[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
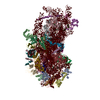
Yorodumi- PDB-5vox: Yeast V-ATPase in complex with Legionella pneumophila effector Si... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 5vox | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Yeast V-ATPase in complex with Legionella pneumophila effector SidK (rotational state 1) | ||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | HYDROLASE / V-ATPase / SidK / rotational state 1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationvacuole-mitochondrion membrane contact site / cell wall mannoprotein biosynthetic process / ATPase-coupled ion transmembrane transporter activity / cellular response to alkaline pH / protein localization to vacuolar membrane / Insulin receptor recycling / Transferrin endocytosis and recycling / polyphosphate metabolic process / ROS and RNS production in phagocytes / Amino acids regulate mTORC1 ...vacuole-mitochondrion membrane contact site / cell wall mannoprotein biosynthetic process / ATPase-coupled ion transmembrane transporter activity / cellular response to alkaline pH / protein localization to vacuolar membrane / Insulin receptor recycling / Transferrin endocytosis and recycling / polyphosphate metabolic process / ROS and RNS production in phagocytes / Amino acids regulate mTORC1 / Golgi lumen acidification / proteasome storage granule assembly / P-type proton-exporting transporter activity / vacuolar transport / vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V1 domain / vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V0 domain / endosomal lumen acidification / vacuole organization / protein targeting to vacuole / proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex / pexophagy / intron homing / intein-mediated protein splicing / fungal-type vacuole / vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex / cellular hyperosmotic response / vacuolar acidification / fungal-type vacuole membrane / phosphatidylinositol-3,5-bisphosphate binding / proton transmembrane transporter activity / proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism / intracellular copper ion homeostasis / ATP metabolic process / H+-transporting two-sector ATPase / Neutrophil degranulation / proton transmembrane transport / cell periphery / transmembrane transport / endocytosis / cytoplasmic stress granule / intracellular calcium ion homeostasis / ATPase binding / protein-containing complex assembly / endonuclease activity / Hydrolases; Acting on ester bonds / intracellular iron ion homeostasis / membrane raft / Golgi membrane / mRNA binding / ATP hydrolysis activity / DNA binding / ATP binding / membrane / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Legionella pneumophila subsp. pneumophila ATCC 43290 (bacteria) Legionella pneumophila subsp. pneumophila ATCC 43290 (bacteria) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 6.8 Å | ||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Zhao, J. | ||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Canada, Canada,  United States, 5items United States, 5items
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: PLoS Pathog / Year: 2017 Journal: PLoS Pathog / Year: 2017Title: Molecular basis for the binding and modulation of V-ATPase by a bacterial effector protein. Authors: Jianhua Zhao / Ksenia Beyrakhova / Yao Liu / Claudia P Alvarez / Stephanie A Bueler / Li Xu / Caishuang Xu / Michal T Boniecki / Voula Kanelis / Zhao-Qing Luo / Miroslaw Cygler / John L Rubinstein /   Abstract: Intracellular pathogenic bacteria evade the immune response by replicating within host cells. Legionella pneumophila, the causative agent of Legionnaires' Disease, makes use of numerous effector ...Intracellular pathogenic bacteria evade the immune response by replicating within host cells. Legionella pneumophila, the causative agent of Legionnaires' Disease, makes use of numerous effector proteins to construct a niche supportive of its replication within phagocytic cells. The L. pneumophila effector SidK was identified in a screen for proteins that reduce the activity of the proton pumping vacuolar-type ATPases (V-ATPases) when expressed in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisae. SidK is secreted by L. pneumophila in the early stages of infection and by binding to and inhibiting the V-ATPase, SidK reduces phagosomal acidification and promotes survival of the bacterium inside macrophages. We determined crystal structures of the N-terminal region of SidK at 2.3 Å resolution and used single particle electron cryomicroscopy (cryo-EM) to determine structures of V-ATPase:SidK complexes at ~6.8 Å resolution. SidK is a flexible and elongated protein composed of an α-helical region that interacts with subunit A of the V-ATPase and a second region of unknown function that is flexibly-tethered to the first. SidK binds V-ATPase strongly by interacting via two α-helical bundles at its N terminus with subunit A. In vitro activity assays show that SidK does not inhibit the V-ATPase completely, but reduces its activity by ~40%, consistent with the partial V-ATPase deficiency phenotype its expression causes in yeast. The cryo-EM analysis shows that SidK reduces the flexibility of the A-subunit that is in the 'open' conformation. Fluorescence experiments indicate that SidK binding decreases the affinity of V-ATPase for a fluorescent analogue of ATP. Together, these results reveal the structural basis for the fine-tuning of V-ATPase activity by SidK. | ||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  5vox.cif.gz 5vox.cif.gz | 1.1 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb5vox.ent.gz pdb5vox.ent.gz | 700 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  5vox.json.gz 5vox.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vo/5vox https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vo/5vox ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vo/5vox ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vo/5vox | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8724MC  8725C  8726C  5uf5C  5ufkC  5voyC  5vozC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 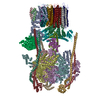
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 2 types, 6 molecules ACEefg
| #1: Protein | Mass: 67796.508 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  References: UniProt: P17255, H+-transporting two-sector ATPase, Hydrolases; Acting on ester bonds #16: Protein | Mass: 65490.320 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Legionella pneumophila subsp. pneumophila ATCC 43290 (bacteria) Legionella pneumophila subsp. pneumophila ATCC 43290 (bacteria)Gene: lp12_0990 / Production host:  |
|---|
-V-type proton ATPase subunit ... , 14 types, 27 molecules BDFGIKHJLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcd
| #2: Protein | Mass: 57815.023 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / References: UniProt: P16140 #3: Protein | Mass: 26508.393 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / References: UniProt: P22203 #4: Protein | Mass: 12738.706 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / References: UniProt: P48836 #5: Protein | | Mass: 29235.023 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / References: UniProt: P32610 #6: Protein | | Mass: 13479.170 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / References: UniProt: P39111 #7: Protein | | Mass: 44241.352 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / References: UniProt: P31412 #8: Protein | | Mass: 54482.609 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / References: UniProt: P41807 #9: Protein | | Mass: 39822.484 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / References: UniProt: P32366 #10: Protein | | Mass: 22610.641 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / References: UniProt: P23968 #11: Protein | | Mass: 17046.361 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / References: UniProt: P32842 #12: Protein | Mass: 16357.501 Da / Num. of mol.: 8 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / References: UniProt: P25515 #13: Protein | | Mass: 95625.484 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / References: UniProt: P32563 #14: Protein | | Mass: 8387.065 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / References: UniProt: Q3E7B6 #15: Protein | | Mass: 4613.678 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE-PROPANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai F20 / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TECNAI F20 |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 1.2 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.11.1_2575: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 6.8 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 23924 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj











