[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-5ng5: multi-drug efflux; membrane transport; RND superfamily; Drug resi... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 5ng5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | multi-drug efflux; membrane transport; RND superfamily; Drug resistance | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / multi-drug efflux / membrane transport / RND superfamily / Drug resistance | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationMacAB-TolC complex / alkane transmembrane transporter activity / alkane transport / Antimicrobial resistance / Iron assimilation using enterobactin / enterobactin transport / enterobactin transmembrane transporter activity / xenobiotic detoxification by transmembrane export across the cell outer membrane / periplasmic side of plasma membrane / efflux pump complex ...MacAB-TolC complex / alkane transmembrane transporter activity / alkane transport / Antimicrobial resistance / Iron assimilation using enterobactin / enterobactin transport / enterobactin transmembrane transporter activity / xenobiotic detoxification by transmembrane export across the cell outer membrane / periplasmic side of plasma membrane / efflux pump complex / xenobiotic detoxification by transmembrane export across the plasma membrane / bile acid transmembrane transporter activity / Secretion of toxins / porin activity / bile acid and bile salt transport / efflux transmembrane transporter activity / xenobiotic transmembrane transporter activity / monoatomic ion channel activity / xenobiotic transport / fatty acid transport / cell outer membrane / response to toxic substance / outer membrane-bounded periplasmic space / monoatomic ion transmembrane transport / response to xenobiotic stimulus / response to antibiotic / identical protein binding / membrane / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 6.5 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Wang, Z. / Fan, G. / Hryc, C.F. / Blaza, J.N. / Serysheva, I.I. / Schmid, M.F. / Chiu, W. / Luisi, B.F. / Du, D. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Elife / Year: 2017 Journal: Elife / Year: 2017Title: An allosteric transport mechanism for the AcrAB-TolC multidrug efflux pump. Authors: Zhao Wang / Guizhen Fan / Corey F Hryc / James N Blaza / Irina I Serysheva / Michael F Schmid / Wah Chiu / Ben F Luisi / Dijun Du /   Abstract: Bacterial efflux pumps confer multidrug resistance by transporting diverse antibiotics from the cell. In Gram-negative bacteria, some of these pumps form multi-protein assemblies that span the cell ...Bacterial efflux pumps confer multidrug resistance by transporting diverse antibiotics from the cell. In Gram-negative bacteria, some of these pumps form multi-protein assemblies that span the cell envelope. Here, we report the near-atomic resolution cryoEM structures of the AcrAB-TolC multidrug efflux pump in resting and drug transport states, revealing a quaternary structural switch that allosterically couples and synchronizes initial ligand binding with channel opening. Within the transport-activated state, the channel remains open even though the pump cycles through three distinct conformations. Collectively, our data provide a dynamic mechanism for the assembly and operation of the AcrAB-TolC pump. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  5ng5.cif.gz 5ng5.cif.gz | 1.2 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb5ng5.ent.gz pdb5ng5.ent.gz | 1010.5 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  5ng5.json.gz 5ng5.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ng/5ng5 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ng/5ng5 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ng/5ng5 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ng/5ng5 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  3636MC  8636C  8640C  5nc5C  5o66C  5v5sC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 39800.660 Da / Num. of mol.: 6 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   #2: Protein | Mass: 53783.355 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: tolC, colE1-i, mtcB, mukA, refI, toc, weeA, b3035, JW5503 Production host:  #3: Protein | Mass: 113665.180 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   #4: Protein | Mass: 5995.157 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   #5: Chemical | Has protein modification | N | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: AcrABTolC in apo state / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#4 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 |
| Specimen | Conc.: 2 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES / Details: AcrABTolC complex in apo state |
| Specimen support | Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 20 K Details: a 3ul aliquot at a concentration of 2 mg per ml was applied onto glow-discharged holey carbon grid (Quantifoil Au R1.21.3, 300 mesh) |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 1 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
| Image scans | Movie frames/image: 45 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING ONLY | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 95410 / Details: auto box by relion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 6.5 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 13544 / Algorithm: BACK PROJECTION / Num. of class averages: 1 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Space: REAL / Target criteria: Cross-correlation coefficient Details: Crystal structures were rigid-body fit into the density map and model optimization was then carried out with Phenix real-space refine. Due to the weaker resolution, stronger stereochemical ...Details: Crystal structures were rigid-body fit into the density map and model optimization was then carried out with Phenix real-space refine. Due to the weaker resolution, stronger stereochemical and secondary structure restraints were used to ensure that alpha-helices and beta-sheets did not deviate far from their expected geometry. Manual adjustments were kept to a minimum to reduce human bias in the modeling procedure, with Coot only being used to fix obvious errors such as C-beta deviations. A final check of MolProbity and cross correlation was done to ensure model quality. |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







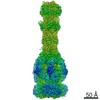
 PDBj
PDBj