 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb5w66.ent.gz pdb5w66.ent.gz | 836.8 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  5w66.json.gz 5w66.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/w6/5w66 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/w6/5w66 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/w6/5w66 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/w6/5w66 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8776MC  8771C  8772C  8773C  8774C  8775C  8777C  5w5yC  5w64C  5w65C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-DNA-directed RNA polymerase I subunit ... , 7 types, 7 molecules ABDGIMN
| #1: Protein | Mass: 186676.969 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / References: UniProt: P10964, DNA-directed RNA polymerase |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 135910.328 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / References: UniProt: P22138, DNA-directed RNA polymerase |
| #4: Protein | Mass: 14599.128 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / References: UniProt: P50106 |
| #7: Protein | Mass: 36264.852 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / References: UniProt: P46669 |
| #9: Protein | Mass: 13676.566 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / References: UniProt: P32529 |
| #13: Protein | Mass: 46721.707 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / References: UniProt: Q01080 |
| #14: Protein | Mass: 26933.518 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / References: UniProt: P47006 |
-DNA-directed RNA polymerases I and III subunit ... , 2 types, 2 molecules CK
| #3: Protein | Mass: 37732.613 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / References: UniProt: P07703 |
|---|---|
| #11: Protein | Mass: 16167.860 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / References: UniProt: P28000 |
-DNA-directed RNA polymerases I, II, and III subunit ... , 5 types, 5 molecules EFHJL
| #5: Protein | Mass: 25117.094 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / References: UniProt: P20434 |
|---|---|
| #6: Protein | Mass: 17931.834 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / References: UniProt: P20435 |
| #8: Protein | Mass: 16525.363 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / References: UniProt: P20436 |
| #10: Protein | Mass: 8290.732 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / References: UniProt: P22139 |
| #12: Protein | Mass: 7729.969 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / References: UniProt: P40422 |
-RNA polymerase I-specific transcription initiation factor ... , 3 types, 3 molecules OPQ
| #15: Protein | Mass: 100690.188 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: RRN6, YBL014C, YBL0311, YBL0312 / Production host:  |
|---|---|
| #16: Protein | Mass: 60435.195 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: RRN7, YJL025W, J1273 / Production host:  |
| #17: Protein | Mass: 59334.262 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: RRN11, YML043C, YM9827.09C / Production host:  |
-DNA chain , 2 types, 2 molecules ST
| #19: DNA chain | Mass: 16803.787 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  |
|---|---|
| #20: DNA chain | Mass: 16360.488 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  |
-RNA chain / Non-polymers , 2 types, 7 molecules R

| #18: RNA chain | Mass: 1915.213 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  |
|---|---|
| #21: Chemical | ChemComp-ZN / |
-Details
| Has protein modification | Y |
|---|---|
| Sequence details | DUE TO LOW RESOLUTION |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: RNA Polymerase I Initial Transcribing Complex State 3 / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#20 / Source: MULTIPLE SOURCES |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.9 MDa / Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.6 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 400 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil S7/2 |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 22500 X / Calibrated defocus min: 1500 nm / Calibrated defocus max: 4500 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 12 sec. / Electron dose: 56.8 e/Å2 / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
| Image scans | Movie frames/image: 40 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Details: CTF amplitude correction was performed following 3D auto refinement in relion. Type: PHASE FLIPPING ONLY | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.9 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 26913 / Symmetry type: POINT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Space: REAL |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj









































